Summary
The results are presented of the local treatment of burns with honeycomb expanded polyurethane. This method of treatment can be used both for the medication of burns of limited extent but variable depth and as a mattress for patients confined to bed. In the first case, the purpose of the treatment, which makes use of the product's absorbent and debriding capacity, is either to cure the lesion or to pave the way for the surgical operation. In the second case use is made of the product's exudate-draining and anti-pressure sore activity, which prevents the lesion from becoming deeper.
Keywords: TREATMENT, BURNS, HONEYCOMB, EXPANDED, POLYURETHANE, LIGASANO
Abstract
Les Auteurs décrivent leur expérience avec le traitement local des brûlures moyennant le polyuréthane expansé en nid d'abeille. Cette méthode peut être utilisée soit pour les médications des brûlures d'étendue limitée mais de profondeur variable soit en forme de matelas, pour le décubitus des patients. Dans le premier cas le but du traitement, qui exploite l'action absorbante ou de débridement du produit, peut être ou la guérison de la lésion ou la préparation à l'intervention chirurgicale. Dans le deuxième cas on exploite l'action de drainage de l'exsudat et l'action contre les escarres de décubitus, qui empêche l'approfondissement des lésions.
Introduction
Honeycomb expanded polyurethane (white Ligasano) has two main action mechanisms:
friction on the lesion-medication interface, causing mechanical debridement of non-viable tissues
absorption of excess exudates
These features, together with the possibility of replacing it at longer time intervals (every 4-6 days), make honeycomb expanded polyurethane an appropriate method of treatment that is particularly suitable for the treatment of burns of limited extent.
However, when used as a mattress on which the patient is laid, Ligasano can also be applied in cases of extensive burns.
Materials and method
Sixteen patients with non-extensive burns of varying depth were treated (11 adults, 3 elderly, 2 children). Two adult patients with extensive burns were placed on a Ligasano mattress. Nine patients in the first group were out-patients.
An assessment is made of the period of healing and out-patient treatment. The follow-up results and the quality of healing are reported.
Results
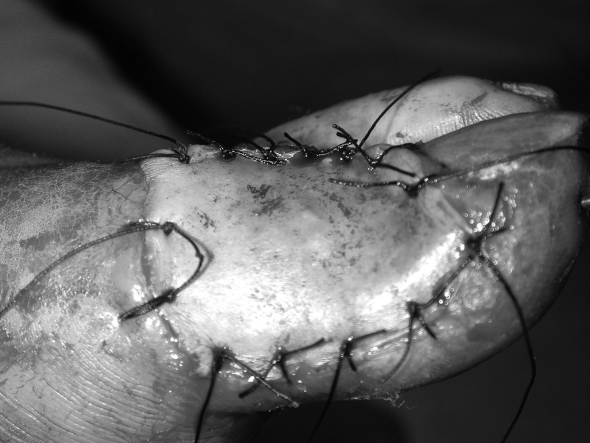
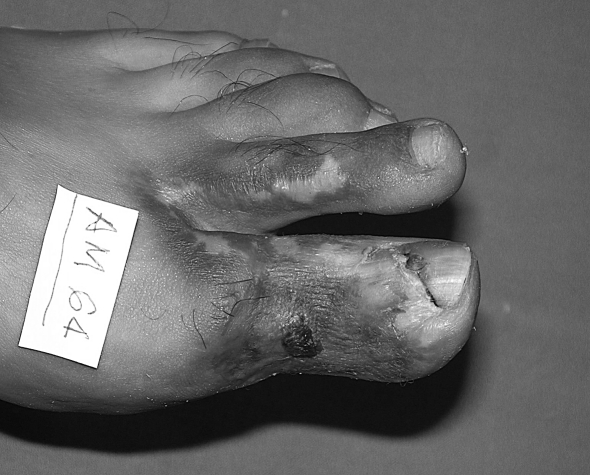
Only one patient in the first group healed after surgery (Figs. 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f ).
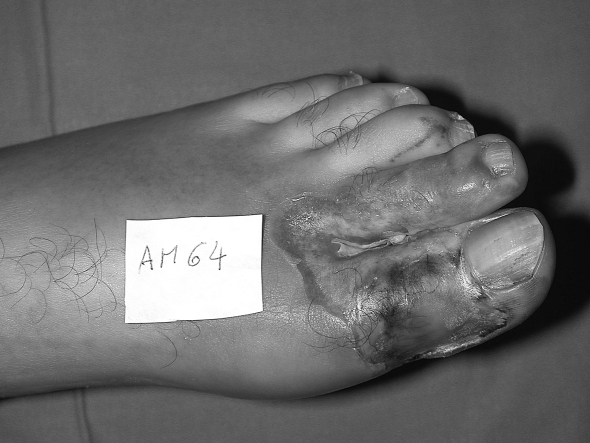
Fig. 1a. Necrosis due to electrocution of left hallux.
Fig. 1b. Application of 15% salicylate Vaseline.
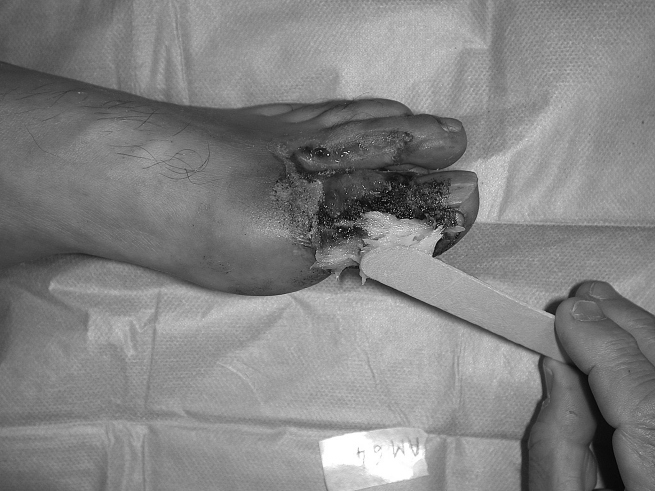
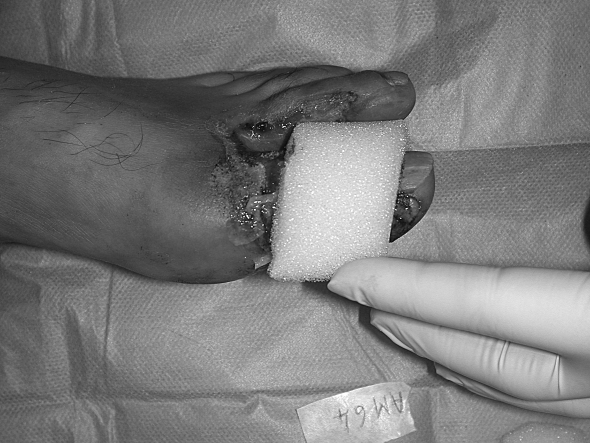
Fig. 1c. Application of white Ligasano.
Fig. 1d. Progressive wound debridement.
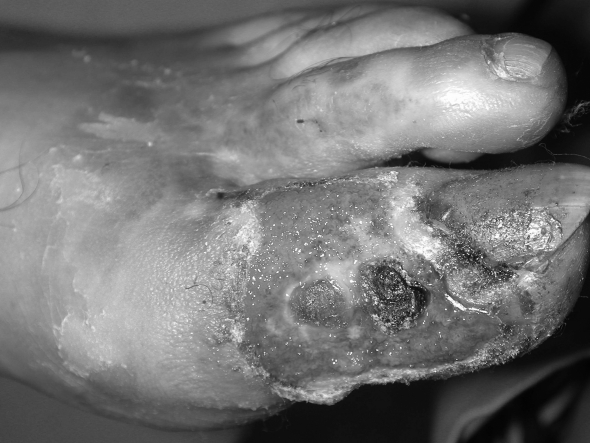
Fig. 1e. Repair with skin graft.
Fig. 1f. Three-month check-up.
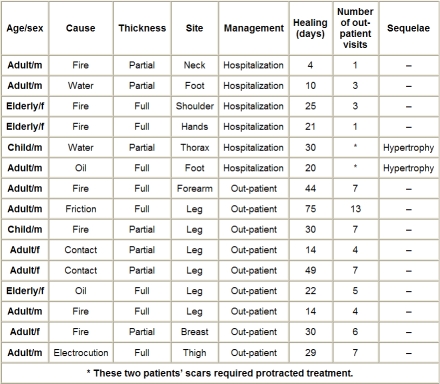
Table I presents the characteristic of the other 15 patients in the same group, who were healed by topical medical therapy alone.
Table I. Characteristics of patients healing after local therapy.
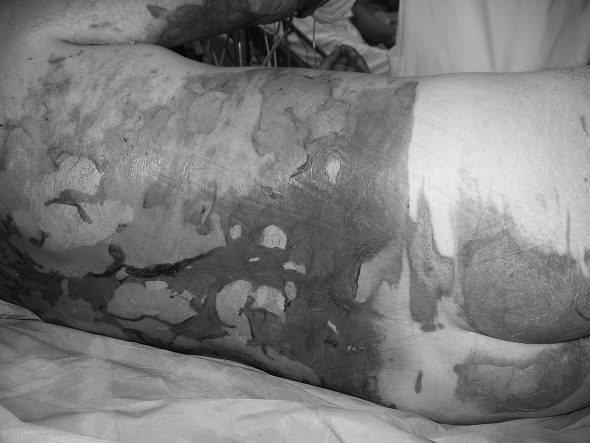
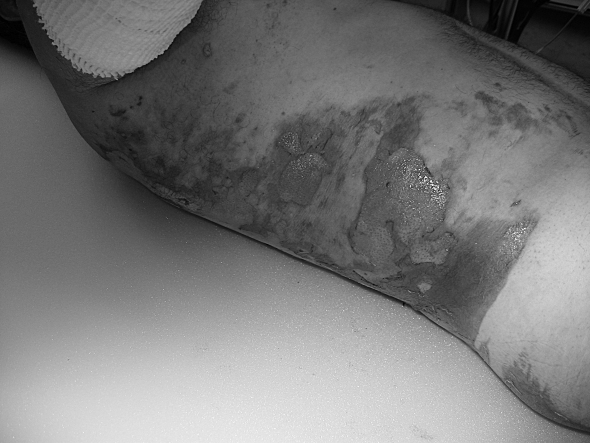
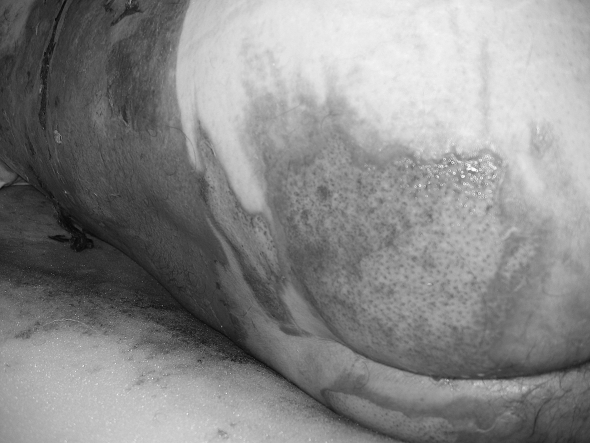
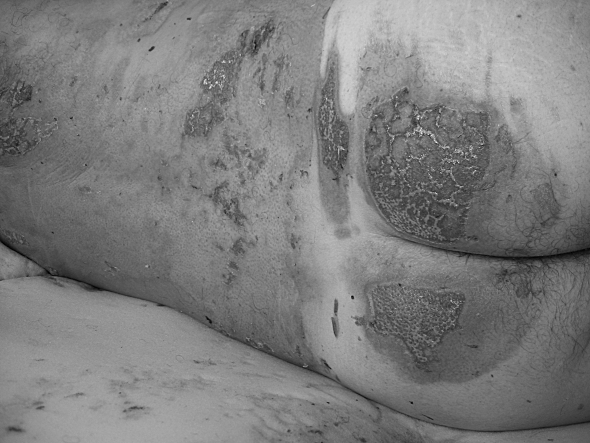
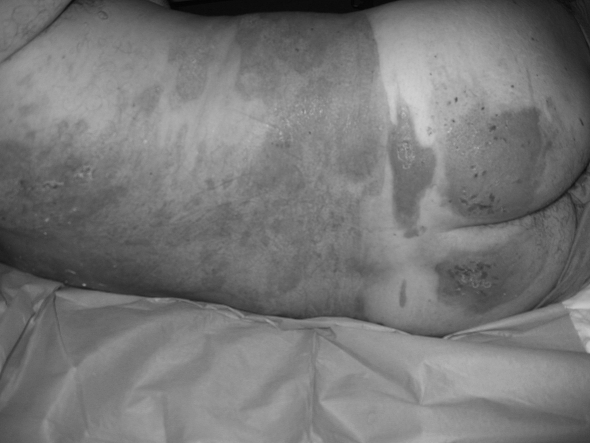
Of the two patients placed on a Ligasano mattress, its intense exudate-draining capacity was used in one and in the other its anti-pressure sore and debridement function (Figs. 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e ).
Fig. 2a. Deep dermal burn in trunk and buttocks.
Fig. 2b. Decubitus on white Ligasano mattress.
Fig. 2c. Initial stage of lesion debridement.
Fig. 2d. Advanced stage of lesion debridement (day 12).
Fig. 2e. Clinical healing (day 20).
Discussion
Honeycomb expanded polyurethane (Ligasano) is used in the local treatment of burns of limited extent, prior to surgical repair, or to facilitate healing. The following indications have to apply in this second case:
dermal burns in critical areas
full-thickness burns in non-operable patients
burns following a skin graft operation
burns in out-patients
Analysis of individual cases also enabled us to make the following considerations:
Ligasano can be used in the local treatment of burns of varying aetiology (electrical, thermal, friction) and of different depth (partial- and full-thickness)
it can also be used to treat paediatric burns
it often happens that burns treated at length with other methods (especially collagenase) are finally cured thanks to the use of Ligasano treatment; Ligasano can also be used in association with collagenase or salicylate Vaseline (also with biotics) when it is desired to achieve a more rapid debridement or necrosectomy2,3 or with rifamycin for local use if it is desired to exploit the latter’s anti-inflammation and anti-oedema effect
in out-patients it makes it possible to apply dressings at some distance of time (every 4-6 days), thus reducing handling manoeuvres and making treatment more comfortable; the speed with which burns heal, as also the action mechanism, also depends on the site because burns in particular mobile areas (neck, hands) heal more rapidly than others
in many cases there is an evident development of scabs duing the process towards clinical healing, probably because of the greater local absorbing-dehydrating effect; in these cases a brief hydrating treatment of the scar is sufficient
when there is a tendency towards scar hypertrophy this is countered by using the routine treatment protocol (hydration, masso/presso therapy, silicone). The long-term results are usually good
when Ligasano is used in mattress form, mainly for the purpose of draining the exudates, the objective assessment of its degree of imbibition (done by squeezing by hand), associated with the patients’ subjective sensation that they are “floating on water”, is the main indication for changing it. When the purpose is to exploit its anti-pressure sore action (it prevents further deepening of the lesions) and that of debridement and re-epithelialization (it reduces the quantity and time of infusion and bladder catheterization), a feeling of “lying on emery paper” replaces the much more painful sensation caused by dressing changes.
Conclusions
The local treatment of burns has the following purposes:
to favour removal of necrotic tissue, which is the main source of bacterial multiplication
to produce, thanks to absorption and control of exudates, an environment for the lesion that promotes a rapid infection-free recovery
Honeycomb expanded polyurethane’s characteristics make it possible to achieve both these purposes.
The anti-infectious action of mechanical debridement can be increased with the association of enzymatic treatment (collagenase) or chemical treatment (salicylate Vaseline) while the anti-infectious action due to absorption of the exudates can be increased by the association of antiseptics and antibiotics for local use.
The debridement of nonviable tissue, the absorption of the exudates, and the anti-infectious action lead to re-epithelialization or the formation of a suitable area for surgical repair using a free skin graft.
References
- 1.Shuck J.M. Clin. Chir. Nord Am. 6 Vol. 11. Piccin; Padua: 1980. Il trattamento ambulatoriale degli ustionati. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Masellis M. Association of salicylic Vaseline with antiseptics or antibiotics in topical treatment of burns.. In: May, Dogo, editors. “Care of the Burn Wound”; Int. Congr. Geneva (1983); Basel: Karger; 1985. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Maviglio P., Mavilio D., De Donno G., Fiume D. The use of salicylate vaseline in the debridement of burns. Annals of the Mediterranean Burns Club. 1990;3:75–8. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Monafo W.W., Ayvazian V.H. Clin. Chir. Nord Am. 6 Vol. 11. Piccin; Padua: 1980. Terapia topica. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Barisoni D. “Le ustioni e il loro trattamento”. Piccin; Padua: 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Falanga V. EWMA, Position document: Wound bed preparation in practice. MEP Ltd; London: 2004. Wound bed preparation: i principi scientifici applicati alla pratica clinica. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Napoli B., D'Arpa N., Masellis A., Masellis M. The local treatment of burns with antibiotics. Annals of Burns and Fire Disasters. 2005;18:122–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]