Abstract
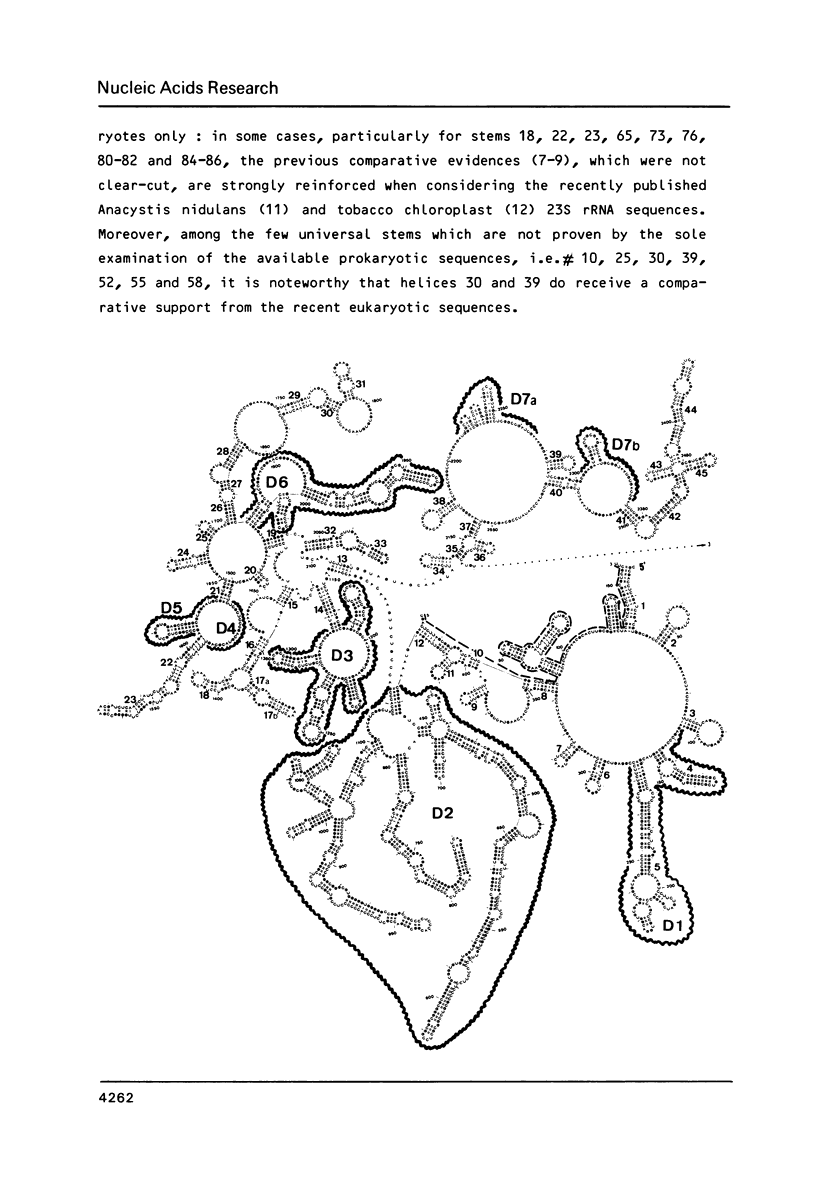
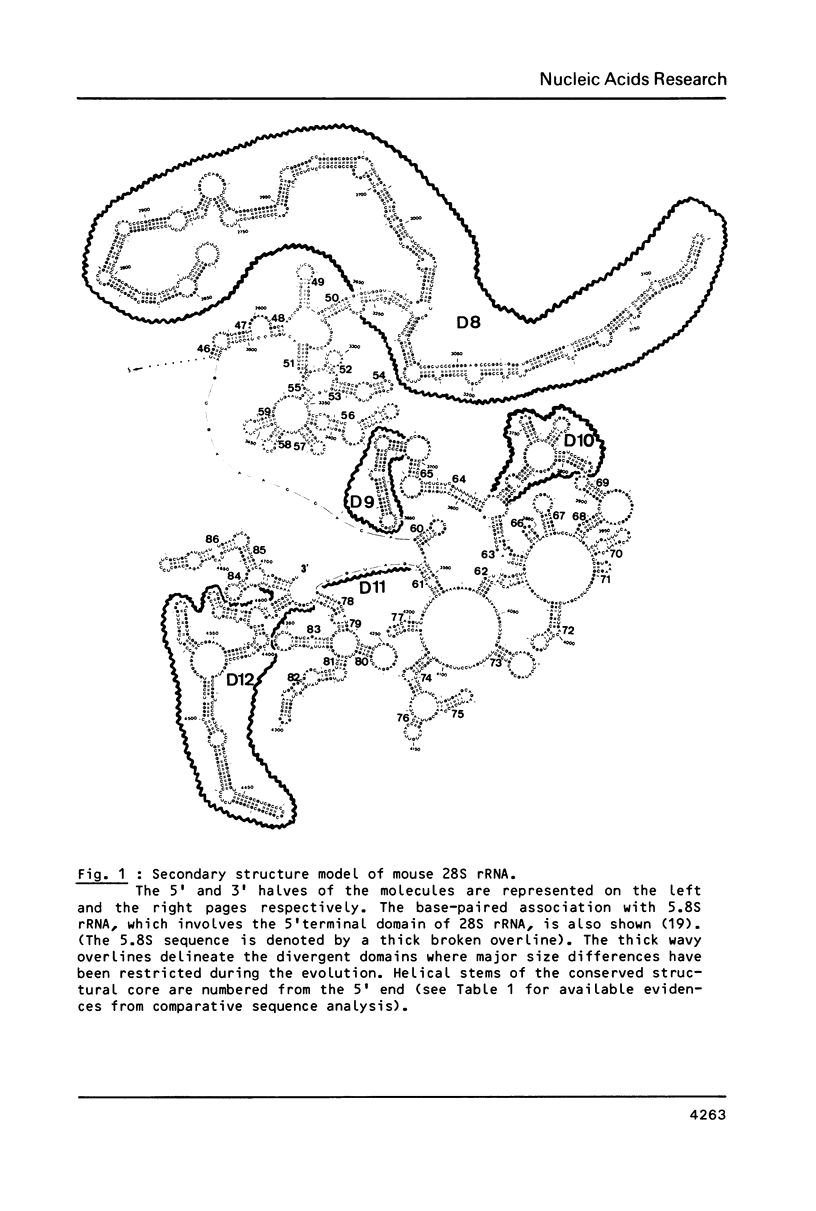
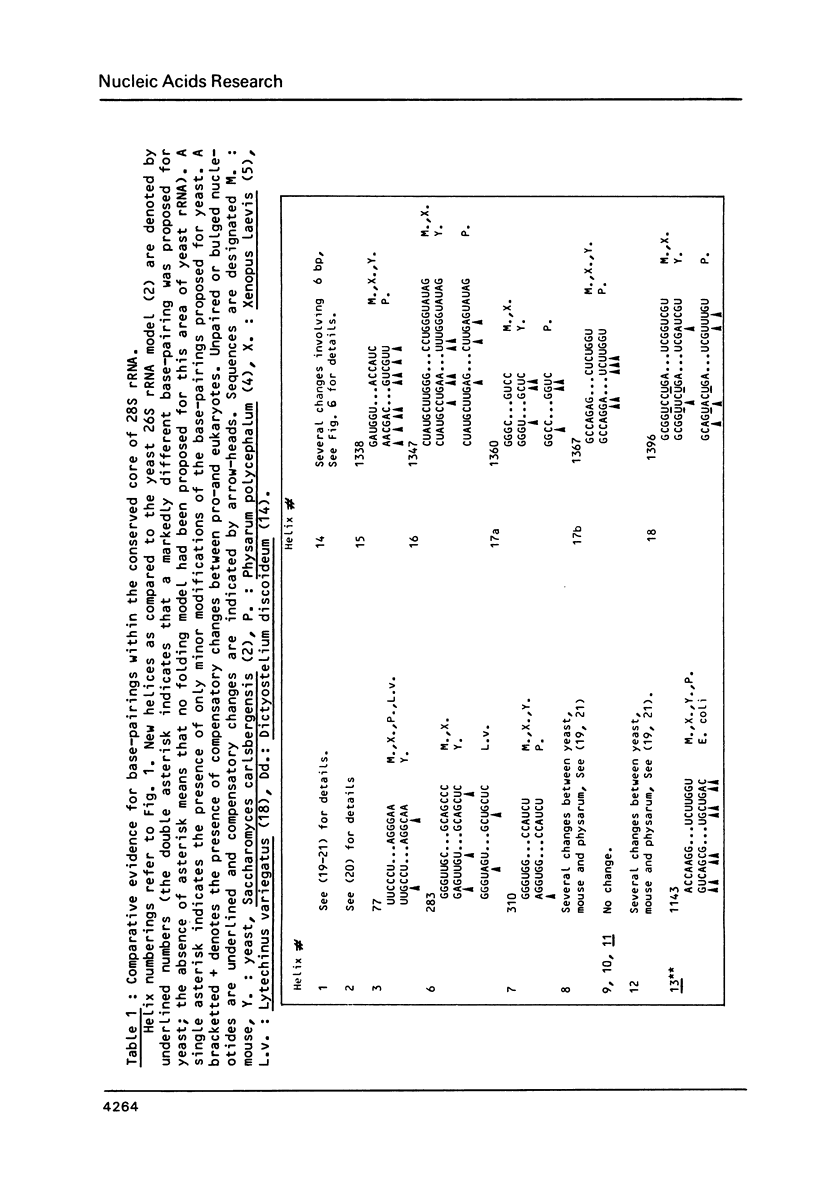
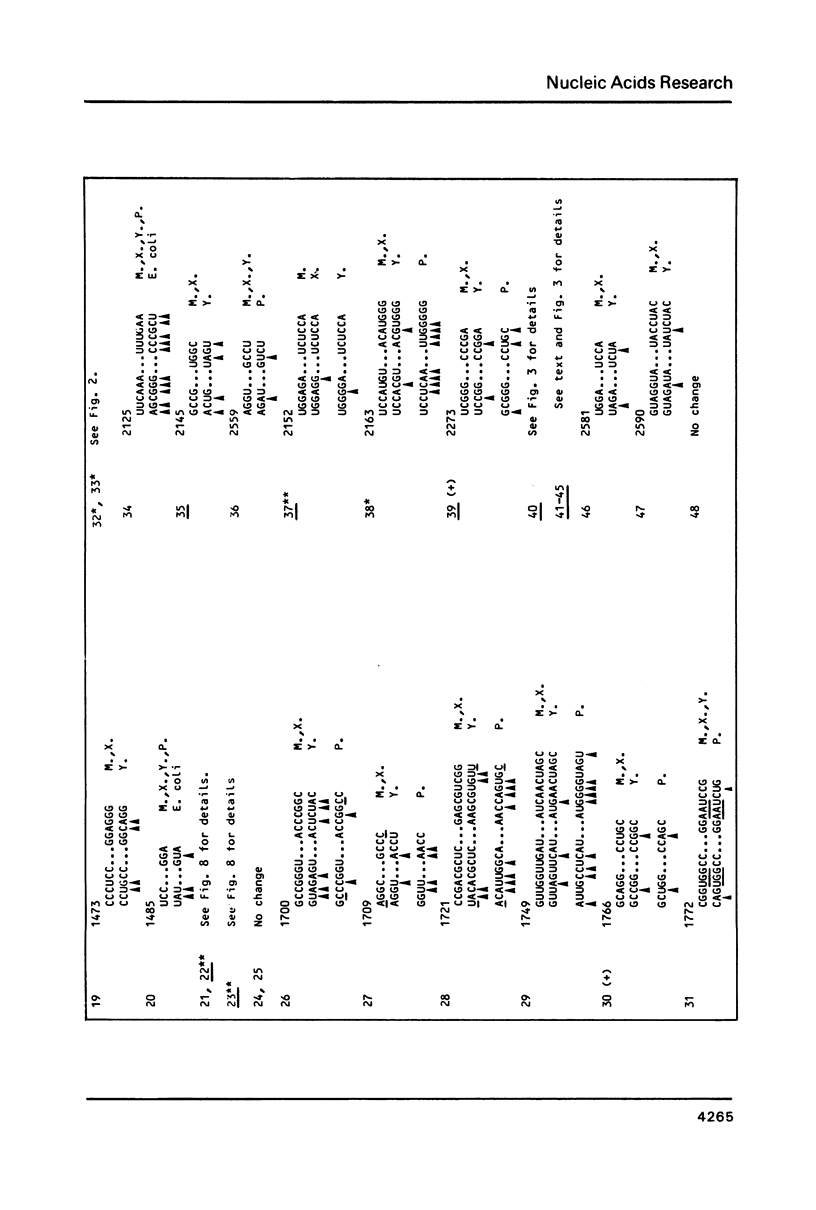
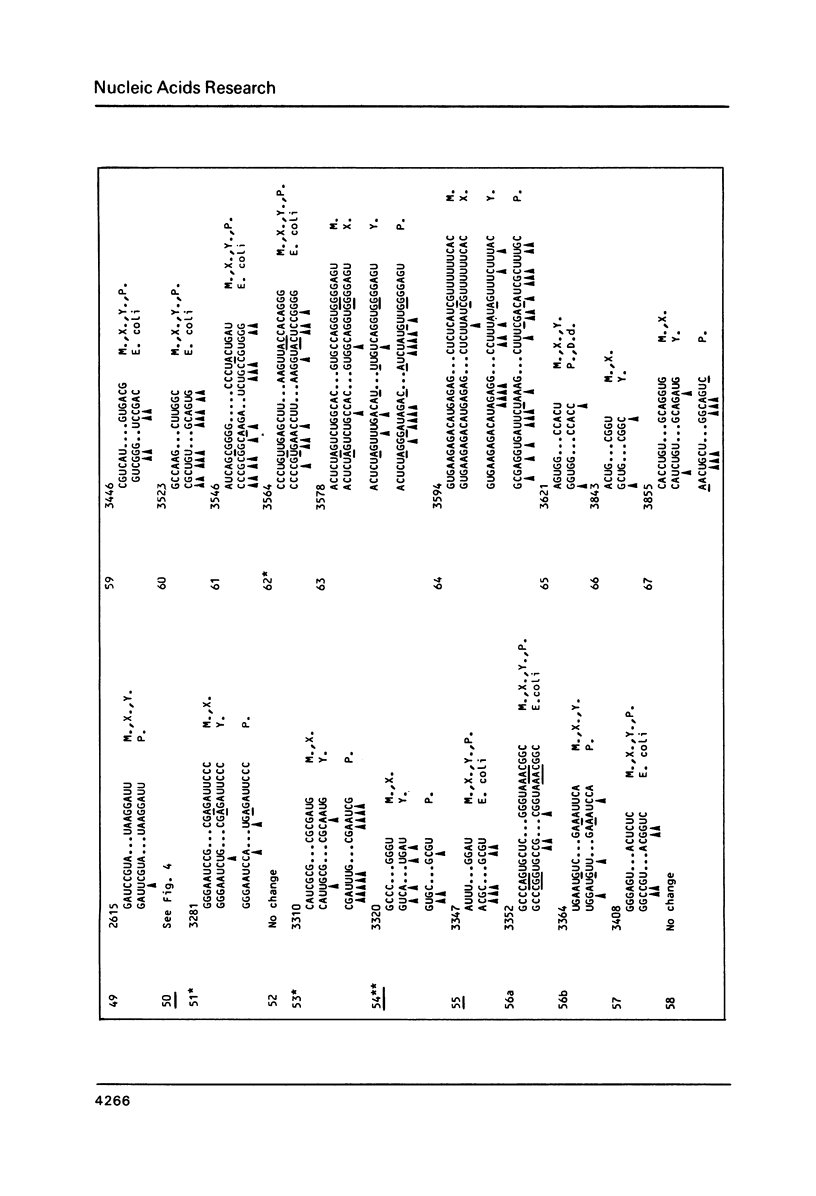
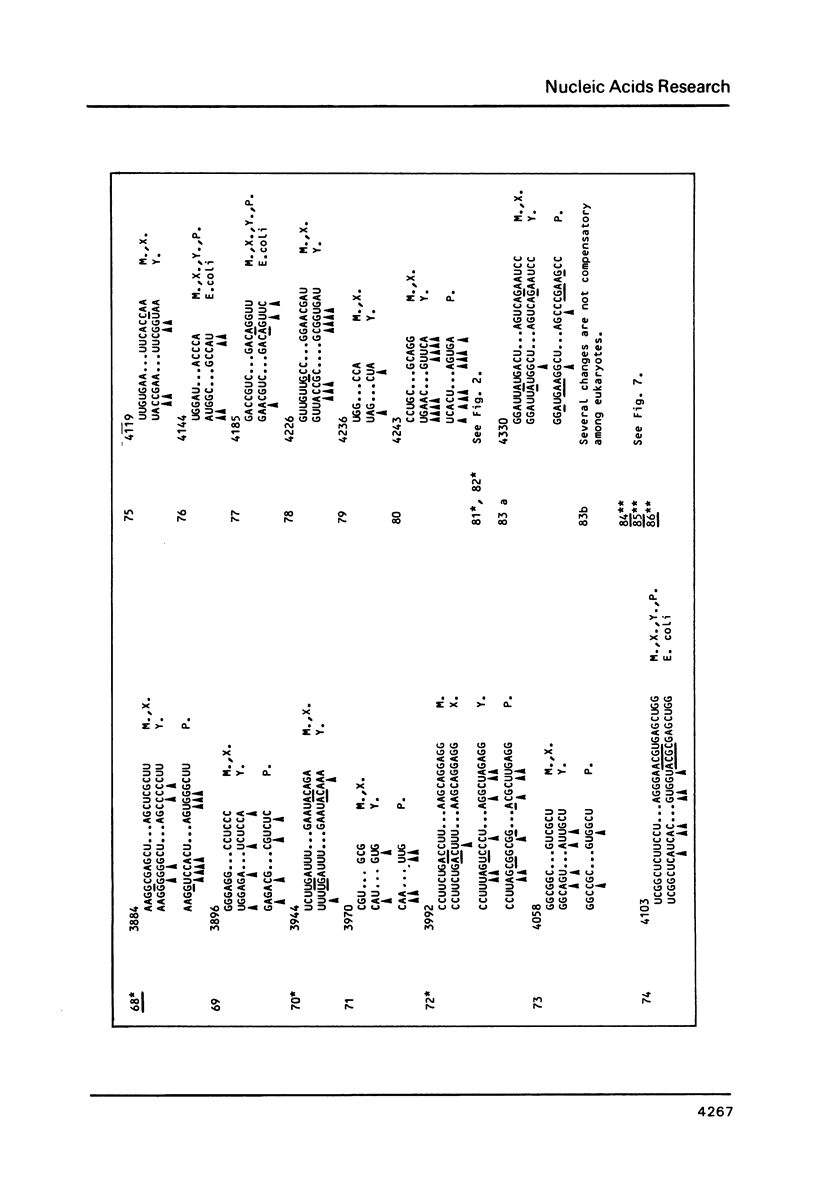
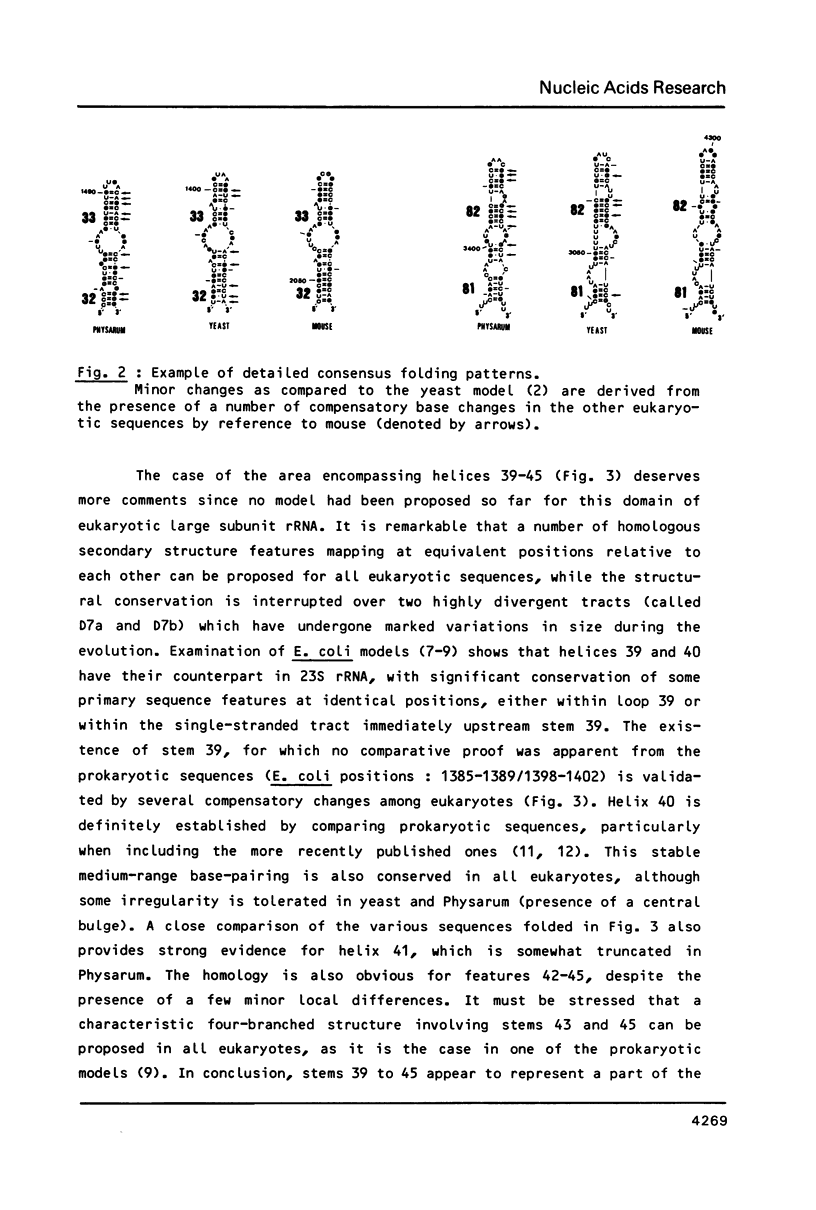
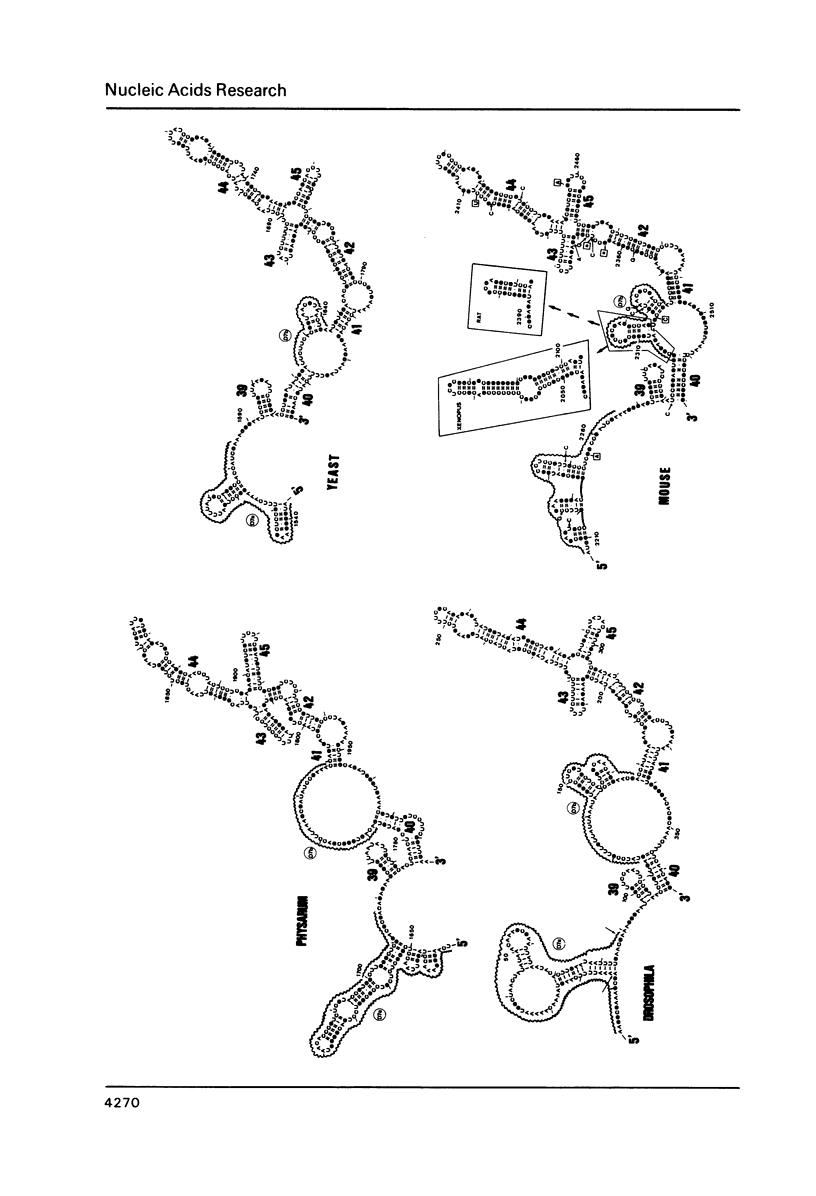
We present a secondary structure model for the entire sequence of mouse 28S rRNA (1) which is based on an extensive comparative analysis of the available eukaryotic sequences, i.e. yeast (2, 3), Physarum polycephalum (4), Xenopus laevis (5) and rat (6). It has been derived with close reference to the models previously proposed for yeast 26S rRNA (2) and for prokaryotic 23S rRNA (7-9). Examination of the recently published eukaryotic sequences confirms that all pro- and eukaryotic large rRNAs share a largely conserved secondary structure core, as already apparent from the previous analysis of yeast 26S rRNA (2). These new comparative data confirm most features of the yeast model (2). They also provide the basis for a few modifications and for new proposals which extend the boundaries of the common structural core (now representing about 85% of E. coli 23S rRNA length) and bring new insights for tracing the structural evolution, in higher eukaryotes, of the domains which have no prokaryotic equivalent and are inserted at specific locations within the common structural core of the large subunit rRNA.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt M. A., Pouyet J., Ebel J. P., Edwards K., Kössel H. Primary and secondary structures of Escherichia coli MRE 600 23S ribosomal RNA. Comparison with models of secondary structure for maize chloroplast 23S rRNA and for large portions of mouse and human 16S mitochondrial rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4303–4324. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):201–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Olvera J., Wool I. G. The structure of rat 28S ribosomal ribonucleic acid inferred from the sequence of nucleotides in a gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7819–7831. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delanversin G., Jacq B. Séquence de la région de la coupure centrale du précurseur de l'ARN ribosomique 26S de Drosophile. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1983;296(22):1041–1044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O. I., Nikolaev N., Hadjiolov A. A., Skryabin K. G., Zakharyev V. M., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. 4. Complete sequence of the 25 S rRNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6953–6958. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotz C., Zwieb C., Brimacombe R., Edwards K., Kössel H. Secondary structure of the large subunit ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli, Zea mays chloroplast, and human and mouse mitochondrial ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3287–3306. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Thurlow D. L., Gerbi S. A., Zimmermann R. A. Specific binding of a prokaryotic ribosomal protein to a eukaryotic ribosomal RNA: implications for evolution and autoregulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2722–2726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindenach B. R., Stafford D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the 18S-26S rRNA intergene region of the sea urchin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1737–1747. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacq B. Sequence homologies between eukaryotic 5.8S rRNA and the 5' end of prokaryotic 23S rRNa: evidences for a common evolutionary origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2913–2932. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Cox R. A. The nucleotide sequence at the 3'-end of Neurospora crassa 25S-rRNA and the location of a 5.8S-rRNA binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1111–1121. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumano M., Tomioka N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S rRNA gene from a blue-green alga, Anacystis nidulans. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michot B., Bachellerie J. P., Raynal F. Sequence and secondary structure of mouse 28S rRNA 5'terminal domain. Organisation of the 5.8S-28S rRNA complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5273–5283. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N. A 5.8 S rRNA-like sequence in prokaryotic 23 S rRNA. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Kop J., Wheaton V., Brosius J., Gutell R. R., Kopylov A. M., Dohme F., Herr W., Stahl D. A., Gupta R. Secondary structure model for 23S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6167–6189. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka T., Nomiyama H., Yoshida H., Kukita T., Kuhara S., Sakaki Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 26S rRNA gene of Physarum polycephalum: its significance in gene evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3163–3167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu H. L., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. Improved methods for structure probing in large RNAs: a rapid 'heterologous' sequencing approach is coupled to the direct mapping of nuclease accessible sites. Application to the 5' terminal domain of eukaryotic 28S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5903–5920. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. M., Kohorn B. D., Wade R. P. The 10 kb Drosophila virilis 28S rDNA intervening sequence is flanked by a direct repeat of 14 base pairs of coding sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3491–3504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roiha H., Glover D. M. Duplicated rDNA sequences of variable lengths flanking the short type I insertions in the rDNA of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5521–5532. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Wyler T., Hagenbüchle O. Changes in size and secondary structure of the ribosomal transcription unit during vertebrate evolution. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 23-S rRNA gene from tobacco chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursi D., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. Nucleotide sequences of the 5.8S rRNAs of a mollusc and a porifer, and considerations regarding the secondary structure of 5.8S rRNA and its interaction with 28S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):8111–8120. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.8111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Planta R. J., Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P. The primary and secondary structure of yeast 26S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6935–6952. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware V. C., Tague B. W., Clark C. G., Gourse R. L., Brand R. C., Gerbi S. A. Sequence analysis of 28S ribosomal DNA from the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7795–7817. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



