Abstract
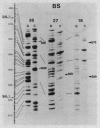
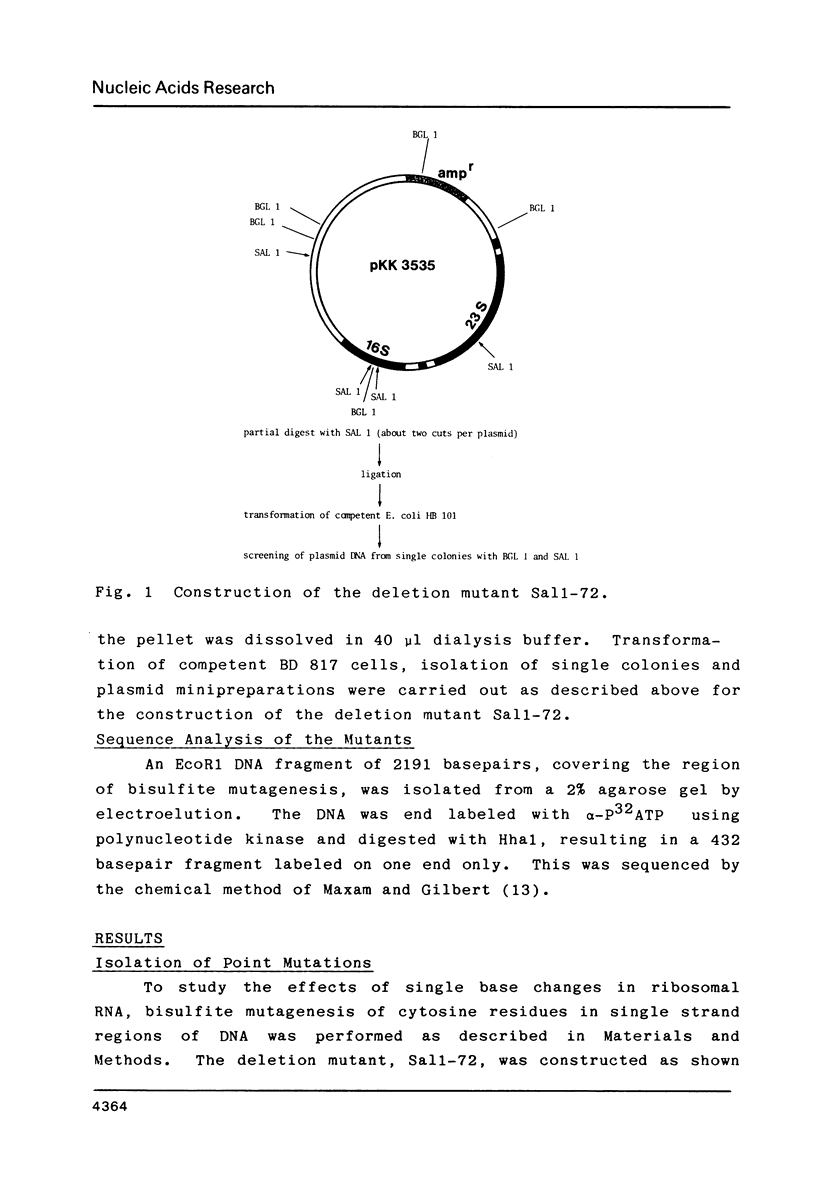
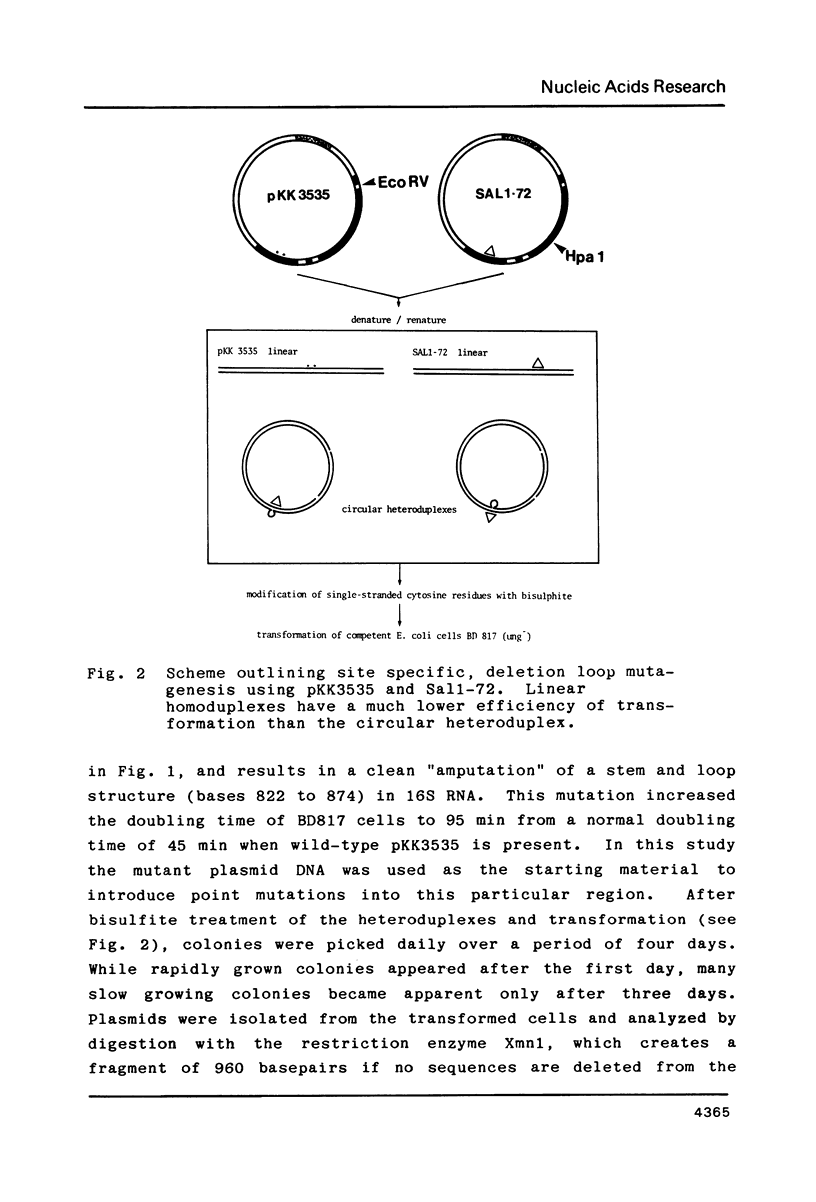
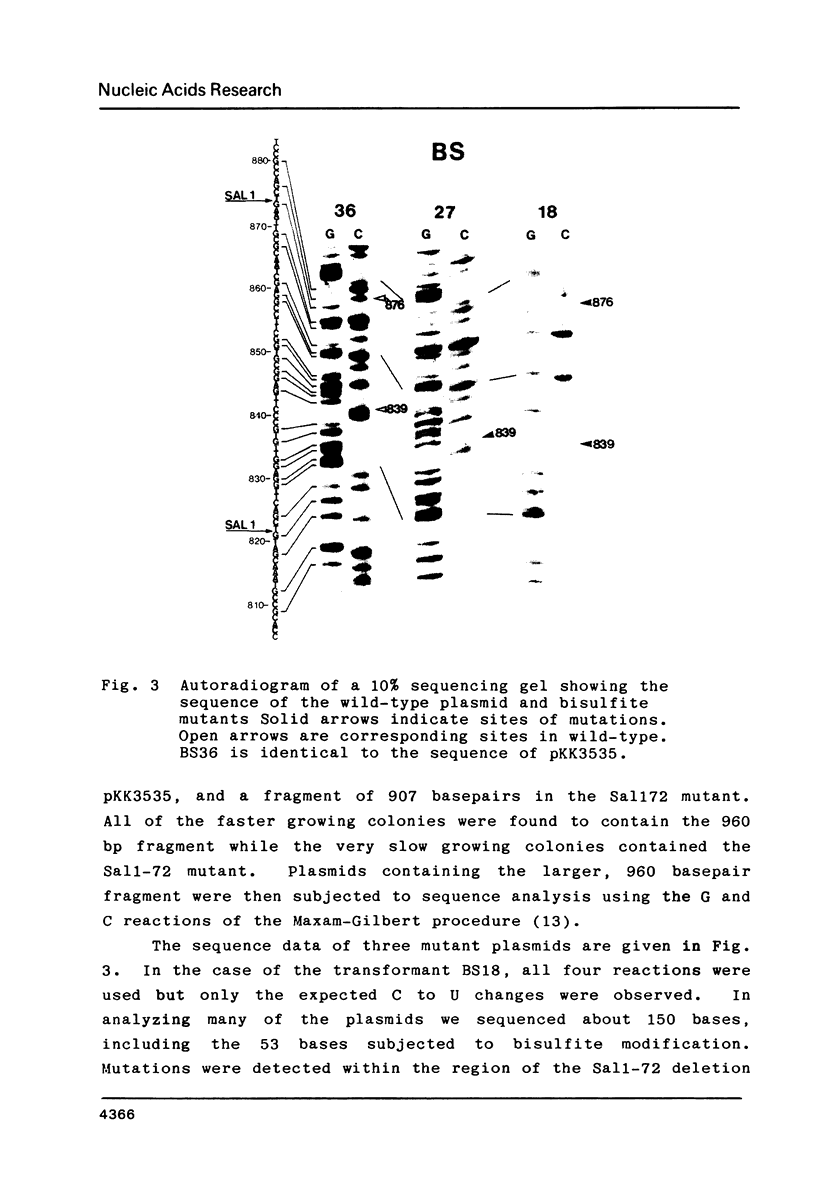
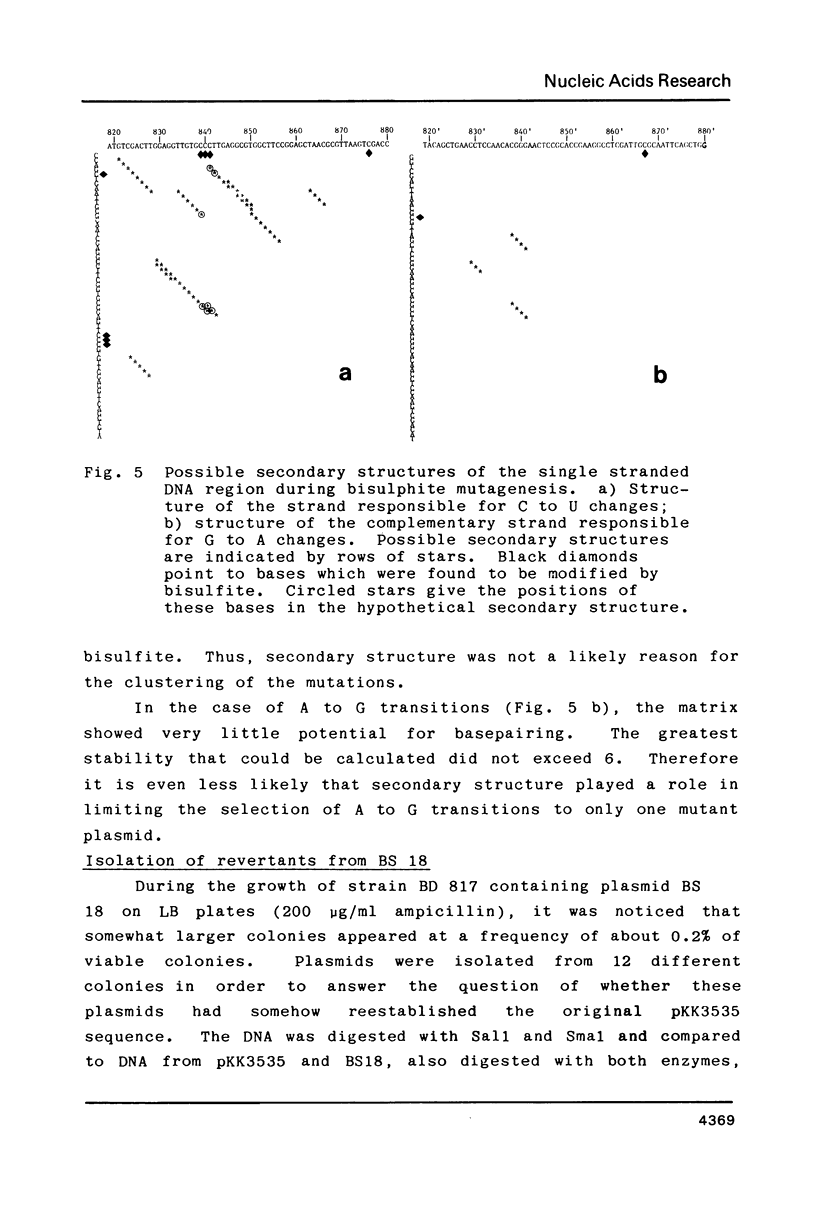
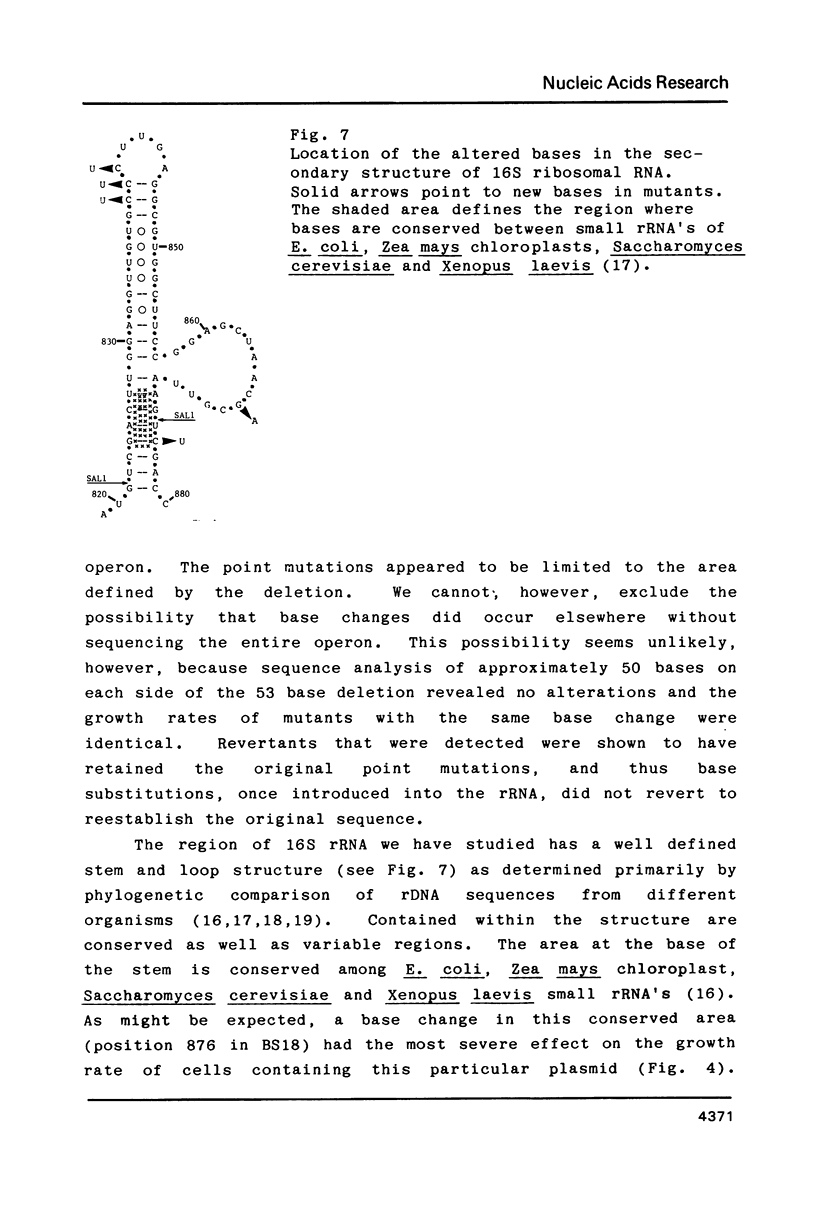
Using the plasmid pKK3535 , which contains the rrnB operon of Escherichia coli in pBR322, a deletion mutation was constructed which lacks bases 822 to 874 in the middle of the 16S ribosomal RNA. This results in an "amputation" of a very distinct stem and loop structure in the RNA. By forming a heteroduplex between the deletion plasmid and the original pKK3535 and by modifying the single-stranded deletion loops with bisulfite, we produced plasmids containing one or two base changes at positions 839, 840, 841, 867 or 876. The clustering of the mutations near the top of the stem, and the inability to get base changes at other positions, suggests that single alterations at particular positions severely affect the formation of a functional ribosome. The ability to recover mutations at these positions is not determined by the secondary structure of the DNA during bisulfite mutagenesis. Restriction enzyme analysis of 12 revertants from a slow growing mutant (altered at positions 839 and 876) shows that they did not compensate for the mutation by re-establishing the original wild type sequence.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brimacombe R., Maly P., Zwieb C. The structure of ribosomal RNA and its organization relative to ribosomal protein. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:1–48. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Ullrich A., Raker M. A., Gray A., Dull T. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbadie-McFarland G., Cohen L. W., Riggs A. D., Morin C., Itakura K., Richards J. H. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis as a general and powerful method for studies of protein function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6409–6413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M., Nomura M. Chromosomal locations of the genes for rRNA in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):458–468. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.458-468.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Stark M. J., Dahlberg A. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of ribosomal RNA. Construction and characterization of deletion mutants. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):397–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Oostra B. A., Ely B. K., Smith A. E. Deletion loop mutagenesis: a novel method for the construction of point mutations using deletion mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5161–5171. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss A., Sain B., Venetianer P. The number of rRNA genes in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):77–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Woese C. R. Secondary structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):403–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6163215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Clarke N. D., Griswold J., Kennedy W. J., Rupp W. D. Identification of the uvrB gene product. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 5;148(1):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J., Gourse R. L., Dahlberg A. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of ribosomal RNA. Analysis of ribosomal RNA deletion mutants using maxicells. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):417–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Zuker M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. Structural organization of the 16S ribosomal RNA from E. coli. Topography and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2153–2172. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Glotz C., Brimacombe R. Secondary structure comparisons between small subunit ribosomal RNA molecules from six different species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3621–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]