Abstract
Background
Depression and anxiety have been shown to be associated with obesity and underweight, but little is known about how the relationship varies across the life course, from adolescence through adulthood. We aimed to investigate the association between adolescent- and adult-onset affective symptoms and body mass index (BMI) change from age 15 to 53 years.
Method
We used data from a British birth cohort born in 1946 and followed up ever since. The relationship between affective symptom profiles, distinguishing adolescent-onset and adult-onset symptoms, and BMI change from adolescence to age 53 years was investigated using multilevel models.
Results
Women with adolescent-onset symptoms had lower mean BMI at age 15 years, faster rates of increase across adulthood, and higher BMI at age 53 years than those with no symptoms. Men with adolescent-onset symptoms had lower BMI at all ages from 15 to 53 years. The BMI trajectories of men and women with adult-onset symptoms did not differ from those with absence of symptoms at all ages.
Conclusions
The relationship between affective symptoms and change in BMI varies by sex and age at onset of symptoms. Adolescence may be an important period for the development of the association between affective symptoms and weight gain in girls. Intervention to prevent increases in BMI across adult life in women with adolescent-onset symptoms, even if they are not overweight at this age, should be considered.
Keywords: Adolescent, affective symptoms, BMI, longitudinal study, obesity
Introduction
Depression is the leading cause of burden of disease in the middle- and high-income countries, according to the World Health Organization’s current report (WHO, 2008). Research into the association between depression and body size, an association which is likely to be bidirectional, has to date mainly focused on obesity. However, a clinical perspective suggests that depression may be associated with underweight as well as overweight. Indeed, a cross-sectional study of 43534 individuals reported a significant U-shaped association between depression and body mass index (BMI) categories (underweight, normal, overweight and obesity) (de Wit et al. 2009). Moreover, both ends of the weight spectrum have been shown to increase the risk of future depression outcomes and suicide (Diverse Populations Collaboration, 2005; Magnusson et al. 2006; Atlantis & Baker, 2008; Bjorge et al. 2008). Findings from existing longitudinal studies of depression and BMI are inconsistent: most showed depression to be associated with subsequent increases in BMI or obesity but some showed an inverse association or no association (Blaine, 2008; Liem et al. 2008). Some of this inconsistency may be due to the differences in the age of the samples at baseline when affective symptoms were measured. Some studies investigated adolescent samples (Bardone et al. 1998; Barefoot et al. 1998; Pine et al. 2001; Goodman & Whitaker, 2002; Richardson et al. 2003; Hasler et al. 2004; Franko et al. 2005; Anderson et al. 2006; Tanofsky-Kraff et al. 2006; Kivimaki et al. 2009; Ternouth et al. 2009), while others were conducted in adults (DiPietro et al. 1992; Haukkala et al. 2001; Roberts et al. 2003; Forman-Hoffman et al. 2007; Kivimaki et al. 2009). It has been hypothesized that associations between depression and BMI may depend on the age at onset of affective symptoms, given that adolescent-onset symptoms appear to differ from adult-onset symptoms with respect to neurobiological correlates and treatment response (Kaufman et al. 2001). A recent meta-analysis supported a positive association between depressive symptoms in adolescence and overweight in later life (Liem et al. 2008). However, most of these studies considered BMI at only one age in later life (Pine et al. 1997, 2001; Bardone et al. 1998; Barefoot et al. 1998; Ternouth et al. 2009), and some did not adjust for adolescent BMI or consider change in BMI (Pine et al. 1997; Bardone et al. 1998). Furthermore, most of these studies had relatively short periods of follow-up, assessing the impact of symptoms on BMI only up to young adulthood (Bardone et al. 1998; Barefoot et al. 1998; Goodman & Whitaker, 2002; Franko et al. 2005; Tanofsky-Kraff et al. 2006). Thus, the long-term influence of adolescent symptoms on BMI remains unclear.
Further, to the best of our knowledge, there has been no study exploring whether any effect of adolescent symptoms on adult BMI is due to those with adolescent-onset symptoms having continued symptoms in adult life, or whether adolescence is a critical period for the establishment of the relationship between symptoms and life-course BMI, irrespective of later symptom experience (Kuh et al. 2003). To investigate these issues, longitudinal studies with multiple measurements of BMI and depression from childhood through adolescence and adulthood are required.
Using data from the Medical Research Council (MRC) National Survey of Health and Development (NSHD) we investigated how longitudinal profiles of affective (depression and anxiety) symptoms were associated with BMI change from adolescence (age 15 years) through adulthood (age 20, 26, 36, 43 and 53 years). We assessed whether life-course BMI varied depending on age at onset of symptoms, distinguishing adolescent-onset symptoms from adult-onset symptoms. Finally, we investigated whether there were sex differences in the association.
Method
British 1946 Birth Cohort
The MRC NSHD initially consisted of a stratified sample of 5362 children born in England, Scotland and Wales during 1 week in March 1946. The cohort has been studied on 21 occasions since birth, most recently in 1999 (Wadsworth et al. 2003). Approval for this most recent data collection was granted by the North Thames Multicentre Research Ethics Committee, and informed consent was given by cohort members.
Every survey member with a valid affective symptoms profile who had at least one recorded value of BMI between 15 and 53 years was included in the analyses (n=4559). Of those allocated an affective symptom profile, only 68 (1.5%) had missing data on BMI at all data collections and were thus excluded from analyses. Those with missing BMI information were most likely to be from the profile with adolescent-onset repeated symptoms (n=35) and least likely to be from the profiles with adolescent-onset symptoms with good adult outcome or with adultonset symptoms (no missing data). There were no participants with BMI data but missing affective symptom profile. Those included in the analyses were not different from those excluded due to missing data on affective symptoms profiles and BMI measures (n=803) in terms of BMI at age 11 years (p=0.90) or childhood (p=0.81) and adult (p=0.95) social class.
Affective symptoms
A broad picture of mental health throughout the life course is available in the NSHD. At 13 and 15 years teacher ratings were collected using a forerunner of the Rutter teacher questionnaire (Rutter, 1967). Teachers described aspects of the children’s personality, behaviour and attitudes on a three-point scale. These questionnaires have previously been subjected to classical linear factor analysis, with one factor comprising 11 items being identified as anxiety/depression and internalizing emotions and behaviours (Jones et al. 1994; van Os et al. 1997; Colman et al. 2007b). This factor is shown to be a good predictor of adult emotional problems (Richards & Abbott, 2009). Frequency and severity of common symptoms of depression and anxiety were assessed in adulthood, with the Present State Examination (Wing et al. 1974) at 36 years, the Psychiatric Symptom Frequency scale (Lindelow et al. 1997) at 43 years, and the 28-item General Health Questionnaire (Goldberg & Hillier, 1979) at age 53 years.
Utilising these measures from adolescence to age 53 years, latent class analysis was previously employed to develop a longitudinal typology of symptom profiles of depression and anxiety (Colman et al. 2007a). This approach solves the problem of the use of different scales for the measurement of symptoms at different ages, and makes it possible to identify groups of individuals with differing experience of psychiatric symptoms over the life course. Since previous factor analyses of the teacher rating scale and the Psychiatric Symptom Frequency scale have failed to identify separate factors for depression and anxiety, a single factor score representing depressive and anxious symptomatology at each of the five ages was estimated after confirmatory factor analysis. Due to the skewed distributions of these scores, a categorical variable with four groups (absence of symptoms, occasional symptoms, moderate symptoms and severe symptoms) was defined at each age. These categorical variables were used in the latent class analysis.
Six distinct profiles were identified up to age 53 years (n=4627): absence of symptoms (44.8% of sample), repeated moderate symptoms (33.6%), adultonset moderate symptoms (11.3%), adolescent symptoms with good adult outcome (5.8%), adult-onset severe symptoms (2.9%) and repeated severe symptoms over the life course (1.7%) (Colman et al. 2007a). Because of our interest in the relationship between symptom timing and BMI we defined four groups according to age at onset of affective symptoms: absence of symptoms, adult-onset symptoms (moderate and severe), repeated symptoms with adolescence onset (moderate and severe), and adolescent symptoms with good adult outcome.
Anthropometry
Heights and weights were measured at age 7, 11 and 15 years by school doctors or nurses. At ages 20 and 26 years, heights and weights were self-reported. At ages 36, 43 and 53 years heights were measured, to the nearest 0.5 cm, by trained research nurses using a portable stadiometer according to a standard protocol. Weight, to the nearest 0.5 kg, in light indoor clothing was also measured at these ages, and was adjusted by subtracting 0.5 kg for women and 1 kg for men as a correction for the clothes worn.
Explanatory factors
Sex was considered as a potential effect modifier of associations between affective symptoms profiles and BMI (Istvan et al. 1992; Carpenter et al. 2000; Richardson et al. 2003). Childhood and adulthood socio-economic status were included as potential confounders (Moore et al. 1997) since they were associated with BMI and mental health in the NSHD (Hardy et al. 2000). Childhood social class was defined using the fathers’ occupation classified as non-manual (professional, managerial or intermediate) or manual (skilled manual, semi-skilled manual, and unskilled) when the participant was aged 11 years, or, if this was unknown, occupation at age 4 years or 15 years (Registrar General, 1971). Adult occupational social class at age 53 years (or earlier if this was unavailable) was again grouped into manual and non-manual. Conduct problems and smoking were also assessed as potential confounders as they are associated with both mental health (Chaiton et al. 2009; Colman et al. 2009) and obesity (Compton et al. 2006; Mamun et al. 2009; Duarte et al. 2010). Adolescent conduct problems, assessed by teachers when study members were aged 13 and 15 years (Colman et al. 2009), and life-course smoking status, based on reports of smoking behaviour at all contacts since age 20 years (Clennell et al. 2008), were also considered as potential confounders.
Statistical analysis
Since affective symptoms were first measured in adolescence, we considered BMI trajectories from adolescence (age 15 years) onwards. Mean BMI at each age was calculated for the four affective symptom profiles and tests of heterogeneity across the groups were performed. As there were up to six outcome records for each individual, the data could be considered as hierarchical in structure, with repeated measures of BMI (‘level 1’) being clustered within survey members (‘level 2’). Thus, multilevel models were used to investigate the influence of affective symptoms profiles on both BMI at baseline (i.e. age 15 years) and the rate of change in BMI with increasing age, while allowing for the hierarchical nature of the data.
We first fitted a model containing age and affective symptoms profile. We modelled the non-linearity of the association between age and BMI by including quadratic and cubic terms. Interaction terms between each affective symptom profile and age were fitted to test whether the rate of linear change in BMI varied across different profiles. The interactions of profile with the higher-order terms for age were tested and were not significant. BMI at age 11 years was then added to assess whether prior childhood BMI accounted for any relationship. Childhood and adulthood social class was added to this model. Finally, the potential confounding effects of smoking status and adolescent conduct problems were assessed. Additionally, in a separate series of models, we considered the impact of BMI at 7 years instead of BMI at 11 years. Analyses were carried out separately for men and women. To assess formally whether associations were different in men and women, tests for sex interaction were applied in models including both men and women. All analyses were performed in stata 10.0 (StataCorp LP, USA).
Results
Affective symptoms profiles and BMI categories
Descriptive statistics for BMI at each age by affective symptoms profile are presented in Table 1. Men with adolescent-onset symptoms had lower BMI than others from age 15 to 43 years (p<0.010 for test for heterogeneity across groups at each age) (Table 1). Women with adolescent-onset symptoms had the lowest mean BMI at age 15 years, but the highest BMI at age 53 years, although the tests for heterogeneity across the four groups were not significant at any age.
Table 1. Descriptive analysis of BMI and possible confounders in four longitudinal profiles of affective symptoms in men and women.
| Affective symptoms profiles |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Absence of symptoms |
Adolescent-onset repeated symptoms |
Adolescent-onset with good adult outcome |
Adult-onset repeated symptoms |
p a | |
| Men | ||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| At age 7 years | 1992 | 15.93 (1.29) | 15.75 (1.32) | 15.71 (1.37) | 16.12 (1.37) | 0.0004 |
| At age 11 years | 2021 | 17.43 (2.09) | 16.92 (2.14) | 17.14 (2.38) | 17.46 (2.10) | <0.0001 |
| At age 15 years | 1871 | 19.79 (2.33) | 19.14 (2.53) | 19.29 (2.80) | 19.93 (2.29) | <0.0001 |
| At age 20 years | 1799 | 22.81 (2.38) | 22.32 (2.56) | 22.28 (2.50) | 22.70 (2.58) | 0.001 |
| At age 26 years | 1799 | 23.61 (2.85) | 23.10 (2.78) | 23.04 (3.12) | 23.47 (2.63) | 0.006 |
| At age 36 years | 1632 | 25.07 (3.12) | 24.41 (3.27) | 24.74 (3.57) | 24.79 (3.38) | 0.009 |
| At age 43 years | 1617 | 25.92 (3.38) | 25.21 (3.56) | 25.59 (3.62) | 25.92 (3.77) | 0.007 |
| At age 53 years | 1452 | 27.45 (3.87) | 27.24 (4.38) | 27.51 (4.31) | 27.48 (3.81) | 0.8 |
| Childhood SC, % manual | 2113 | 57.7 | 60.8 | 57.8 | 57.6 | 0.61 |
| Adult SC, % manual | 2106 | 41.7 | 46.8 | 49.6 | 35.3 | 0.003 |
| Lifelong smoking status, % never smoker |
1693 | 24.8 | 20.7 | 30.7 | 23.1 | 0.01 |
| Conduct problems, % yes | 2199 | 7.0 | 7.2 | 9.2 | 11.7 | 0.05 |
| Women | ||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| At age 7 years | 1869 | 15.72 (1.43) | 15.72 (1.77) | 15.63 (1.70) | 15.73 (1.51) | 0.9 |
| At age 11 years | 1868 | 17.45 (2.42) | 17.50 (2.90) | 17.26 (2.62) | 17.55 (2.48) | 0.8 |
| At age 15 years | 1693 | 20.72 (2.81) | 20.49 (3.21) | 20.19 (2.88) | 20.96 (3.06) | 0.05 |
| At age 20 years | 1708 | 21.89 (2.83) | 21.74 (2.96) | 21.62 (2.96) | 21.97 (2.96) | 0.6 |
| At age 26 years | 1759 | 22.40 (3.05) | 22.31 (3.53) | 22.15 (2.82) | 22.55 (3.24) | 0.6 |
| At age 36 years | 1648 | 23.60 (3.79) | 23.47 (4.26) | 23.36 (4.16) | 23.73 (4.14) | 0.8 |
| At age 43 years | 1608 | 25.13 (4.37) | 25.07 (5.04) | 25.62 (5.49) | 25.29 (4.72) | 0.7 |
| At age 53 years | 1495 | 27.19 (5.08) | 27.55 (5.58) | 28.00 (6.24) | 27.51 (5.57) | 0.5 |
| Childhood SC, % manual | 2113 | 55.7 | 63.6 | 64.5 | 56.6 | 0.004 |
| Adult SC, % manual | 2029 | 25.9 | 33.2 | 31.6 | 31.8 | 0.01 |
| Lifelong smoking status, % never smoker |
1694 | 33.2 | 32.6 | 49.6 | 22.2 | <0.0001 |
| Conduct problems, % yes | 2017 | 6.5 | 5.4 | 2.2 | 8.3 | 0.06 |
BMI, Body mass index; SC, social class.
Values are given as mean (standard deviation) or percentage.
p Value for heterogeneity across groups.
Affective symptoms profiles and BMI change across the life course
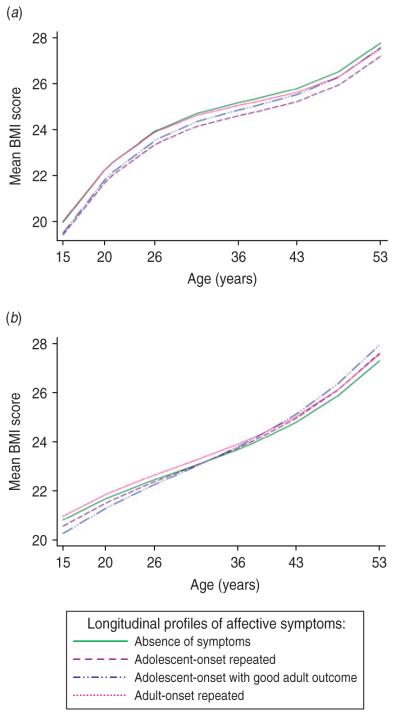
To assess BMI change across the period of nearly 40 years we applied the method of multilevel modelling. Among women, those with adolescent-onset symptoms with good adult outcome had 0.55 kg/m2 lower BMI at age 15 years (p=0.030) than women with absence of symptoms (Table 2, Fig. 1b). A similar difference was observed for women with adolescent-onset repeated symptoms, although this was not significant at the 5% level (p=0.070). Women with adolescent-onset repeated symptoms and those with adolescent-onset symptoms with good adult outcome had significantly higher rates of BMI increase during adulthood (p=0.046 and 0.010, respectively) than those with absence of symptoms, resulting in women with these profiles having higher BMI by age 53 years (Table 2). At age 53 years women with adolescent symptoms with good adult outcome had an estimated BMI which was 0.63 kg/m2 higher than those with absence of symptoms. The group with adult-onset symptoms did not differ with respect to BMI trajectory compared with those with absence of symptoms.
Table 2. Results from multilevel models of BMI trajectories (between 15 and 53 years) by longitudinal profilesa of affective symptoms in men and women (models also include age, age2, age3).
| Men (n=2366) |
Women (n=2193) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | 95% CI | p | Coefficient | 95% CI | p | p b | |
| Profile 2c | −0.55 | −0.77 to −0.33 | <0.0001 | −0.25 | −0.52 to 0.02 | 0.070 | 0.023 |
| Profile 3c | −0.47 | −0.88 to −0.05 | 0.027 | −0.55 | −1.05 to −0.05 | 0.030 | 0.70 |
| Profile 4c | 0.05 | −0.24 to 0.34 | 0.74 | 0.16 | −0.19 to 0.52 | 0.37 | 0.58 |
| Profile 2 by age (year)d | −0.001 | −0.12 to 0.10 | 0.88 | 0.02 | 0.00 to 0.03 | 0.046 | 0.13 |
| Profile 3 by age (year)d | 0.01 | −0.01 to 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 0.01 to 0.06 | 0.010 | 0.24 |
| Profile 4 by age (year)d | −0.01 | −0.02 to 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.003 | −0.02 to 0.02 | 0.78 | 0.022 |
BMI, Body mass index; CI, confidence interval.
Profile 1=absence of symptoms; profile 2=adolescent-onset repeated symptoms; profile 3=adolescent-onset symptoms with good adult outcome; profile 4=adult-onset repeated symptoms.
p Value for sex×profile interaction.
Coefficients represent the mean difference in BMI at age 15 years between each profile and profile 1.
Coefficients represent the mean difference in BMI change per year (from 15 to 53 years) between each profile and profile 1.
Fig. 1.
Predicted body mass index (BMI) mean between ages 15 and 53 years for (a) men and (b) women in four longitudinal profiles of affective symptoms: absence of symptoms, adolescent-onset repeated symptoms, adolescent-onset with good adult outcome; and adult-onset repeated symptoms.
Among men, two profiles – repeated symptoms with adolescent onset (p<0.001) and adolescent-onset symptoms with good adult outcome (p=0.030) – had significantly lower mean BMI across adulthood than those with absence of symptoms (Table 2, Fig. 1a). For example, the mean BMI at 15 years for those with adolescent-onset repeated symptoms was 0.55 kg/m2 (95% confidence interval −0.77 to −0.33) lower than for those with no symptoms (Table 2). A sex×profile interaction (p=0.023) indicated that this association was significantly stronger in men than women. Men with adult-onset symptoms had a similar BMI trajectory to those with absence of symptoms.
The results of the analysis using unadjusted models in the sample with full information on confounders (n=3375) (Table 3, model 1) were similar to those in the full sample. Adding BMI at age 11 years in men (Table 3, model 2) reduced the strength of association between affective symptoms profiles and BMI, suggesting that men with adolescent-onset symptoms were also thinner than others in childhood. Adjusting the basic model for BMI at age 7 years (data not shown) attenuated only the association with the profile of adolescent-onset symptoms with good adult outcome.
Table 3. Results from multilevel modelsa of BMI trajectories (between 15 and 53 years) by longitudinal profilesb of affective symptoms in men and women with full information on confounders.
| Model 1 |
Model 2 |
Model 3 |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | 95% CI | p | Coefficient | 95% CI | p | Coefficient | 95% CI | p | |
| Men (n=1727) | |||||||||
| Profile 2c | −0.57 | −0.82 to −0.31 | <0.0001 | −0.16 | −0.35 to 0.02 | 0.090 | −0.18 | −0.36 to 0.01 | 0.059 |
| Profile 3c | −0.36 | −0.80 to 0.07 | 0.11 | −0.13 | −0.44 to 0.18 | 0.42 | −0.15 | −0.46 to 0.16 | 0.35 |
| Profile 4c | 0.03 | −0.29 to 0.34 | 0.86 | −0.01 | −0.23 to 0.22 | 0.97 | 0.03 | −0.20 to 0.25 | 0.82 |
| Profile 2 by age (year)d | −0.004 | −0.12 to 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.004 | −0.01 to 0.02 | 0.48 | 0.01 | −0.02 to 0.01 | 0.45 |
| Profile 3 by age (year)d | 0.01 | −0.01 to 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.01 | −0.01 to 0.03 | 0.33 | 0.01 | −0.01 to 0.03 | 0.34 |
| Profile 4 by age (year)d | −0.01 | −0.02 to 0.01 | 0.20 | −0.01 | −0.02 to 0.00 | 0.18 | −0.01 | −0.02 to 0.00 | 0.18 |
| Women (n=1673) | |||||||||
| Profile 2c | −0.35 | −0.65 to −0.04 | 0.028 | −0.36 | −0.57 to −0.15 | 0.0010 | −0.44 | −0.65 to −0.23 | <0.0001 |
| Profile 3c | −0.69 | −1.22 to −0.16 | 0.011 | −0.53 | −0.89 to −0.16 | 0.0040 | −0.58 | −0.94 to −0.22 | 0.0020 |
| Profile 4c | −0.05 | −0.43 to 0.33 | 0.79 | −0.09 | −0.36 to 0.16 | 0.47 | −0.11 | −0.37 to 0.14 | 0.39 |
| Profile 2 by age (year)d | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.01 | −0.01 to 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.01 | −0.01 to 0.03 | 0.16 |
| Profile 3 by age (year)d | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.06 | 0.028 | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.05 | 0.030 | 0.03 | 0.00 to 0.05 | 0.030 |
| Profile 4 by age (year)d | 0.00 | −0.02 to 0.02 | 0.99 | −0.002 | −0.02 to 0.02 | 0.98 | −0.003 | −0.02 to 0.02 | 0.98 |
BMI, Body mass index; CI, confidence interval.
Model 1 – adjusted for age, age2 and age3; model 2 – additionally adjusted for BMI at age 11 years; model 3 – additionally adjusted for BMI at age 11 years and childhood and adult social class.
Profile 1=absence of symptoms; profile 2=adolescent-onset repeated symptoms; profile 3=adolescent-onset symptoms with good adult outcome; profile 4=adult-onset repeated symptoms.
Coefficients represent the mean difference in BMI at age 15 years between each profile and profile 1.
Coefficients represent the mean difference in BMI change per year (from 15 to 53 years) between each profile and profile 1.
The association between adolescent-onset symptom profiles and BMI in women altered only slightly after adjustment for BMI at age 11 years (Table 3, model 2), thus suggesting that, for a given BMI at age 11 years, women with adolescent-onset symptoms had lower BMI than women with absence of symptoms at age 15 years. No such effect was observed after adjusting for BMI at age 7 years (data not shown).
Further adjustment for social class in childhood and adulthood had little additional impact on the association between symptoms profiles and BMI in either sex (Table 3, model 3). Smoking and adolescent conduct disorders did not confound the associations either (data not shown).
Discussion
In this study investigating the association between longitudinal profiles of affective symptoms and BMI change from adolescence to age 53 years, associations varied by sex and age at onset of affective symptoms. Among women, those with adolescent-onset symptoms had faster rates of increase in BMI across adult life than others, resulting in them having the highest BMI at age 53 years. Men with adolescent-onset symptoms had lower BMI at all ages than others. The BMI trajectories of men and women with adult-onset symptoms did not differ from those without symptoms.
Strengths and limitations
Our study is unique in having multiple measures of both mental health and BMI in both adolescence and adulthood. An advantage, compared with previous longitudinal studies, is thus that the effect of age of onset of the mental health problems on BMI change across the life course can be explored (Colman et al. 2007a). BMI measures were available at six ages between 15 and 26 years and, hence, the BMI trajectory could be modelled in more detail than in previous studies. Height and weight were measured in the NSHD at all except at two ages in early adulthood, thus minimising the possibility of reporting bias at the majority of ages. The magnitude of the bias due to self-reports at ages 20 and 26 years is likely to be small (Schutz & Woringer, 2002).
The British 1946 birth cohort is reasonably representative of the British born population of the same age (Wadsworth et al. 2003) and thus strengthens the generalizability of our findings. Since all the participants were born in 1946, our results are not confounded by age, although we cannot exclude the sociocultural influences specific to this cohort.
As we used multilevel models it was not necessary for each individual to have all outcome measures recorded, but to obtain unbiased estimates in the presence of missing data it must be assumed that responses are missing at random (MAR); that is, the probability of any BMI measure being missing may depend upon observed, but not unobserved, measures. Loss to follow-up and missing data are unavoidable in long running birth cohort studies such as the NSHD. However, there is no reason to suspect that any differences in the characteristics of those with missing data compared with the rest would have a substantial impact on our findings.
Comparison with previous studies
Previous longitudinal studies have reported that depression in adolescence is a risk factor for the development and persistence of high BMI (Pine et al. 1997, 2001; Bardone et al. 1998; Barefoot et al. 1998; Goodman & Whitaker, 2002; Richardson et al. 2003; Hasler et al. 2004, 2005; Franko et al. 2005; Anderson et al. 2006; Tanofsky-Kraff et al. 2006; Liem et al. 2008). A recent review of 11 studies suggested that depressive symptoms at age 6–19 years were associated with a 1.90- to 3.50-fold increased risk of subsequent overweight assessed after a period of 1–15 years (Liem et al. 2008). We found a faster increase in BMI during adulthood in women with adolescent symptoms, resulting in this group having the highest mean BMI in their fifties. A recent study showed that the association between common mental disorder and obesity became stronger with age between 35 and 70 years (Kivimaki et al. 2009). Consistent with our findings, little or no differences in rates of obesity were observed between ages 35 and 55 years in that study. BMI exhibits strong tracking in the current study (Wills et al. 2009), and hence, this has implications for the health of women with adolescent symptoms as they age. If women with adolescent-onset symptoms in the current study continue on their current rapidly increasing BMI trajectories, their rates of obesity will be considerably higher at older ages than those with absence of symptoms.
Depressive symptoms in adolescence are commonly found to be associated with overweight or obesity in women (Blaine, 2008), whilst results in men suggest an inverse or non-significant relationship (Pine et al. 1997; Richardson et al. 2003; Anderson et al. 2006). Consistent with our findings, Anderson et al. (2006) reported lower weight in men, and higher weight gain in women, with early onset of depression and/or anxiety across the life course up to the mean age of 33.1 years. The 1970 Birth Cohort Study also showed that childhood emotional problems predicted faster weight gain by age 30 years in women, but not in men (Ternouth et al. 2009). We show in an older cohort that this rise in BMI in women continues until mid-life.
The inverse association between adolescent-onset affective symptoms and BMI in men in the current study was largely explained by their lower BMI at age 11 years, suggesting that they were also thin in childhood. This finding is in agreement with the data suggesting the directional relationship from low BMI to future depressive symptoms and/or suicide (Magnusson et al. 2006; Bjorge et al. 2008). However, in women with adolescent-onset affective symptoms, BMI at 11 years did not account for the lower BMI at age 15 years, suggesting that these women exhibited a slower mean increase in BMI between 11 and 15 years compared with those with absence of symptoms. Thus it is possible that relative weight loss occurred in these women after of around the time of onset of symptoms. This, together with the fact that these women subsequently increased BMI faster than others, suggests that they may be more prone to greater weight change. The absence of data on affective symptoms before age 13 years, however, does not allow us to say whether symptoms were present before any change in relative weight. Since affective symptoms can exist in prepubertal children (Green et al. 2005), even an early childhood measure of these symptoms would not necessarily indicate the direction of effect. In our opinion there is little sense in attempting to elucidate the direction of the relationship, since it is most likely to be bidirectional.
Previous studies have not investigated whether the BMI of those with affective symptoms in adolescence varied depending on the presence of adult symptoms. In those with adolescent-onset symptoms, we found similar BMI trajectories for those with good adult outcome and those with continuing symptoms, high-lighting the importance of adolescence in the development of the relationship.
Plausible mechanisms
The co-occurrence of depression and weight change raises a question of common cause. Such a process could operate through neurobiological pathways, such as the serotonergic system and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (Stunkard et al. 2003; Bornstein et al. 2006). Shared genetic risk factors and adverse environmental factors in early life, for example, parental loss or physical and sexual abuse (Harris, 2001; Williamson et al. 2002; Noll et al. 2007), may act independently or through a gene–environment interaction, leading simultaneously to weight change and affective symptoms.
During adolescence, rates of depression begin to rise and BMI increases, both more rapidly in girls (Maughan, 2002). Gonadal hormones may be involved in the joint susceptibility in girls to both depression and increases in BMI. Stressful events during adolescence could also have a joint impact on affective symptoms and BMI (Ge et al. 2001). Sexual abuse in childhood, for instance, was shown to play a critical role in both development depression (Teicher et al. 2009) and obesity (Noll et al. 2007) in women. Depression may also lead to detrimental changes in health behaviours resulting in, for example, poor lifelong eating and exercise habits (Jaffee et al. 2002; Stice et al. 2002), which could explain the significant weight gain in adulthood in women with adolescent-onset affective symptoms.
This longitudinal investigation suggests that adolescent-onset affective symptoms are associated with rapid weight gain across the life course in women, but not in men. Our findings indicate that interventions to reduce increases in BMI across the life course in women with adolescent-onset depression should be considered, irrespective of the BMI of adolescents at the time of diagnosis of depression.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Medical Research Council (to D.G., M.R., D.K. and R.H.), by Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research (Population Health Investigator Award to I.C.) and by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust Specialist Biomedical Research Centre (to M.H.).
Footnotes
Declaration of Interest
None.
References
- Anderson SE, Cohen P, Naumova EN, Must A. Association of depression and anxiety disorders with weight change in a prospective community-based study of children followed up into adulthood. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. 2006;160:285–291. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.160.3.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlantis E, Baker M. Obesity effects on depression: systematic review of epidemiological studies. International Journal of Obesity. 2008;32:881–891. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardone AM, Moffitt TE, Caspi A, Dickson N, Stanton WR, Silva PA. Adult physical health outcomes of adolescent girls with conduct disorder, depression, and anxiety. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 1998;37:594–601. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199806000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barefoot JC, Heitmann BL, Helms MJ, Williams RB, Surwit RS, Siegler IC. Symptoms of depression and changes in body weight from adolescence to mid-life. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 1998;22:688–694. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0800647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorge T, Engeland A, Tverdal A, Smith GD. Body mass index in adolescence in relation to cause-specific mortality: a follow-up of 230,000 Norwegian adolescents. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2008;168:30–37. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwn096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaine B. Does depression cause obesity?: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies of depression and weight control. Journal of Health Psychology. 2008;13:1190–1197. doi: 10.1177/1359105308095977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein SR, Schuppenies A, Wong ML, Licinio J. Approaching the shared biology of obesity and depression: the stress axis as the locus of gene-environment interactions. Molecular Psychiatry. 2006;11:892–902. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter KM, Hasin DS, Allison DB, Faith MS. Relationships between obesity and DSM-IV major depressive disorder, suicide ideation, and suicide attempts: results from a general population study. American Journal of Public Health. 2000;90:251–257. doi: 10.2105/ajph.90.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaiton MO, Cohen JE, O’Loughlin J, Rehm J. A systematic review of longitudinal studies on the association between depression and smoking in adolescents. BMC Public Health. 2009;9:356. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-9-356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clennell S, Kuh D, Guralnik JM, Patel KV, Mishra GD. Characterisation of smoking behaviour across the life course and its impact on decline in lung function and all-cause mortality: evidence from a British birth cohort. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. 2008;62:1051–1056. doi: 10.1136/jech.2007.068312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman I, Murray J, Abbott RA, Maughan B, Kuh D, Croudace TJ, Jones PB. Outcomes of conduct problems in adolescence: 40 year follow-up of national cohort. British Medical Journal. 2009;338:a2981. doi: 10.1136/bmj.a2981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman I, Ploubidis GB, Wadsworth ME, Jones PB, Croudace TJ. A longitudinal typology of symptoms of depression and anxiety over the life course. Biological Psychiatry. 2007a;62:1265–1271. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman I, Wadsworth ME, Croudace TJ, Jones PB. Forty-year psychiatric outcomes following assessment for internalizing disorder in adolescence. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2007b;164:126–133. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2007.164.1.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton MT, Daumit GL, Druss BG. Cigarette smoking and overweight/obesity among individuals with serious mental illnesses: a preventive perspective. Harvard Review of Psychiatry. 2006;14:212–222. doi: 10.1080/10673220600889256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wit LM, van Straten A, van Herten M, Penninx BW, Cuijpers P. Depression and body mass index, a U-shaped association. BMC Public Health. 2009;9:14. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-9-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPietro L, Anda RF, Williamson DF, Stunkard AJ. Depressive symptoms and weight change in a national cohort of adults. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 1992;16:745–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diverse Populations Collaboration Weight-height relationships and body mass index: some observations from the diverse populations collaboration. American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 2005;128:220–229. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.20107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duarte CS, Sourander A, Nikolakaros G, Pihlajamaki H, Helenius H, Piha J, Kumpulainen K, Moilanen I, Tamminen T, Almqvist F, Must A. Child mental health problems and obesity in early adulthood. Journal of Pediatrics. 2010;156:93–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.06.066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman-Hoffman VL, Yankey JW, Hillis SL, Wallace RB, Wolinsky FD. Weight and depressive symptoms in older adults: direction of influence? Journals of Gerontology B Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences. 2007;62:S43–S51. doi: 10.1093/geronb/62.1.s43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko DL, Striegel-Moore RH, Thompson D, Schreiber GB, Daniels SR. Does adolescent depression predict obesity in black and white young adult women? Psychological Medicine. 2005;35:1505–1513. doi: 10.1017/S0033291705005386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge X, Conger RD, Elder GH., Jr. Pubertal transition, stressful life events, and the emergence of gender differences in adolescent depressive symptoms. Developmental Psychology. 2001;37:404–417. doi: 10.1037//0012-1649.37.3.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg DP, Hillier VF. A scaled version of the General Health Questionnaire. Psychological Medicine. 1979;9:139–145. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700021644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman E, Whitaker RC. A prospective study of the role of depression in the development and persistence of adolescent obesity. Pediatrics. 2002;110:497–504. doi: 10.1542/peds.110.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H, McGinnity A, Meltzer H, Ford T, Goodman R. Mental Health of Children and Young People in Britain 2004. Palgrave MacMillan; London: 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R, Wadsworth M, Kuh D. The influence of childhood weight and socioeconomic status on change in adult body mass index in a British national birth cohort. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 2000;24:725–734. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. Recent developments in understanding the psychosocial aspects of depression. British Medical Bulletin. 2001;57:17–32. doi: 10.1093/bmb/57.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasler G, Pine DS, Gamma A, Milos G, Ajdacic V, Eich D, Rossler W, Angst J. The associations between psychopathology and being overweight: a 20-year prospective study. Psychological Medicine. 2004;34:1047–1057. doi: 10.1017/s0033291703001697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasler G, Pine DS, Kleinbaum DG, Gamma A, Luckenbaugh D, Ajdacic V, Eich D, Rossler W, Angst J. Depressive symptoms during childhood and adult obesity: the Zurich Cohort Study. Molecular Psychiatry. 2005;10:842–850. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haukkala A, Uutela A, Salomaa V. Depressive symptoms, cynical hostility, and weight change: a 3-year follow-up among middle-aged men and women. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 2001;8:116–133. [Google Scholar]
- Istvan J, Zavela K, Weidner G. Body weight and psychological distress in NHANES I. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 1992;16:999–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffee SR, Moffitt TE, Caspi A, Fombonne E, Poulton R, Martin J. Differences in early childhood risk factors for juvenile-onset and adult-onset depression. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2002;59:215–222. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.59.3.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P, Rodgers B, Murray R, Marmot M. Child development risk factors for adult schizophrenia in the British 1946 birth cohort. Lancet. 1994;344:1398–1402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J, Martin A, King RA, Charney D. Are child-, adolescent-, and adult-onset depression one and the same disorder? Biological Psychiatry. 2001;49:980–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(01)01127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivimaki M, Batty GD, Singh-Manoux A, Nabi H, Sabia S, Tabak AG, Akbaraly TN, Vahtera J, Marmot MG, Jokela M. Association between common mental disorder and obesity over the adult life course. British Journal of Psychiatry. 2009;195:149–155. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.108.057299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuh D, Ben Shlomo Y, Lynch J, Hallqvist J, Power C. Life course epidemiology. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. 2003;57:778–783. doi: 10.1136/jech.57.10.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem ET, Sauer PJ, Oldehinkel AJ, Stolk RP. Association between depressive symptoms in childhood and adolescence and overweight in later life: review of the recent literature. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. 2008;162:981–988. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.162.10.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindelow M, Hardy R, Rodgers B. Development of a scale to measure symptoms of anxiety and depression in the general UK population: The Psychiatric Symptom Frequency Scale. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health. 1997;51:549–557. doi: 10.1136/jech.51.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson PK, Rasmussen F, Lawlor DA, Tynelius P, Gunnell D. Association of body mass index with suicide mortality: a prospective cohort study of more than one million men. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2006;163:1–8. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwj002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamun AA, O’Callaghan MJ, Cramb SM, Najman JM, Williams GM, Bor W. Childhood behavioral problems predict young adults’ BMI and obesity: evidence from a birth cohort study. Obesity. 2009;17:761–766. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maughan B. Depression and psychological distress: a life course perspective. In: Kuh D, Hardy R, editors. A Life Course Approach to Women’s Health. Oxford University Press; Oxford: 2002. pp. 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Moore ME, Stunkard A, Srole L. Obesity, social class, and mental illness. 1962. Obesity Research. 1997;5:503–508. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1997.tb00678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll JG, Zeller MH, Trickett PK, Putnam FW. Obesity risk for female victims of childhood sexual abuse: a prospective study. Pediatrics. 2007;120:e61–e67. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-3058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine DS, Cohen P, Brook J, Coplan JD. Psychiatric symptoms in adolescence as predictors of obesity in early adulthood: a longitudinal study. American Journal of Public Health. 1997;87:1303–1310. doi: 10.2105/ajph.87.8.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine DS, Goldstein RB, Wolk S, Weissman MM. The association between childhood depression and adulthood body mass index. Pediatrics. 2001;107:1049–1056. doi: 10.1542/peds.107.5.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Registrar General . Classification of Occupations. HMSO; London, UK: 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Richards M, Abbott R. [Accessed 23 October 2009];Childhood mental health and life chances in post-war Britain: insights from three national birth cohort studies. The Smith Institute. 2009 ( http://www.smith-institute.org.uk/pdfs/life_chances_report.pdf)
- Richardson LP, Davis R, Poulton R, McCauley E, Moffitt TE, Caspi A, Connell F. A longitudinal evaluation of adolescent depression and adult obesity. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. 2003;157:739–745. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.157.8.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts RE, Deleger S, Strawbridge WJ, Kaplan GA. Prospective association between obesity and depression: evidence from the Alameda County Study. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 2003;27:514–521. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter M. A children’s behaviour questionnaire for completion by teachers: preliminary findings. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 1967;8:1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1967.tb02175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutz Y, Woringer V. Obesity in Switzerland: a critical assessment of prevalence in children and adults. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 2002;26(Suppl. 2):S3–S11. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stice E, Presnell K, Spangler D. Risk factors for binge eating onset in adolescent girls: a 2-year prospective investigation. Health Psychology. 2002;21:131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunkard AJ, Faith MS, Allison KC. Depression and obesity. Biological Psychiatry. 2003;54:330–337. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(03)00608-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanofsky-Kraff M, Cohen ML, Yanovski SZ, Cox C, Theim KR, Keil M, Reynolds JC, Yanovski JA. A prospective study of psychological predictors of body fat gain among children at high risk for adult obesity. Pediatrics. 2006;117:1203–1209. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teicher MH, Samson JA, Polcari A, Andersen SL. Length of time between onset of childhood sexual abuse and emergence of depression in a young adult sample: a retrospective clinical report. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2009;70:684–691. doi: 10.4088/jcp.08m04235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ternouth A, Collier D, Maughan B. Childhood emotional problems and self-perceptions predict weight gain in a longitudinal regression model. BMC Medicine. 2009;7:46. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-7-46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Os J, Jones P, Lewis G, Wadsworth M, Murray R. Developmental precursors of affective illness in a general population birth cohort. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1997;54:625–631. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830190049005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth ME, Butterworth SL, Hardy RJ, Kuh DJ, Richards M, Langenberg C, Hilder WS, Connor M. The life course prospective design: an example of benefits and problems associated with study longevity. Social Science and Medicine. 2003;57:2193–2205. doi: 10.1016/s0277-9536(03)00083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson DF, Thompson TJ, Anda RF, Dietz WH, Felitti V. Body weight and obesity in adults and self-reported abuse in childhood. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 2002;26:1075–1082. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills AK, Hardy JR, Black S, Kuh DJ. Trajectories of overweight and body mass index in adulthood and blood pressure at age 53: the 1946 British birth cohort study. Journal of Hypertension. 2009 doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328335de7b. Published online: 29 December 2009. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328335de7b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing JK, Cooper JE, Sartorius N. The Measurement and Classification of Psychiatric Symptoms. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1974. [Google Scholar]
- WHO [Accessed 23 October 2009];The global burden of disease: 2004. 2008 update ( http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GBD_report_2004update_part4.pdf)