Abstract
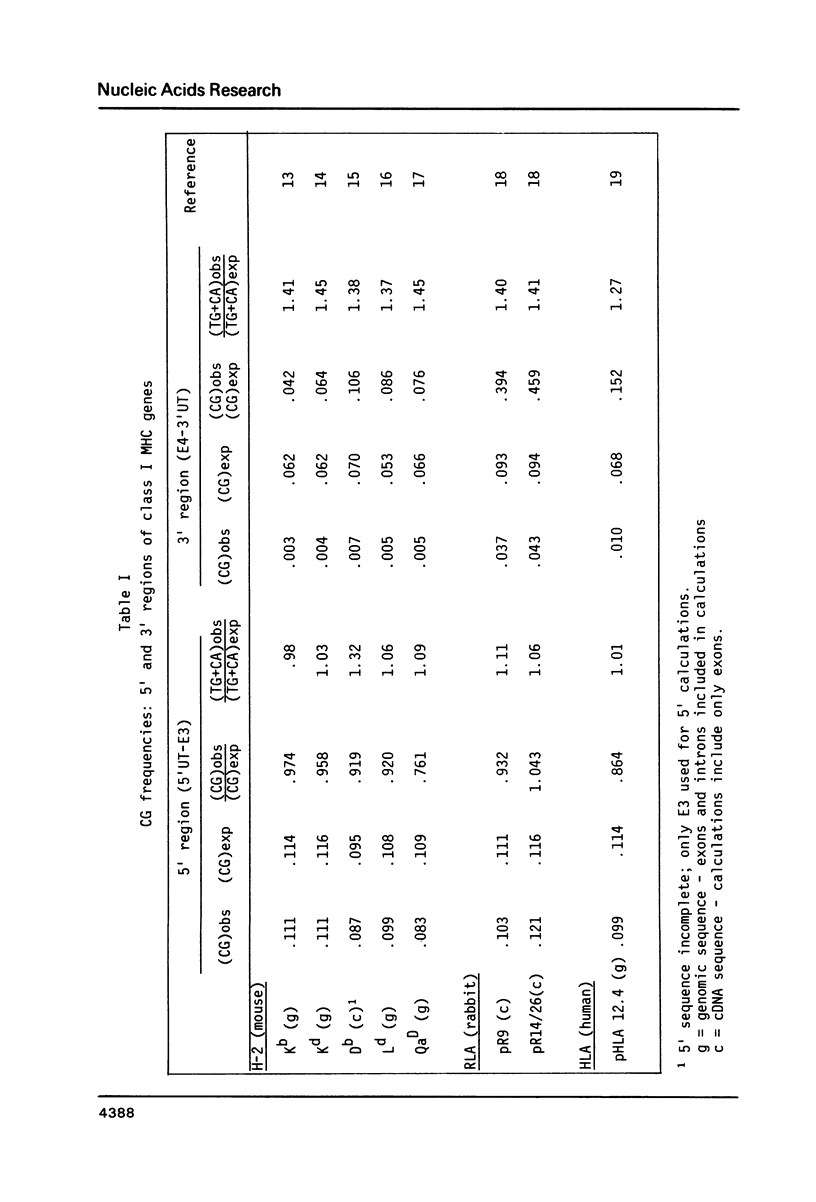
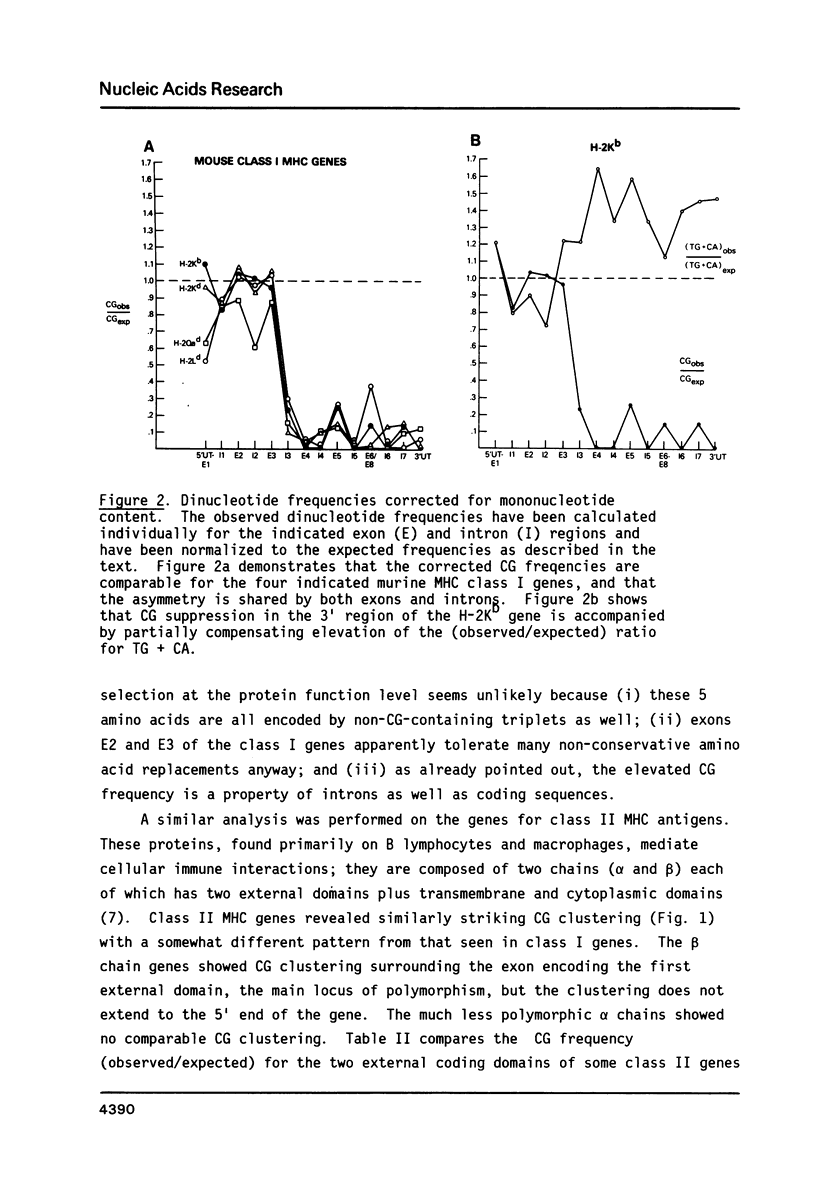
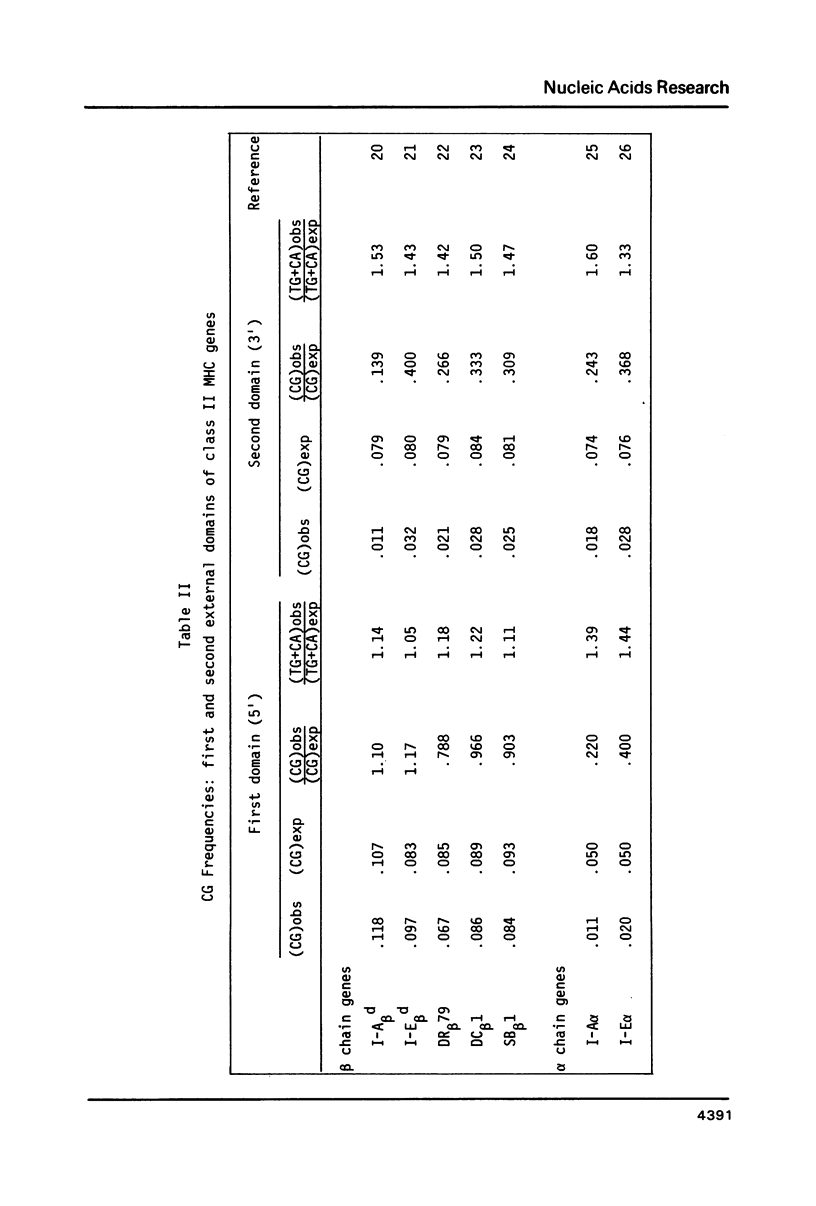
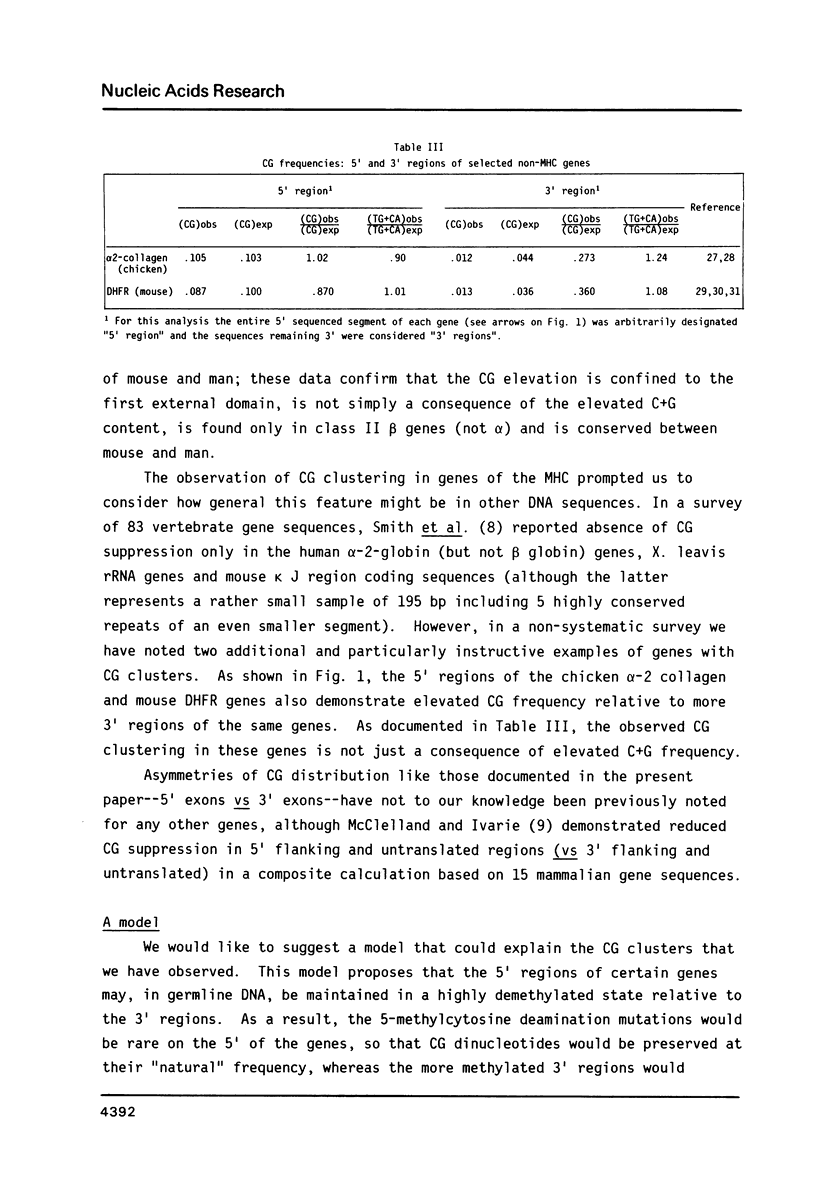
In the DNA of higher vertebrates the dinucleotide CG is unique in two respects: it occurs far less frequently than would be expected on the basis of the content of cytosine and guanine in a given DNA segment ("CG suppression") and it contains predominantly 5-methyl-cytosine, the only modified nucleotide common in vertebrate DNA. Here we point out the existence of CG clusters, i.e. localized lapses in the usual CG suppression, in two categories of DNA segments from vertebrates: around the polymorphic exons of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes and in the 5' regions of certain other genes. These observations contradict the recent suggestion that CG frequency is uniform over long contiguous segments of DNA containing several genes. A model for the origin of these CG clusters as a consequence of regional demethylation of germline DNA is supported by analysis of other sequence features of these regions as well as by previously published data on the methylation status in sperm DNA of two of these CG-rich regions.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J., Kanter M. R., Williams V. E., 2nd, McDevitt H. O. Regions of allelic hypervariability in the murine A alpha immune response gene. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1499–1504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Simonsen C. C., McEwan R. N., Schimke R. T. Structure of amplified normal and variant dihydrofolate reductase genes in mouse sarcoma S180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7887–7897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Margulies D. H., Shykind B., Seidman J. G., Ozato K. Exon shuffling: mapping polymorphic determinants on hybrid mouse transplantation antigens. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):755–757. doi: 10.1038/300755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball E. S., Coligan J. E. Structure of class I major histocompatibility antigens. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1983;9:1–63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4517-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Roberts L., Dobberstein B. Mouse histocompatibility genes: structure and organisation of a Kd gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):245–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Servenius B., Andersson G., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Exon-intron organization and complete nucleotide sequence of a human major histocompatibility antigen DC beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7313–7317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon G. G., Fraser N. W. CpG frequency in large DNA segments. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(3-4):286–288. doi: 10.1007/BF02099976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Hunkapiller T., Hood L. Nucleotide sequence of a light chain gene of the mouse I-A subregion: A beta d. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):750–754. doi: 10.1126/science.6410508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Malissen B., Jordan B. R. Exon/intron organization and complete nucleotide sequence of an HLA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):893–897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon C., Ohkubo H., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Unusual methylation pattern of the alpha 2 (l) collagen gene. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas J., Steinmetz M., Hunkapiller T., Jones P., Hood L. DNA sequence of the gene encoding the E alpha Ia polypeptide of the BALB/c mouse. Science. 1982 Dec 17;218(4578):1229–1232. doi: 10.1126/science.6815800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., Sher B. T., Sun Y. H., Eakle K. A., Hood L. DNA sequence of a gene encoding a BALB/c mouse Ld transplantation antigen. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):679–682. doi: 10.1126/science.7058332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Schimke R. T. Structure and genomic organization of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Maki R. A., Clayton L. K., Tonegawa S. Complete primary structures of the E beta chain and gene of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5520–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Kaufman J. F., Korman A. J., Strominger J. L. HLA-DR antigens: structure, separation of subpopulations, gene cloning and function. Immunol Rev. 1982;66:133–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Waterman M. S., Sadler J. R. Statistical characterization of nucleic acid sequence functional domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2205–2220. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Sciaky-Gallili N., Razin A., Cedar H. Pattern of methylation of two genes coding for housekeeping functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2422–2426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Ohkubo H., Sobel M. E., Yamada Y., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Structure of the promoter for chicken alpha 2 type I collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5334–5338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Tate V., Boedtker H., Doty P. Structure of the pro alpha 2 (I) collagen gene. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):129–135. doi: 10.1038/294129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


