Abstract
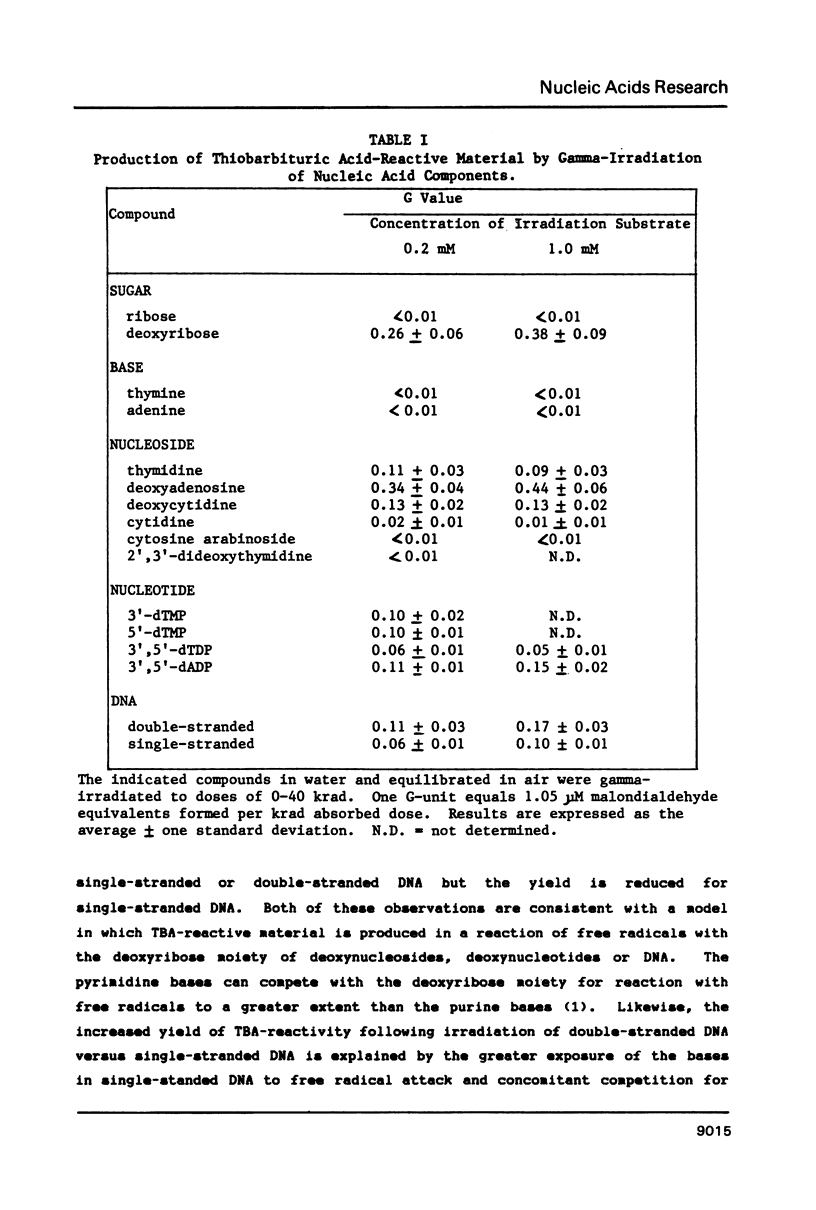
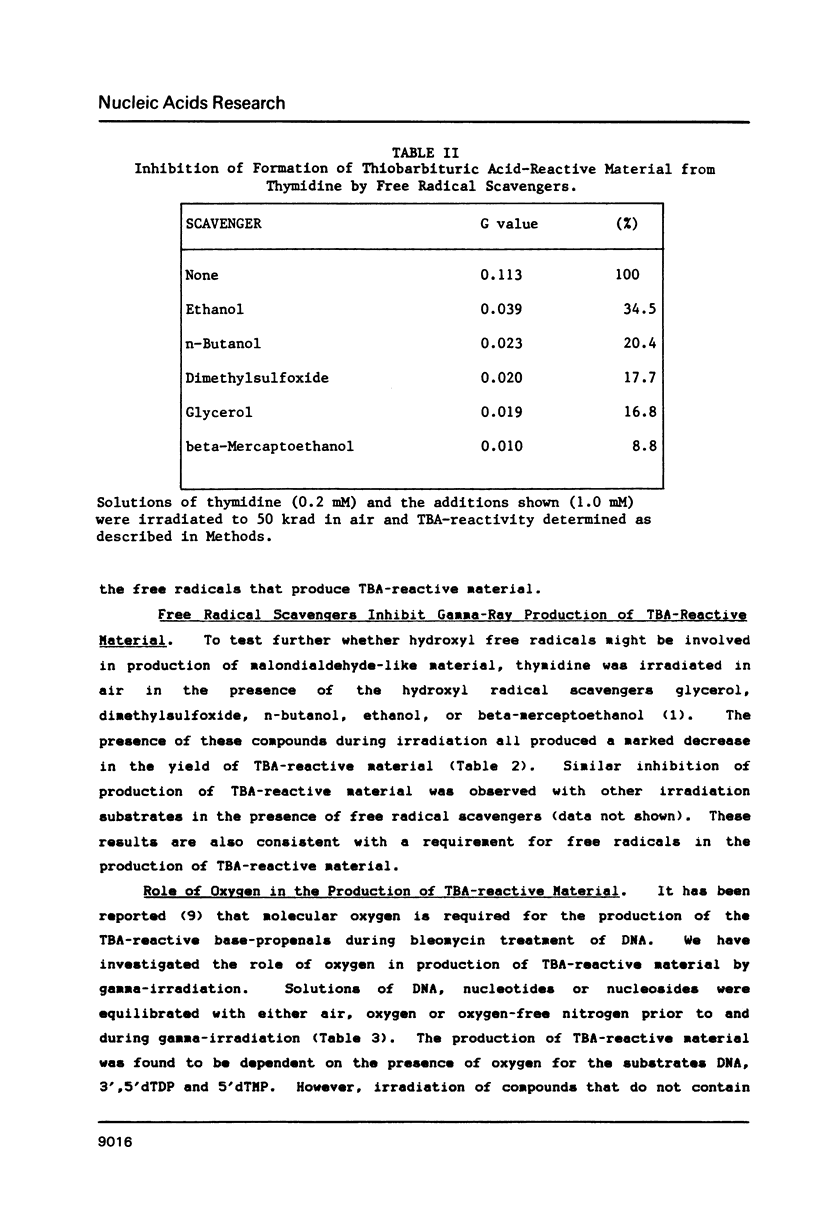
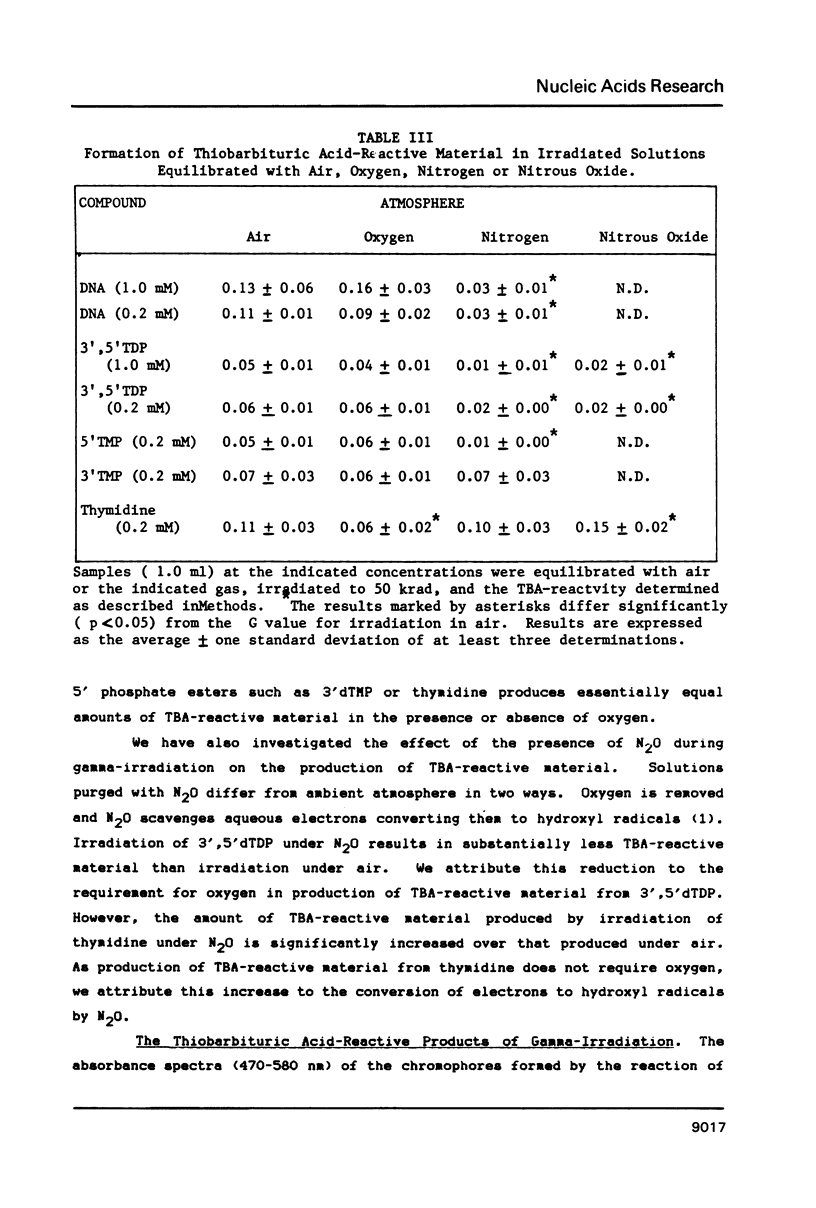
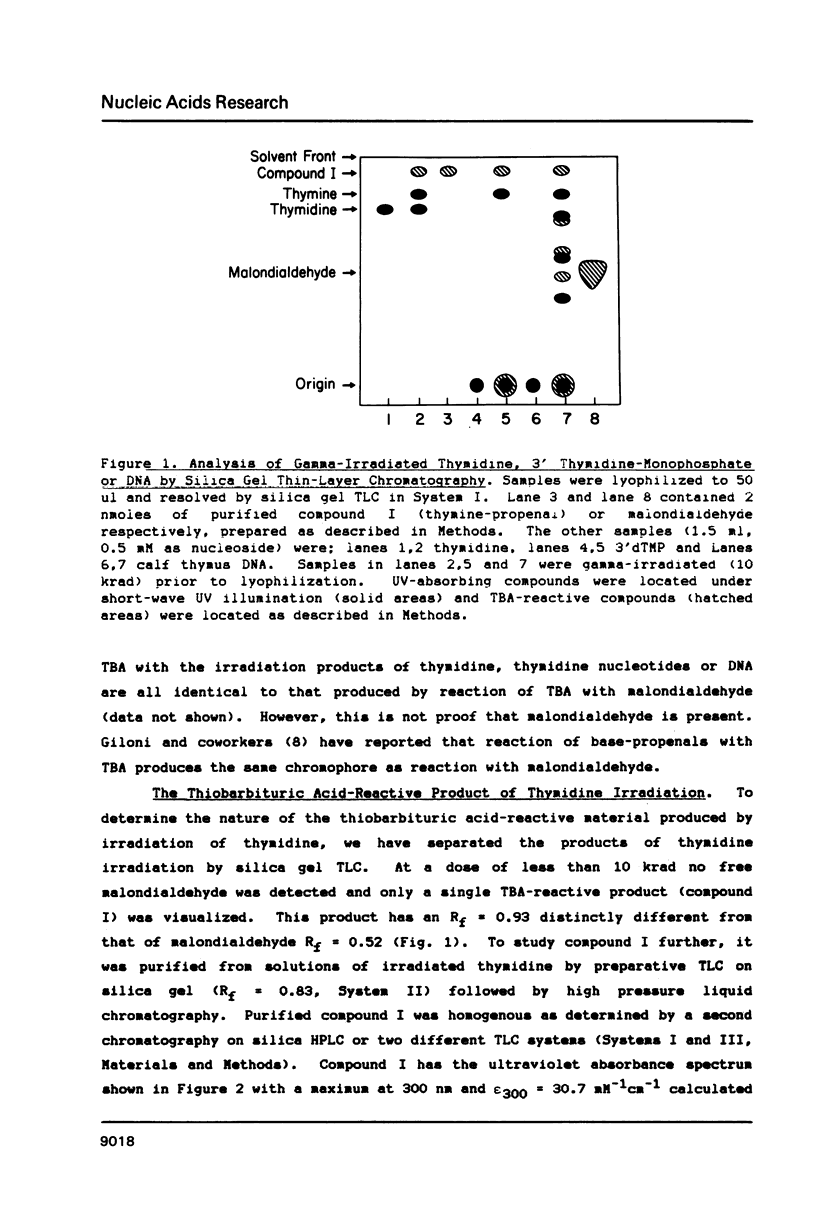
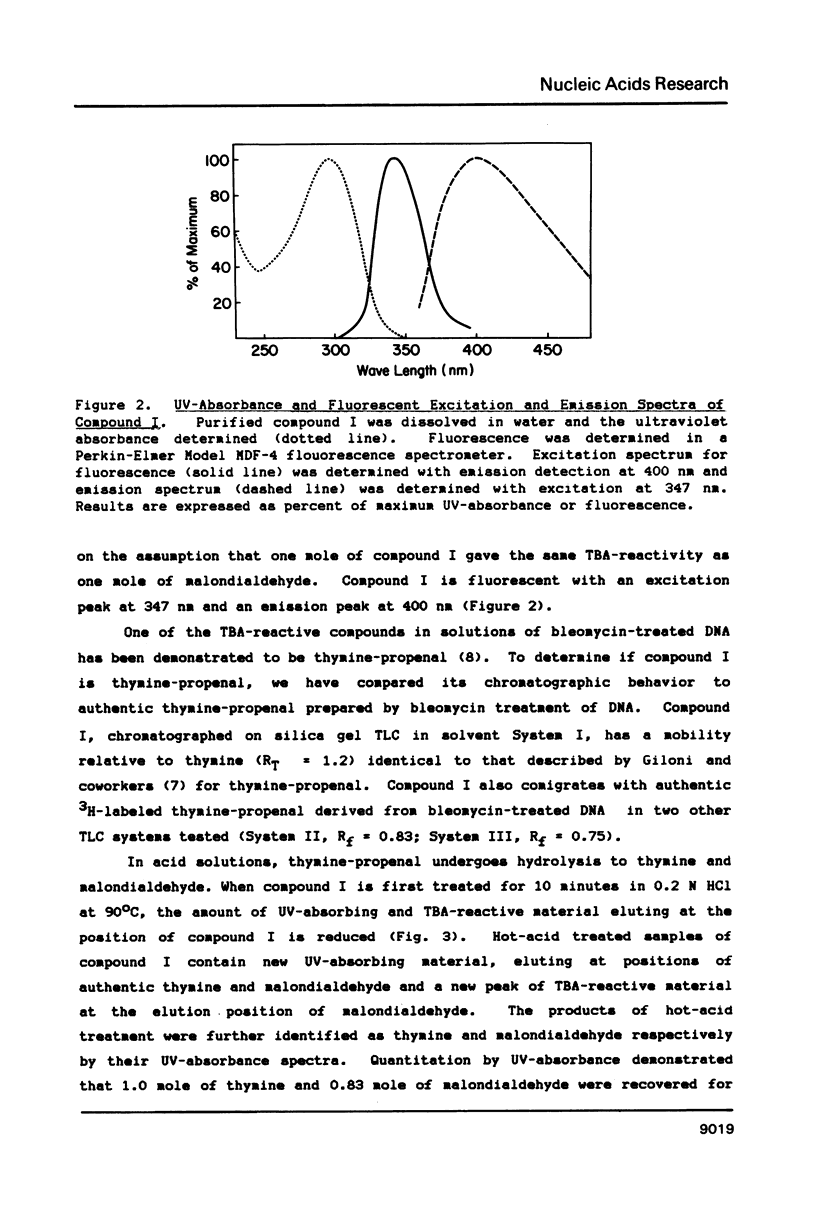
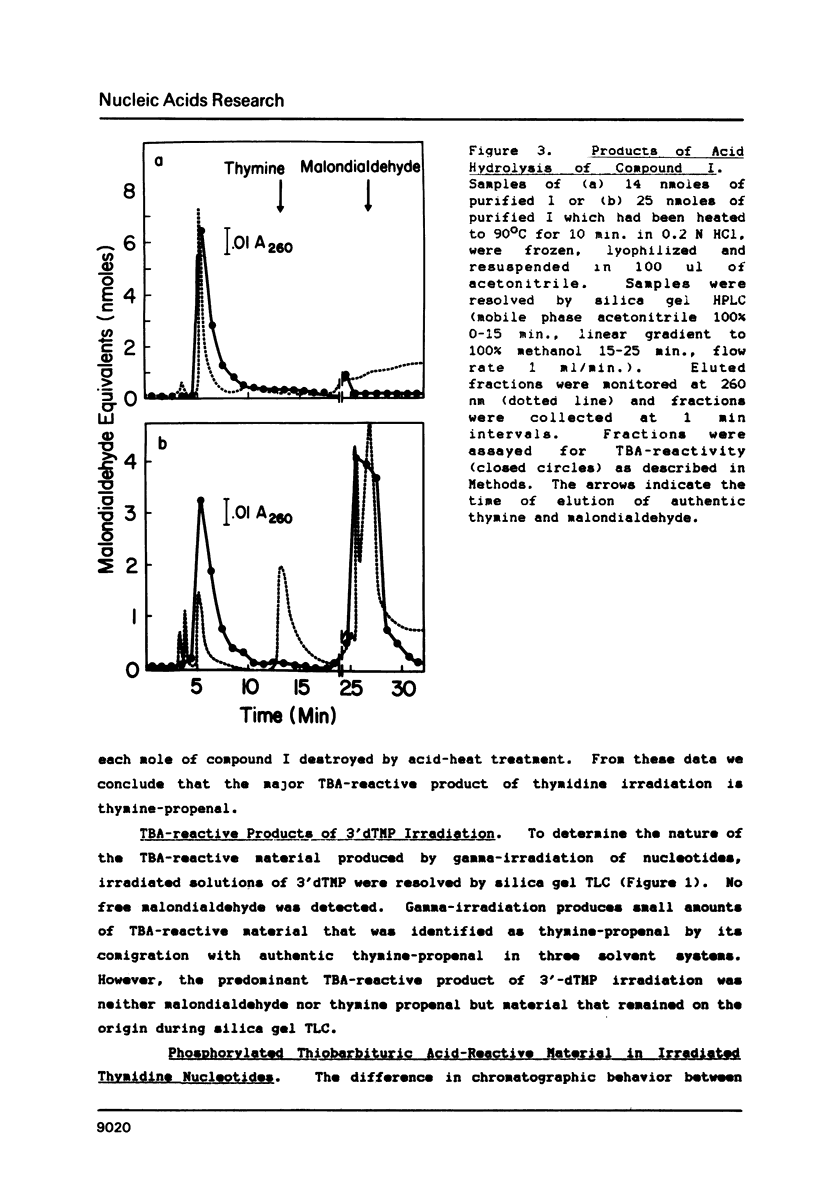
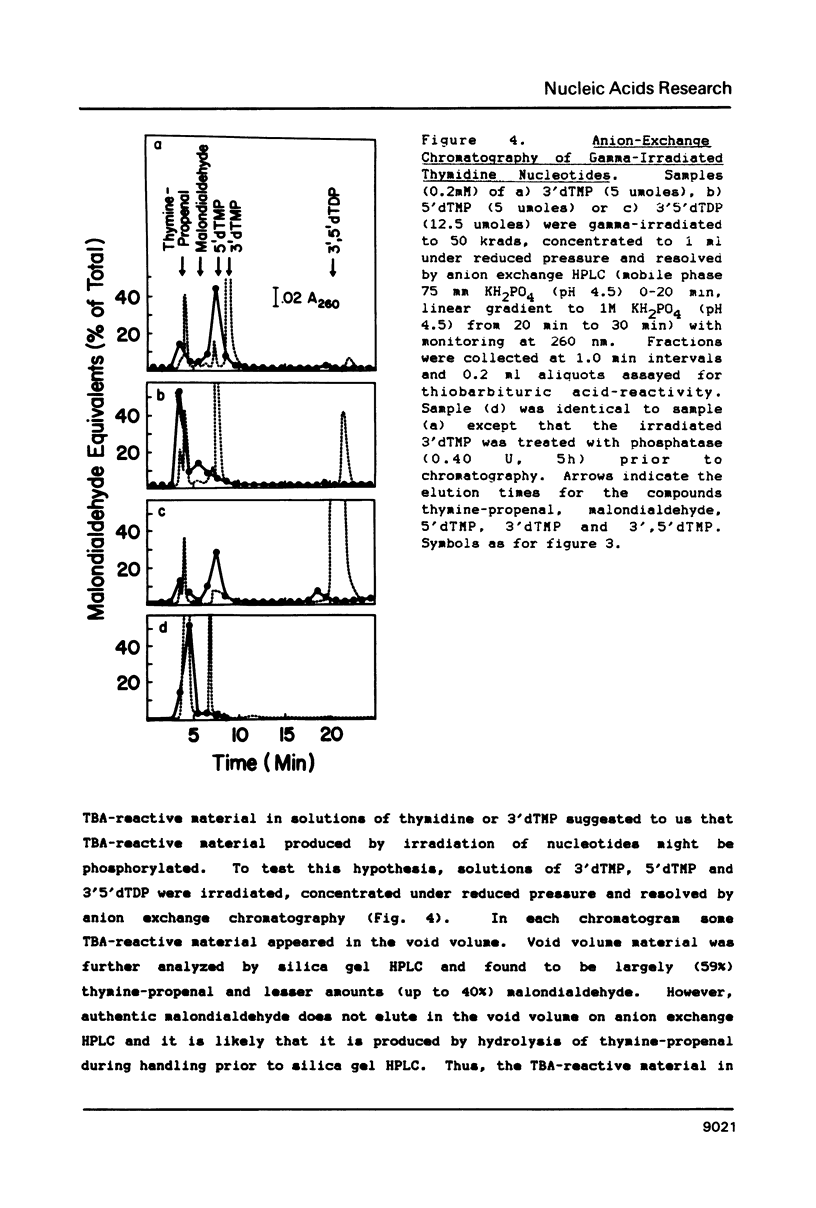
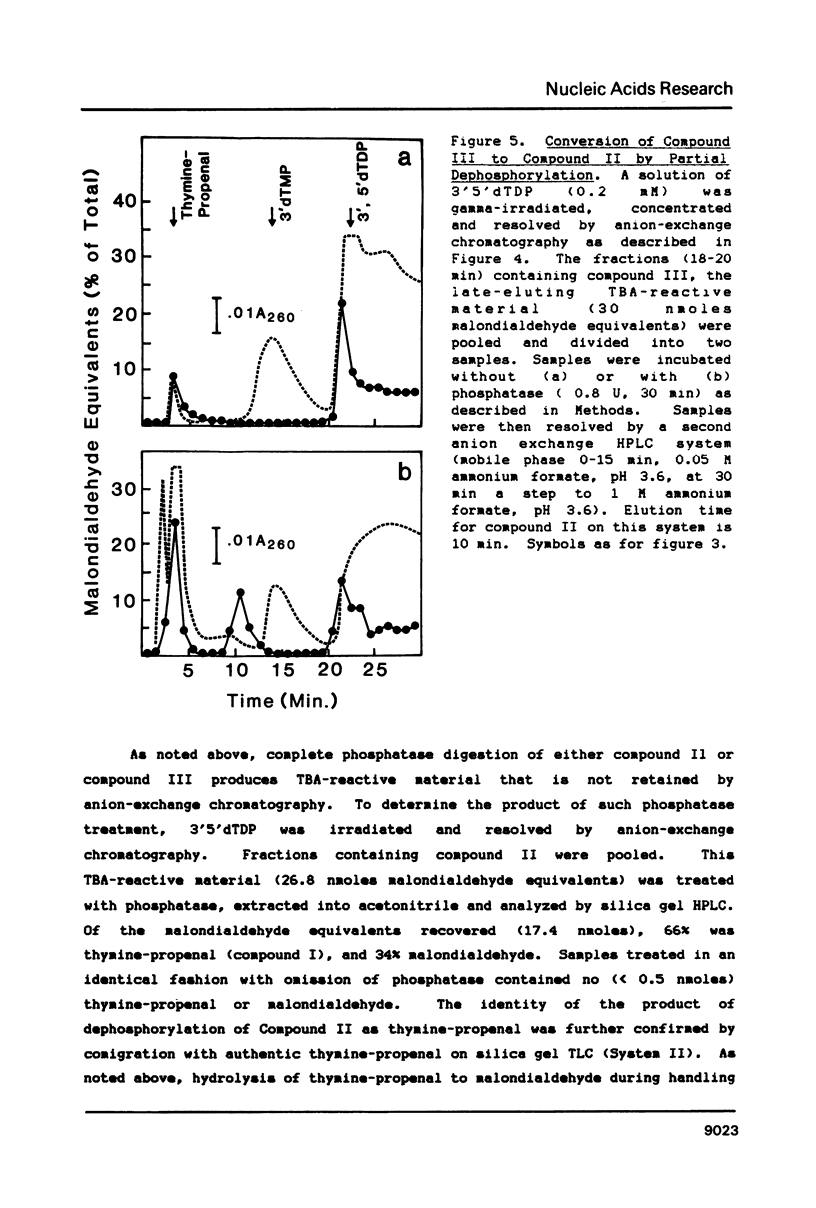
Gamma-irradiation of DNA, deoxynucleosides, or deoxynucleotides produces material that reacts with thiobarbituric acid to form a chromophore with maximum absorbance at 532 nm. This material is not malondialdehyde. We have identified a new radiation product (thymin-1'-yl)-propenal as the TBA-reactive product of gamma-irradiation of thymidine. Thymine-propenal has been described by other investigators as a product of bleomycin-treatment of DNA. Irradiation of thymidine nucleotides produces phosphorylated precursors to thymine-propenal. Studies of the requirements for formation of TBA-reactivity indicate a mechanism involving reaction of a free radical with the deoxyribose moiety and molecular oxygen. On the basis of these results it is proposed that gamma-irradiation produces TBA-reactive material in DNA by the same reaction sequence in which bleomycin catalyzes the formation of base-propenals in DNA. Bleomycin and gamma-irradiation differ in the extent to which the sequence proceeds to completion with release of free base-propenals.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burger R. M., Berkowitz A. R., Peisach J., Horwitz S. B. Origin of malondialdehyde from DNA degraded by Fe(II) x bleomycin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11832–11838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. M., Peisach J., Horwitz S. B. Stoichiometry of DNA strand scission and aldehyde formation by bleomycin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8612–8614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giloni L., Takeshita M., Johnson F., Iden C., Grollman A. P. Bleomycin-induced strand-scission of DNA. Mechanism of deoxyribose cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8608–8615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman A. P., Takeshita M., Pillai K. M., Johnson F. Origin and cytotoxic properties of base propenals derived from DNA. Cancer Res. 1985 Mar;45(3):1127–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge J. M. Free-radical damage to lipids, amino acids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids determined by thiobarbituric acid reactivity. Int J Biochem. 1982;14(7):649–653. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(82)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner W. D., Grunberg S. M., Haseltine W. A. Sites and structure of gamma radiation-induced DNA strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11750–11754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner W. D., Rodriguez L. O., Hecht S. M., Haseltine W. A. gamma Ray induced deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks. 3' Glycolate termini. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):711–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F., Pillai K. M., Grollman A. P., Tseng L., Takeshita M. Synthesis and biological activity of a new class of cytotoxic agents: N-(3-oxoprop-1-enyl)-substituted pyrimidines and purines. J Med Chem. 1984 Aug;27(8):954–958. doi: 10.1021/jm00374a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp D. S., Smith K. C. Chemical nature of chain breaks produced in DNA by x-irradiation in vitro. Radiat Res. 1970 Apr;42(1):34–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krushinskaia N. P., Shal'nov M. I. O prirode razryvov v tsepi DNK pri obluchenii vodnykh rastvorov. Radiobiologiia. 1967 Jan-Feb;7(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Frohlinde D., Bothe E. Identification of a major pathway of strand break formation in poly U induced by OH radicals in presence of oxygen. Z Naturforsch C. 1984 Mar-Apr;39(3-4):315–319. doi: 10.1515/znc-1984-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich M., Hagen U. Base liberation and concomitant reactions in irradiated DNA solutions. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;19(6):507–517. doi: 10.1080/09553007114550701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Kozarich J. W., Stubbe J. The mechanism of free base formation from DNA by bleomycin. A proposal based on site specific tritium release from Poly(dA.dU). J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4694–4697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



