Abstract
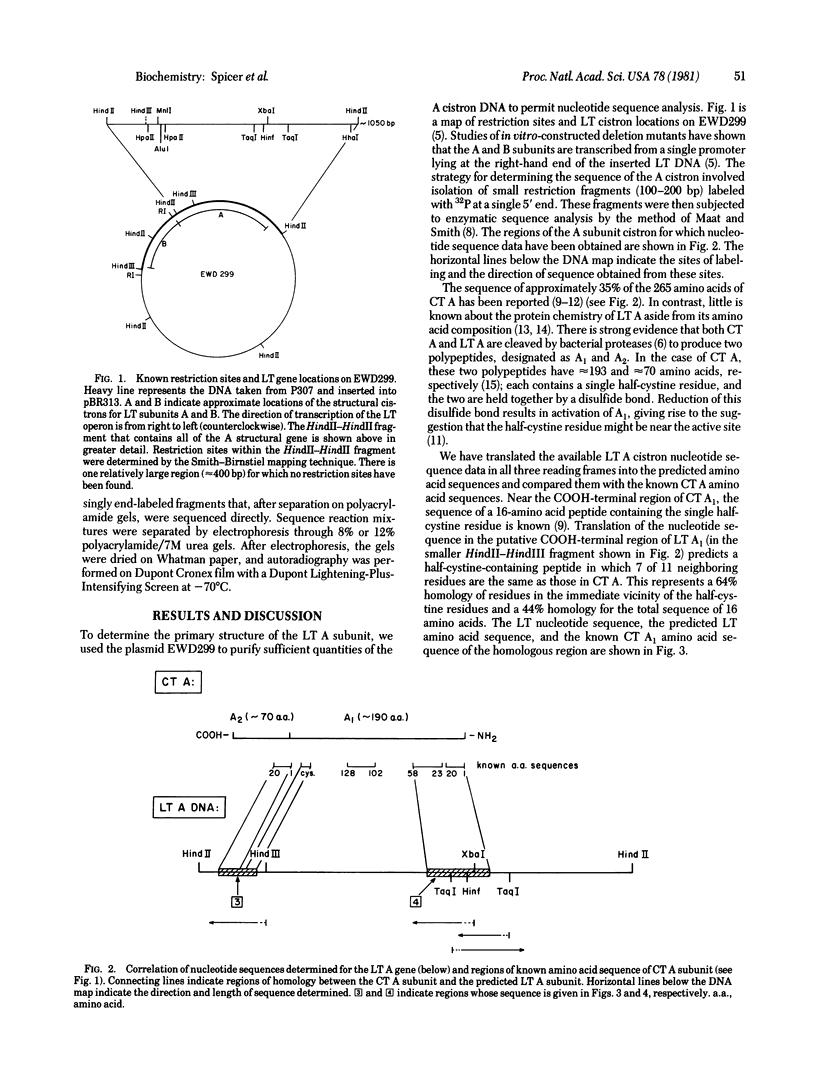
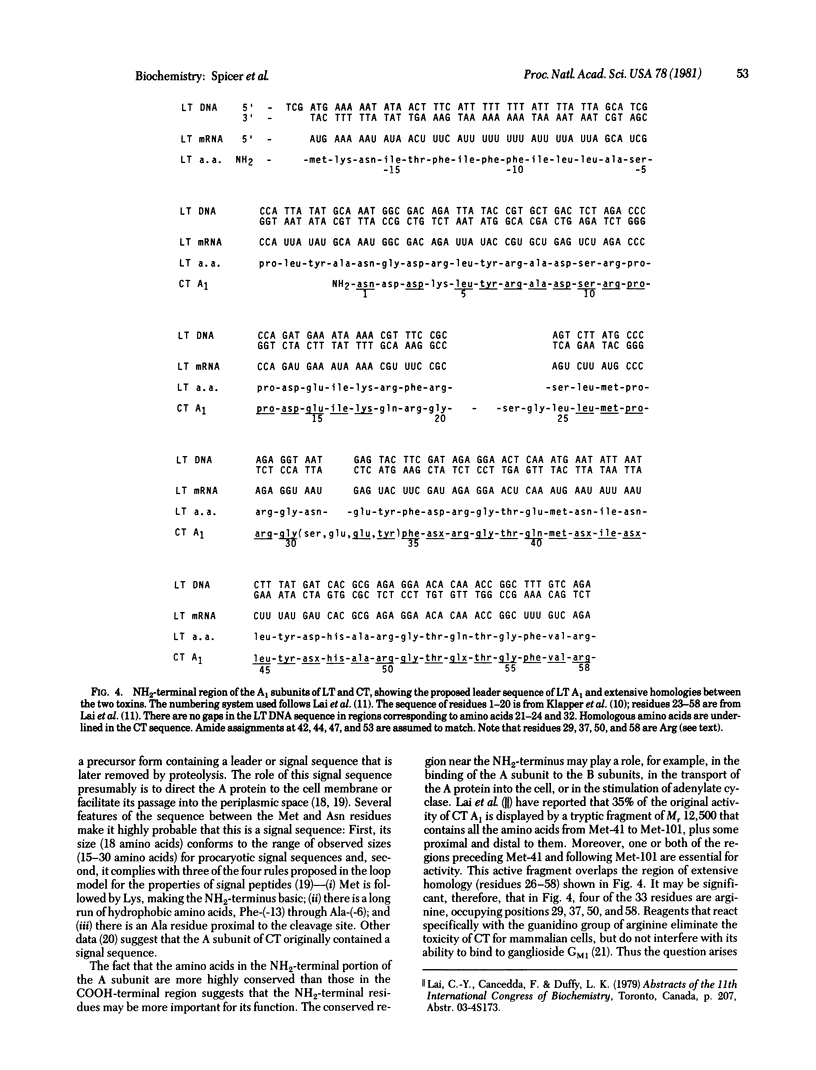
The genes coding for the heat-labile enterotoxin LT produced by Escherichia coli have been cloned into the plasmid pBR313. Using DNA derived from the resulting chimeric plasmid, we determined the nucleotide sequence of two regions of the gene coding for the enzymatically active A subunit of LT. Translation of the nucleotide sequence gives the primary structure of the NH2-terminal and COOH-terminal regions of the LT A subunit. This permits direct comparison of the LT A subunit with the A subunit of cholera toxin. Our results show that the two toxins possess homologous sequences, of varying degrees, in both regions of their primary structure. The order of the component A1 and A2 polypeptides is A1-A2. The nucleotide sequence predicts the existence of a signal sequence of 18 amino acids at the NH2-terminus of the A subunit.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang C. N., Blobel G., Model P. Detection of prokaryotic signal peptidase in an Escherichia coli membrane fraction: endoproteolytic cleavage of nascent f1 pre-coat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):361–365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological cross-reactivity between a heat-labile enterotoxin(s) of Escherichia coli and subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1036-1039.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. The molecular nature of heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) of escherichia coli. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):406–407. doi: 10.1038/277406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Gill D. M., Falkow S. Cistrons encoding Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):850–858. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.850-858.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D., Tai P. C. The mechanism of protein secretion across membranes. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):433–438. doi: 10.1038/283433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Richardson S. H. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase catalyzed by heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: comparison with cholera toxin. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Immunological study of the heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.564-570.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Finkelstein R. A., Capra J. D. Subunit structure and N-terminal amino acid sequence of the three chains of cholera enterotoxin. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jul;13(7):605–611. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. Y., Cancedda F., Chang D. Primary structure of cholera toxin subunit A1: isolation, partial sequences and alignment of the BrCN fragments. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth I., Holmgren J. Protein reagent modification of cholera toxin: characterization of effects on antigenic, receptor-binding and toxic properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Dec;91(2):263–277. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maat J., Smith A. J. A method for sequencing restriction fragments with dideoxynucleoside triphosphates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4537–4545. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markel D. E., Hejtmancik K. E., Peterson J. W., Kurosky A. Structure, function, and antigenicity of cholera toxin. J Supramol Struct. 1979;10(2):137–149. doi: 10.1002/jss.400100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez E., Lai C. Y., Wodnar-Filipowicz A. Location and the primary structure around the disulfide bonds in cholera toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 15;67(4):1435–1443. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movva N. R., Nakamura K., Inouye M. Amino acid sequence of the signal peptide of ompA protein, a major outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):27–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. The assembly of proteins into biological membranes: The membrane trigger hypothesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:23–45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


