Abstract
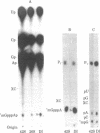
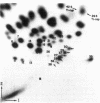
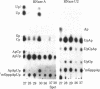
An 18S defective interfering (DI) RNA population was isolated from the cytoplasm of baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells infected with Semliki Forest virus from the 10th undiluted passage. The RNA was approximately 2000 nucleotides long and contained a 5'-terminal cap with the structure 7mGpppAp and a poly(A) tract. The DI RNA contained large TI oligonucleotides derived from both the 42S RNA-specific region and the 3' one-third of the genome common to 42S and 26S RNA. Several of the large oligonucleotides were present in nonequimolar ratios, suggesting that the RNA population is heterogeneous. As this population is approximately uniform in size, this suggests that the DI RNAs may be generated by internal deletions involving different regions of the genome. The 5'-terminal cap-containing RNase T1 oligonucleotide was isolated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis from uniformly 32P-labeled RNA and shown to be heterogeneous. Five T1 caps with the structure 7mGpppA-U(A-U)nC-A-U-G(n = 4-8) were identified. The two major T1 caps (n = 4 and 6) comprised about 75% of the total yield of T1 caps. The T1 caps were different from the genomic 42S RNA T1 cap (7mGpppA-U-G), suggesting that the extreme 5' end of the genome is not conserved in this defective interfering RNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruton C. J., Kennedy S. I. Defective-interfering particles of Semliki Forest Virus: structural differences between standard virus and defective-interfering particles. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):383–395. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohner D., Monroe S., Weiss B., Schlesinger S. Oligonucleotide mapping studies of standard and defective Sindbis virus RNA. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):794–798. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.794-798.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild G. M., Stollar V. Defective interfering particles of Sindbis virus. V. Sequence relationships between SVSTD 42 S RNA and intracellular defective viral RNAs. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):175–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species of standard and defective-interfering Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):491–511. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Simons K., von Bonsdorff C. H. Studies in subviral components of Semliki Forest virus. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(4):235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Söderlund H. Structure and replication of alpha-viruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;82:15–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46388-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Kort L., Kolakofsky D. Further characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs: a model for their generation. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):539–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Sullivan M., Maizel J. V., Jr Characterization of a new isolate of poliovirus defective interfering particles. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):759–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Jacobson A., Lee Y. F., Dunn J., Wimmer E. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus: mapping of the deletion and evidence that the deletions in the genomes of DI(1), (2) and (3) are located in the same region. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 25;128(2):179–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrault J., Semler B. L. Internal genome deletions in two distinct classes of defective interfering particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Hewlett M. J., Baltimore D., Coffin J. M. The genome of Uukuniemi virus consists of three unique RNA segments. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. The nucleotide sequences of the 5'-terminal T1 oligonucleotides of Semliki-Forest-virus 42-S and 26-S RNAs are different. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(3):435–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark C., Kennedy S. I. The generation and propagation of defective-interfering particles of Semliki Forest virus in different cell types. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):285–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Guttman N., Baltimore D., Lodishi H. F. Complete translation of poliovirus RNA in a eukaryotic cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4157–4161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Gross H. S. Replicative form of Semliki Forest virus RNA contains an unpaired guanosine. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):754–756. doi: 10.1038/282754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Localization of the 26-S RNA sequence on the viral genome type 42-S RNA isolated from SFV-infected cells. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):190–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wachter R., Fiers W. Preparative two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of 32 P-labeled RNA. Anal Biochem. 1972 Sep;49(1):184–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]