Abstract
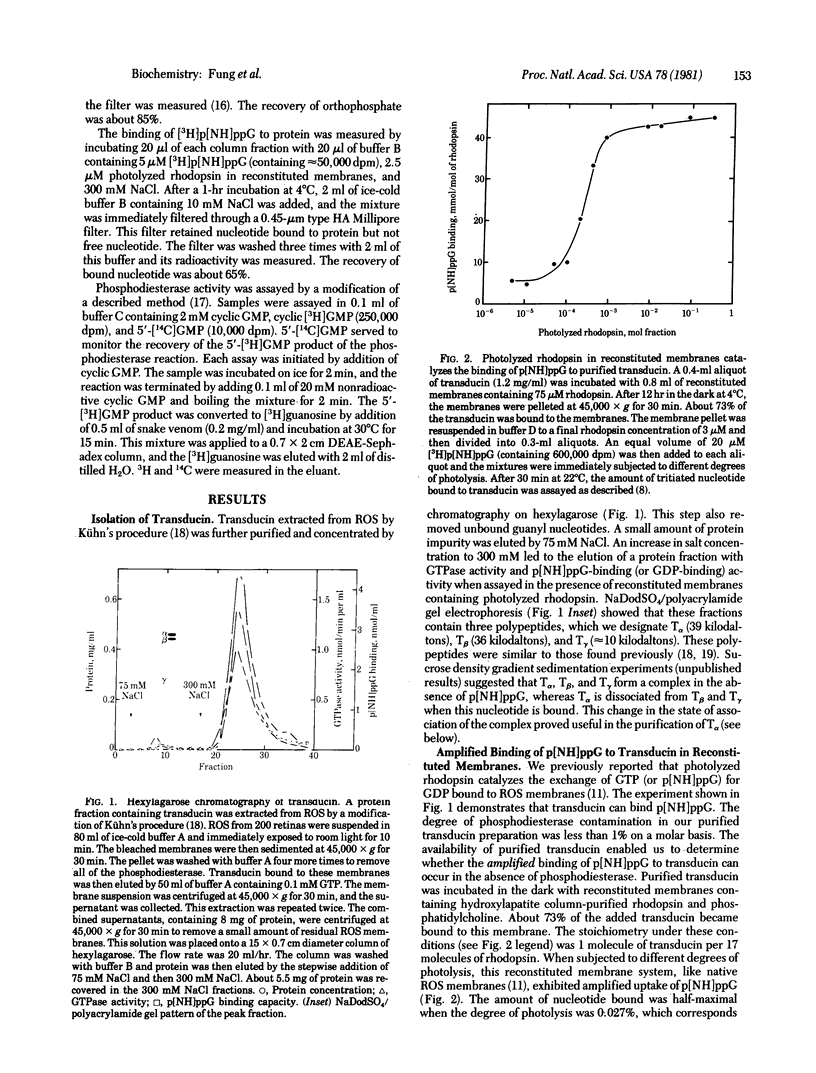
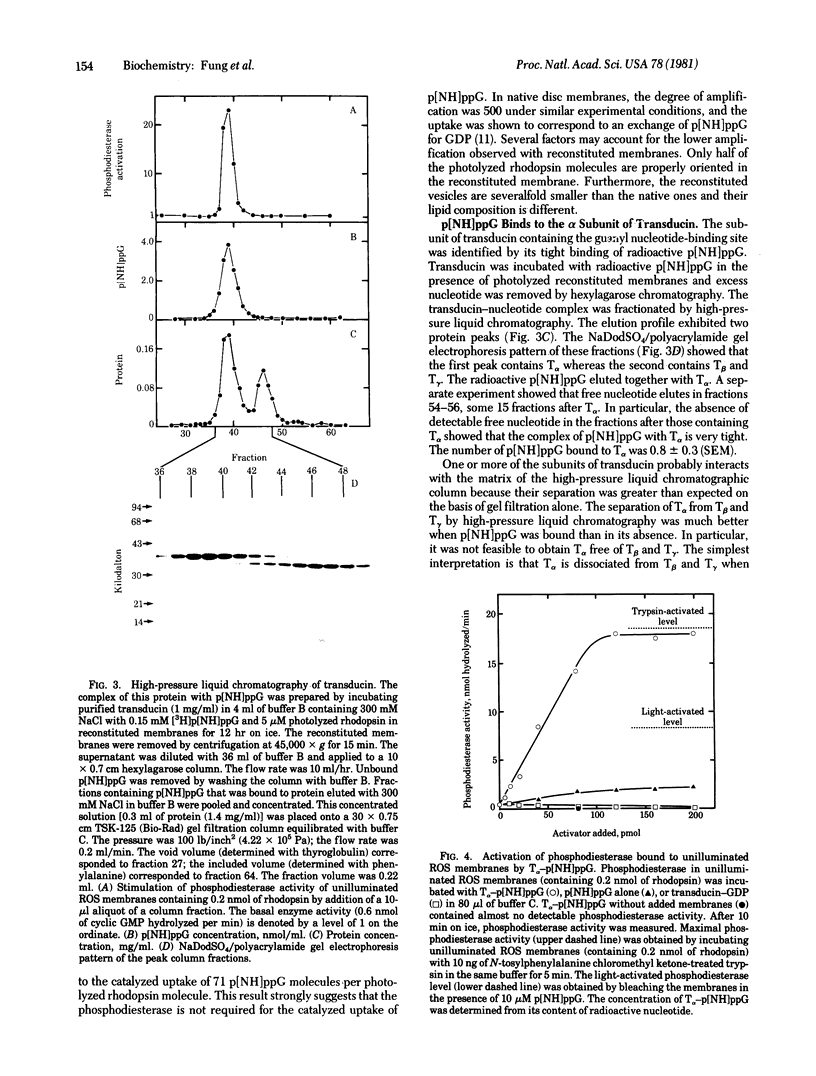
Photolyzed rhodopsin catalyzes the exchange of GTP for FDP bound to a protein in retinal rod outer segments. We previously proposed that the GTP complex of this protein regulates the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase and that it may be the first amplified intermediate in visual excitation [Fung, B. K.-K. & Stryer, L. (1980) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 2500-2504]. We report here the identification and characterization of transducin, a regulatory protein consisting of three kinds of polypeptide chains: T alpha (39 kilodaltons), T beta (36 kilodaltons), and T gamma (approximately 10 kilodaltons). Reconstituted membranes containing transducin and rhodopsin but no phosphodiesterase exhibit GTPase activity and amplified binding of guanosine 5'[beta, gamma-imido]triphosphate (p[NH]ppG), a nonhydrolyzable analog of GTP, on illumination. A single photolyzed rhodopsin molecule led to the uptake of p[NH]ppG by 71 molecules of transducin. High-pressure liquid chromatography showed that the binding site for GTP is on the alpha subunit of transducin. The isolation of the complex of ;[NH]ppG with T alpha enabled us to determine whether this species is the activator of the phosphodiesterase. We found that phosphodiesterase on unilluminated disc membranes can indeed be fully activated by addition of T alpha containing bound p[NH]ppG. These findings strongly suggest that transducin is the first amplified information-carrying intermediate in the cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehr W., Devlin M. J., Applebury M. L. Isolation and characterization of cGMP phosphodiesterase from bovine rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11669–11677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godchaux W., 3rd, Zimmerman W. F. Membrane-dependent guanine nucleotide binding and GTPase activities of soluble protein from bovine rod cell outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7874–7884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Hubbell W. L. Lipid requirements for Rhodopsin regenerability. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4517–4523. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., Bownds M. D. Visual transduction in vertebrate photoreceptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:17–34. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B. Isolation and recombination of bovine rod outer segment cGMP phosphodiesterase and its regulators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):505–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y. The role of guanosine 5'-triphosphate in polypeptide chain elongation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 21;505(1):95–127. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok-Keung Fung B., Stryer L. Photolyzed rhodopsin catalyzes the exchange of GTP for bound GDP in retinal rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2500–2504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H. Light- and GTP-regulated interaction of GTPase and other proteins with bovine photoreceptor membranes. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):587–589. doi: 10.1038/283587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Pugh E. N., Jr The control of phosphodiesterase in rod disk membranes: kinetics, possible mechanisms and significance for vision. Vision Res. 1979;19(4):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(79)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Rasmussen H., Dowling J. E. Electrical and adaptive properties of rod photoreceptors in Bufo marinus. II. Effects of cyclic nucleotides and prostaglandins. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Dec;70(6):771–791. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.6.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki N., Baraban J. M., Keirns J. J., Boyce J. J., Bitensky M. W. Purification and properties of the light-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase of rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6320–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Bitensky M. W. Light-regulated enzymes of vertebrate retinal rods. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;11:265–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGINO Y., MIYOSHI Y. THE SPECIFIC PRECIPITATION OF ORTHOPHOSPHATE AND SOME BIOCHEMICAL APPLICATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2360–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Appleman M. M. Characterization of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases of rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3145–3150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. L., Bownds M. D. Amplitude, kinetics, and reversibility of a light-induced decrease in guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate in frog photoreceptor membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1979 May;73(5):629–653. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.5.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee R., Liebman P. A. Light-activated phosphodiesterase of the rod outer segment. Kinetics and parameters of activation and deactivation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8902–8909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]