Abstract
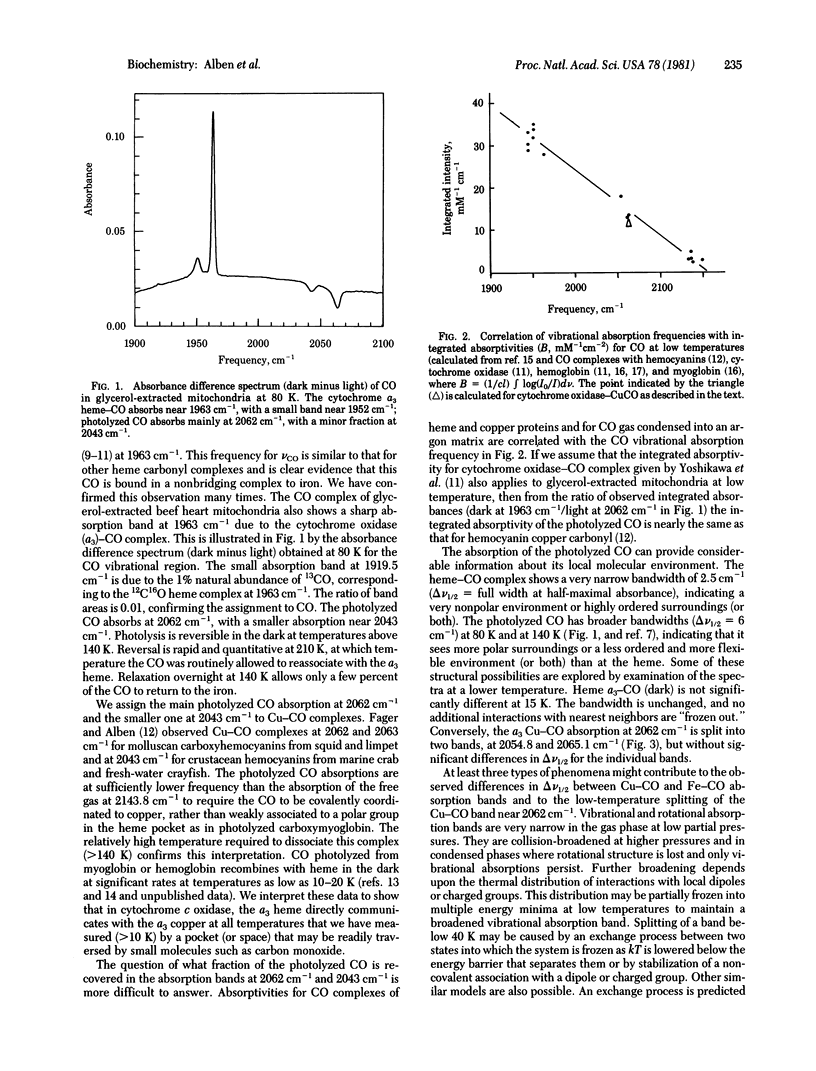
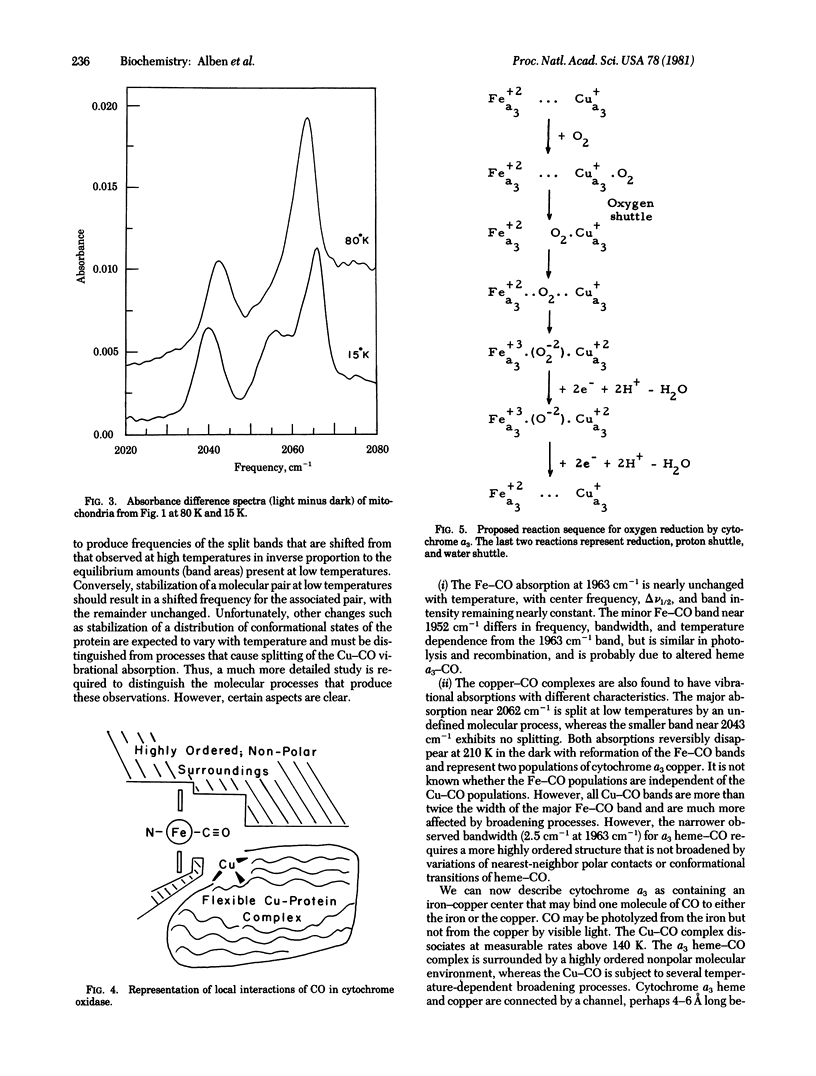
Carbon monoxide bound to iron or copper in substrate-reduced mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase (ferrocytochrome c:oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.9.3.1) from beef heart has been used to explore the structural interaction of the a3 heme-copper pocket at 15 K and 80 K in the dark and in the presence of visible light. The vibrational absorptions of CO measured by a Fourier transform infrared interferometer occur in the dark at 1963 cm-1, with small absorptions near 1952 cm-1, and are due to a3 heme--CO complexes. These disappear in strong visible light and are replaced by a major absorption at 2062 cm-1 and a minor one at 2043 cm-1 due to Cu--CO. Relaxation in the dark is rapid and quantitative at 210 K, but becomes negligible below 140 K. The multiple absorptions indicate structural heterogeneity of cytochrome oxidase in mitochondria. The Cu--CO absorptions (vCO) are similar to those in hemocyanin--CO complexes from molluscs (vCO - 2062 cm-1) and crustaceans (vCO = 2043 cm-1). The 2062 cm-1 Cu--CO absorption of cytochrome oxidase is split into two bands at 15 K. Analysis of spectral data suggest the presence of a very nonpolar heme--Cu pocket in which the heme-CO complex is highly ordered, but in which the Cu--CO complex is much more flexible, especially above 80 K. A function for these structures in oxygen reduction is proposed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Erecińska M., Wilson D. F. Cytochrome c oxidase: a synopsis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 May;188(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fager L. Y., Alben J. O. Structure of the carbon monoxide binding site of hemocyanins studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 5;11(25):4786–4792. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden C. For aging research the best is yet to be. Science. 1976 Jun 11;192(4244):1082–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.192.4244.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung D. W., Chávez E., Brierley G. P. Energy-dependent exchange of K+ in heart mitochondria. K+ influx. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Oct;183(2):452–459. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90380-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay J. G., Wilson D. F. Reaction of cytochrome C oxidase with CO: involvement of the invisible copper. FEBS Lett. 1974 Nov 1;48(1):45–49. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroedl N. A., Hartzell C. R. Oxidative titrations of reduced cytochrome aa3: influence of cytochrome c and carbon monoxide on the midpoint potential values. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):4966–4971. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrock M., Yonetani T. Low-temperature flash photolysis studies of cytochrome oxidase and its environment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 23;462(3):718–730. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrock M., Yonetani T. Study of cytochrome oxidase co-binding site using low-temperature flash photolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 15;434(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. J., Brittain T., Greenwood C., Springall J. P. Variable-temperature magnetic-circular-dichroism spectra of cytochrome c oxidase and its derivatives. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):327–336. doi: 10.1042/bj1650327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweedle M. F., Wilson L. J. Electronic state of heme in cytochrome oxidase III. The magnetic susceptibility of beef heart cytochrome oxidase and some of its derivatives from 7-200 K. Direct evidence for an antiferromagnetically coupled Fe (III)/Cu (II) pair. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8065–8071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gelder B. F., Beinert H. Studies of the heme components of cytochrome c oxidase by EPR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Sep 16;189(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. A., O'Toole M. C., Caughey W. S. Quantitative infrared spectroscopy of CO complexes of cytochrome c oxidase, hemoglobin and myoglobin: evidence for one CO per heme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 6;62(1):48–53. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa S., Choc M. G., O'Toole M. C., Caughey W. S. An infrared study of CO binding to heart cytochrome c oxidase and hemoglobin A. Implications re O2 reactions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5498–5508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


