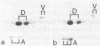Abstract
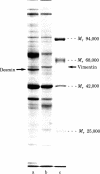
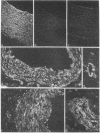
Smooth muscle cells of the digestive, respiratory, and urogenital tracts contain desmin as their major, if not exclusive, intermediate-size filament constituent and also show a predominance of gamma-type smooth muscle actin. We have now examined smooth muscle tissue of different blood vessels (e.g., aorta, small arteries, arterioles, venules, and vena cava) from various mammals (man, cow, pig, rabbit, rat) by one- and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of cell proteins and by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to different intermediate-sized filament proteins. Intermediate-sized filaments of vascular smooth muscle cells contain abundant amounts of vimentin and little, if any, desmin. On gel electrophoresis, vascular smooth muscle vimentin appears as two isoelectric variants of apparent pI values of 5.30 and 5.29, shows the characteristic series of proteolytic fragments, and is one of the major cell proteins. Thus vimentin has been demonstrated in a smooth muscle cell present in the body. Vascular smooth muscle cells are also distinguished by the predominance of a smooth muscle-specific alpha-type actin, whereas gamma-type smooth muscle actin is present only as a minor component. It is proposed that the intermediate filament and actin composition of vascular smooth muscle cells reflects a differentiation pathway separate from that of other smooth muscle cells and may be related to special functions and pathological disorders of blood vessels.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett G. S., Fellini S. A., Croop J. M., Otto J. J., Bryan J., Holtzer H. Differences among 100-A filamentilament subunits from different cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4364–4368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. S., Fellini S. A., Holtzer H. Immunofluorescent visualization of 100 A filaments in different cultured chick embryo cell types. Differentiation. 1978;12(2):71–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb00992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. S., Fellini S. A., Toyama Y., Holtzer H. Redistribution of intermediate filament subunits during skeletal myogenesis and maturation in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):577–584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral F., Gottesman M. M. Phosphorylation of the 10-nm filament protein from Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6203–6206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. R., Chamley-Campbell J., Gröschel-Stewart U., Small J. V., Anderson P. Antibody staining of 10-nm (100-A) filaments in cultured smooth, cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. J Cell Sci. 1979 Jun;37:303–322. doi: 10.1242/jcs.37.1.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley-Campbell J., Campbell G. R., Ross R. The smooth muscle cell in culture. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):1–61. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke P. A filamentous cytoskeleton in vertebrate smooth muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):539–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellini S. A., Bennett G. S., Toyama Y., Holtzer H. Biochemical and immunological heterogeneity of 100 A filament subunits from different chick cell types. Differentiation. 1978;12(2):59–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb00991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Appelhans B., Schmid E., Freudenstein C., Osborn M., Weber K. Identification and characterization of epithelial cells in mammalian tissues by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to prekeratin. Differentiation. 1979;15(1):7–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Appelhans B., Schmid E., Freudenstein C., Osborn M., Weber K. The organization of cytokeratin filaments in the intestinal epithelium. Eur J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;19(3):255–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Denk H., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Ultrastructural, biochemical, and immunologic characterization of Mallory bodies in livers of griseofulvin-treated mice. Fimbriated rods of filaments containing prekeratin-like polypeptides. Lab Invest. 1979 Feb;40(2):207–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Freudenstein C., Appelhans B., Osborn M., Weber K., Keenan T. W. Intermediate-sized filaments of the prekeratin type in myoepithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):633–654. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Intermediate-sized filaments of human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):570–580. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Winter S., Osborn M., Weber K. Widespread occurrence of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin-type in cultured cells from diverse vertebrates. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):25–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Weber K., Osborn M., Schmid E., Freudenstein C. Antibody to prekeratin. Decoration of tonofilament like arrays in various cells of epithelial character. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):429–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Chaponnier C., Hüttner I. Cytoplasmic filaments and gap junctions in epithelial cells and myofibroblasts during wound healing. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):561–568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Bell P. B., Lazarides E. Coexistence of desmin and the fibroblastic intermediate filament subunit in muscle and nonmuscle cells: identification and comparative peptide analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3894–3898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. The synthesis and distribution of desmin and vimentin during myogenesis in vitro. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90408-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Gibson W. Identification and characterization of multiple forms of actin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):793–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Desmin and vimentin coexist at the periphery of the myofibril Z disc. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Garrels J. I. Characterization of the mRNAs for alpha-, beta- and gamma-actin. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):767–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. 10 nm filaments in normal and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Lazarides E. Invariance and heterogeneity in the major structural and regulatory proteins of chick muscle cells revealed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1450–1454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., Cotman C. W. Synaptic proteins. Characterization of tubulin and actin and identification of a distinct postsynaptic density polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1978 Oct;79(1):173–183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Balzer D. R., Jr Specificity of desmin to avian and mammalian muscle cells. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Hubbard B. D. Immunological characterization of the subunit of the 100 A filaments from muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4344–4348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. The distribution of desmin (100 A) filaments in primary cultures of embryonic chick cardiac cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Mar 15;112(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Balzer D. R., Jr, Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of subunit proteins of intermediate filaments from chicken muscle and nonmuscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):819–823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Klebanoff S. J. The smooth muscle cell. I. In vivo synthesis of connective tissue proteins. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jul;50(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein P. A., Spudich J. A. Actin microheterogeneity in chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):120–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid E., Tapscott S., Bennett G. S., Croop J., Fellini S. A., Holtzer H., Franke W. W. Differential location of different types of intermediate-sized filaments in various tissues of the chicken embryo. Differentiation. 1979;15(1):27–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V., Sobieszek A. Studies on the function and composition of the 10-NM(100-A) filaments of vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Sci. 1977 Feb;23:243–268. doi: 10.1242/jcs.23.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A. Actin nascent chains are substrates for cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Rich A. Chick cytoplasmic actin and muscle actin have different structural genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2346–2350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Immunofluorescent staining of keratin fibers in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Shih C., Green H. Keratin cytoskeletons in epithelial cells of internal organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2813–2817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. At least six different actins are expressed in a higher mammal: an analysis based on the amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal tryptic peptide. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):783–802. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The complete amino acid sequence of actins from bovine aorta, bovine heart, bovine fast skeletal muscle, and rabbit slow skeletal muscle. A protein-chemical analysis of muscle actin differentiation. Differentiation. 1979;14(3):123–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Protein synthesis and actin heterogeneity in calf muscle cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]