Abstract
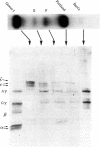
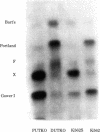
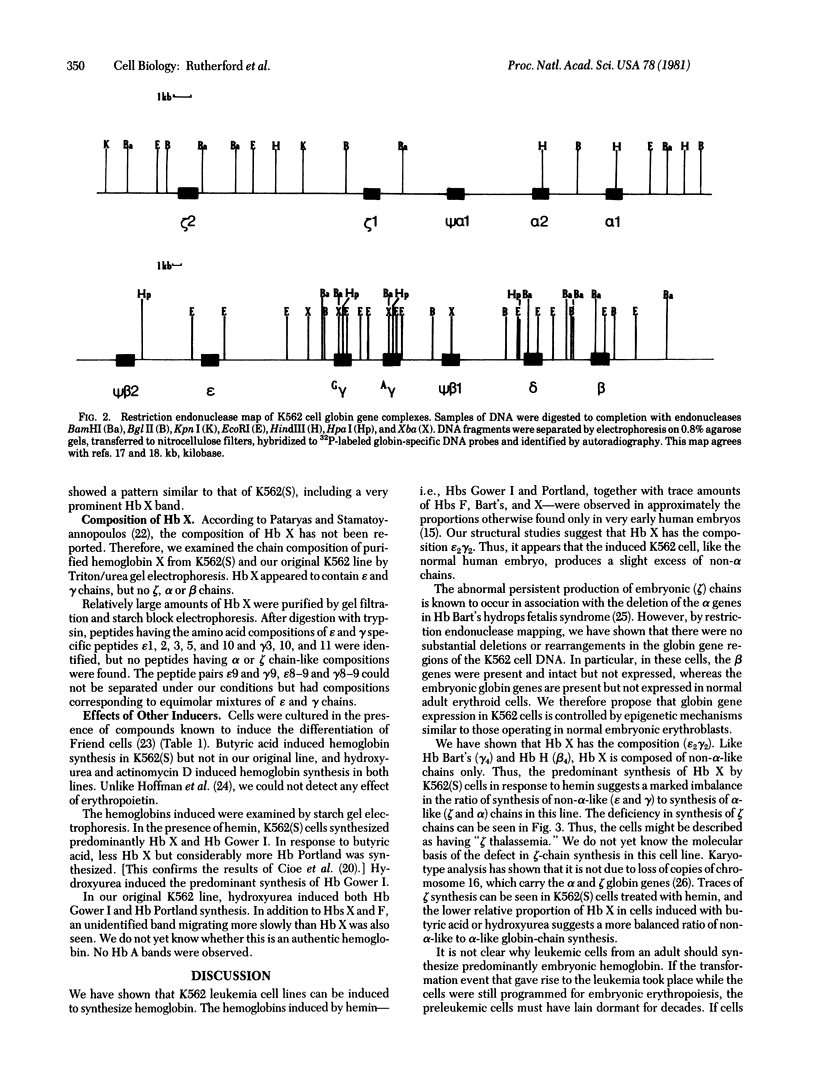
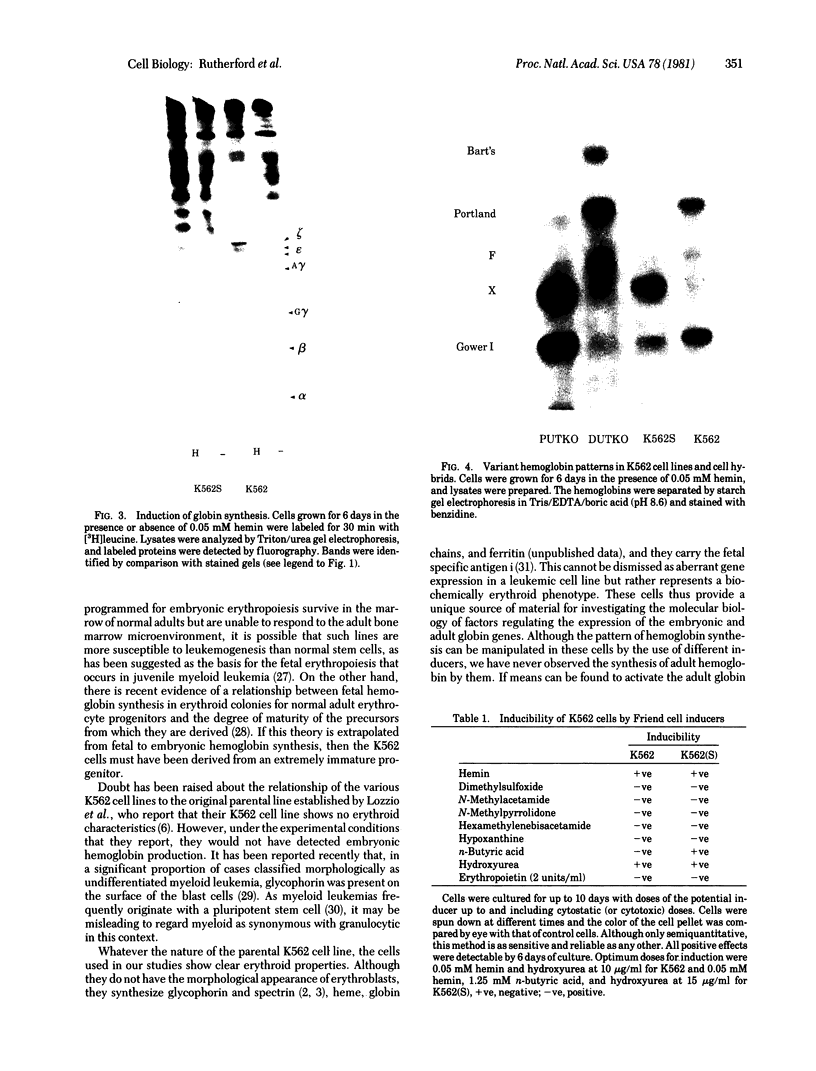
K562 human leukemia cells synthesize embryonic hemoglobins after culture in the presence of hemin. We have rigorously identified these hemoglobins by globin chain analysis and peptide mapping. No adult hemoglobin could be detected, and beta-globin synthesis was less than 2 ppm of total protein synthesis. Persistent embryonic globin gene expression is known to occur as a consequence of globin gene deletions. However, restriction endonuclease mapping showed that the globin gene complexes in K562 cells are indistinguishable from normal. Hemin increased the rate of embryonic globin synthesis. The pattern of hemoglobin synthesis proved to be stable when cells from different laboratories were compared. One line, however, synthesized large amounts of Hb X and very little Hb Portland in response to hemin. Hb X has been previously detected in human embryos; we show here that it has the composition epsilon 2 gamma 2 and is diagnostic of imbalanced chain synthesis or "zeta thalassemia." We have identified several agents that induce hemoglobin synthesis in K562 cells. Different inducers induced different patterns of embryonic hemoglobin synthesis but never any adult hemoglobin synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter B. P., Goff S. C., Efremov G. D., Gravely M. E., Huisman T. H. Globin chain electrophoresis: a new approach to the determination of the G gamma/A gamma ratio in fetal haemoglobin and to studies of globin synthesis. Br J Haematol. 1980 Apr;44(4):527–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb08706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L. C., Gahmberg C. G., Teerenhovi L., Vuopio P. Glycophorin A as a cell surface marker of early erythroid differentiation in acute leukemia. Int J Cancer. 1979 Dec 15;24(6):717–720. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L. C., Jokinen M., Gahmberg C. G. Induction of erythroid differentiation in the human leukaemia cell line K562. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):364–365. doi: 10.1038/278364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L. C., Nilsson K., Gahmberg C. G. K562--a human erythroleukemic cell line. Int J Cancer. 1979 Feb;23(2):143–147. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capp G. L., Rigas D. A., Jones R. T. Evidence for a new haemoglobin chain (zeta-chain). Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):278–280. doi: 10.1038/228278b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Naughton M. A., Weatherball D. J. Abnormal human haemoglobins. Separation and characterization of the alpha and beta chains by chromatography, and the determination of two new variants, hb Chesapeak and hb J (Bangkok). J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):91–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisseroth A., Nienhuis A., Turner P., Velez R., Anderson W. F., Ruddle F., Lawrence J., Creagan R., Kucherlapati R. Localization of the human alpha-globin structural gene to chromosome 16 in somatic cell hybrids by molecular hybridization assay. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E. F., Lawn R. M., Maniatis T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human beta-like globin gene cluster. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):959–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M. K562 human leukaemic cells express fetal type (i) antigen on different glycoproteins from circulating erythrocytes. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):405–407. doi: 10.1038/285405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale R. E., Clegg J. B., Huehns E. R. Human embryonic haemoglobins Gower 1 and Gower 2. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):162–164. doi: 10.1038/280162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R., Murnane M. J., Benz E. J., Jr, Prohaska R., Floyd V., Dainiak N., Forget B. G., Furthmayr H. Induction of erythropoietic colonies in a human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):1182–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Zeuthen J., Eriksson I., Terasaki P., Bernoco M., Rosén A., Masucci G., Povey S., Ber R. Hybridization of a myeloid leukemia-derived human cell line (K562) with a human Burkitt's lymphoma line (P3HR-1). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Apr;64(4):725–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauer J., Shen C. K., Maniatis T. The chromosomal arrangement of human alpha-like globin genes: sequence homology and alpha-globin gene deletions. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B., Machado E. A., Fuhr J. E., Lair S. V., Bamberger E. G. Effects of sodium butyrate on human chronic myelogenous leukaemia cell line K562. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):709–710. doi: 10.1038/281709b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi S., Lanyon W. G., Paul J., Williamson R., Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B., Pritchard J., Pootrakul S., Boon W. H. The severe form of alpha thalassaemia is caused by a haemoglobin gene deletion. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):389–392. doi: 10.1038/251389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T., Kalmantis T., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Cellular regulation of hemoglobin switching: evidence for inverse relationship between fetal hemoglobin synthesis and degree of maturity of human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6420–6424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pataryas H. A., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Hemoglobins in human fetuses: evidence for adult hemoglobin production after the 11th gestational week. Blood. 1972 May;39(5):688–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressley L., Higgs D. R., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. Gene deletions in alpha thalassemia prove that the 5' zeta locus is functional. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3586–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford T. R., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. K562 human leukaemic cells synthesise embryonic haemoglobin in response to haemin. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):164–165. doi: 10.1038/280164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford T. R., Weatherall D. J. Deficient heme synthesis as the cause of noninducibility of hemoglobin synthesis in a Friend erythroleukemia cell line. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Edwards J. A., Donohoe W. T. Haemoglobin and red cell enzyme changes in juvenile myeloid leukaemia. Br Med J. 1968 Mar 16;1(5593):679–681. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5593.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]