Abstract
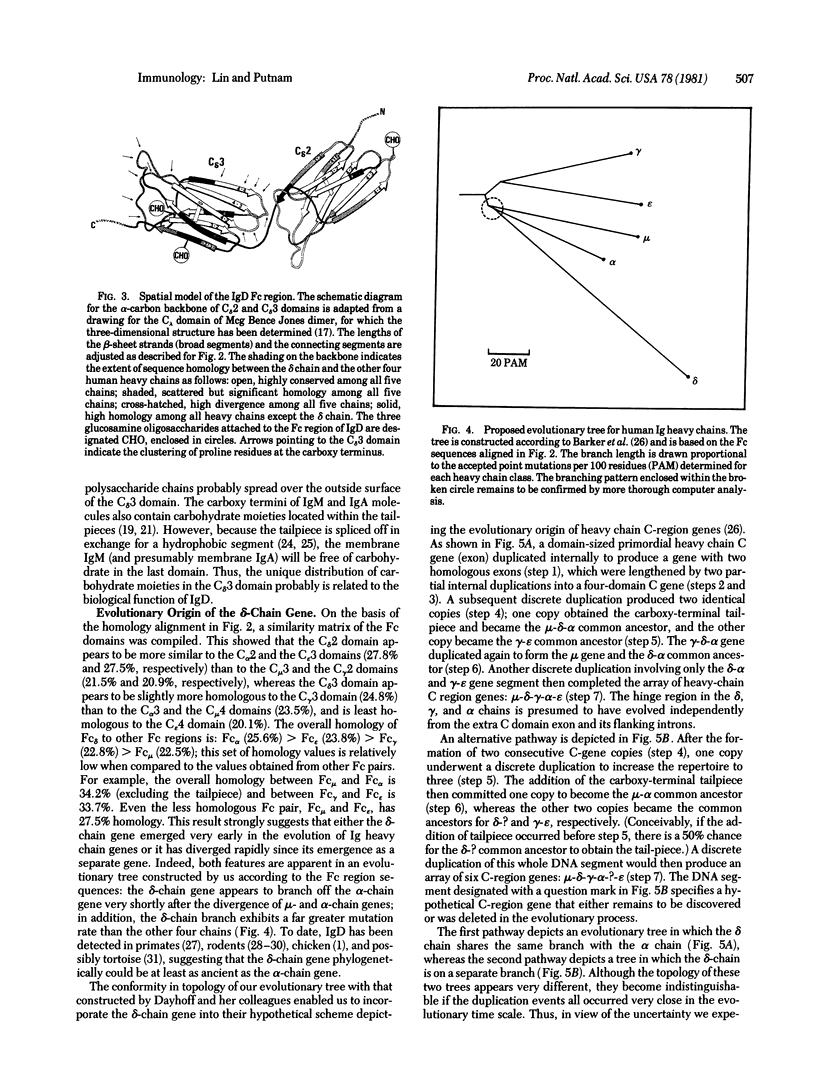
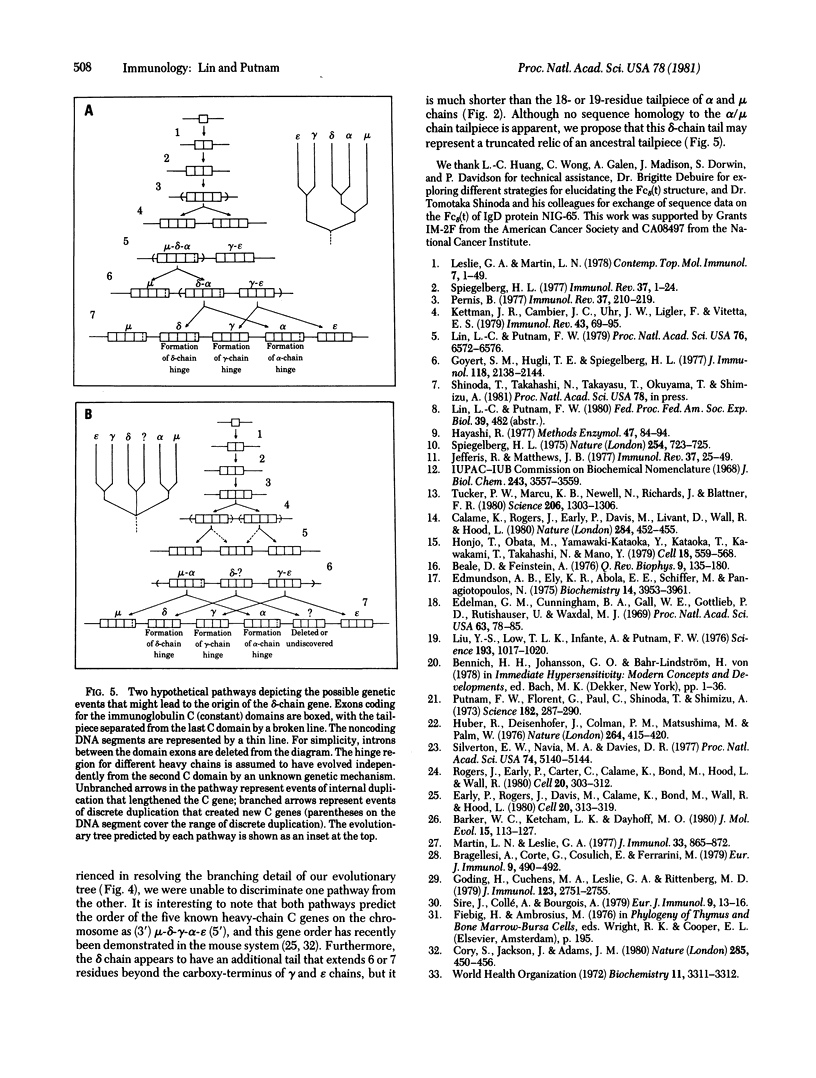
We have determined the complete amino acid sequence of a tryptic Fc delta fragment generated from an intact human IgD (WAH); it is 226 residues long and includes the second (C delta 2) and the third (C delta 3) constant domains of the delta chain. Comparison of the homology of the Fc sequence of the five human immunoglobulin classes suggests that either the delta-chain gene evolved from the alpha-chain gene soon after the divergence of a mu-alpha common ancestor or it evolved from an ancestral gene distinct from both the mu-alpha and the gamma-epsilon common ancestors. Comparative study using a spatial model of the Fc region indicates that the structure of the C delta 3 domain differs extensively from that of the carboxy-terminal domains of other heavy chain classes; this, together with the unique hinge region structure, probably reflects the biological role of IgD as a receptor molecule on the B-lymphocyte surface.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargellesi A., Corte G., Cosulich E., Ferrarini M. Presence of serum IgD and IgD-containing plasma cells in the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):490–492. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., Ketcham L. K., Dayhoff M. O. Origins of immunoglobulin heavy chain domains. J Mol Evol. 1980 May;15(2):113–127. doi: 10.1007/BF01732665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale D., Feinstein A. Structure and function of the constant regions of immunoglobulins. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 May;9(2):135–180. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame K., Rogers J., Early P., Davis M., Livant D., Wall R., Hood L. Mouse Cmu heavy chain immunoglobulin gene segment contains three intervening sequences separating domains. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):452–455. doi: 10.1038/284452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Jackson J., Adams J. M. Deletions in the constant region locus can account for switches in immunoglobulin heavy chain expression. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):450–456. doi: 10.1038/285450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A., Gall W. E., Gottlieb P. D., Rutishauser U., Waxdal M. J. The covalent structure of an entire gammaG immunoglobulin molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):78–85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding H., Cuchens M. A., Leslie G. A., Rittenberg M. B. Cross-reactivity of rat, mouse, and human IgD. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2751–2755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyert S. M., Hugli T. E., Spiegelberg H. L. Sites of "spontaneous" degradation of IgD. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2138–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R. Carboxypeptidase Y in sequence determination of peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:84–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Obata M., Yamawaki-Katoaka Y., Kataoka T., Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Mano Y. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 1 chain gene. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Deisenhofer J., Colman P. M., Matsushima M., Palm W. Crystallographic structure studies of an IgG molecule and an Fc fragment. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):415–420. doi: 10.1038/264415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Matthews J. B. Structural studies of human IgD paraproteins. Immunol Rev. 1977;37:25–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettman J. R., Cambier J. C., Uhr J. W., Ligler F., Vitetta E. S. The role of receptor IgM and IgD in determining triggering and induction of tolerance in murine B cells. Immunol Rev. 1979;43:69–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie G. A., Martin L. N. Structure and function of serum and membrane immunoglobulin D (IgD). Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1978;7:1–49. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0779-3_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. C., Putnam F. W. Structural studies of human IgD: isolation by a two-step purification procedure and characterization by chemical and enzymatic fragmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6572–6576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. S., Low T. L., Infante A., Putnam F. W. Complete covalent structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1017–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.821146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. N., Leslie G. A. Lymphocyte surface IgD and IgM in Macaca monkeys: ontogeny, tissue distribution and occurrence on individual lymphocytes. Immunology. 1977 Dec;33(6):865–872. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis B. Lymphocyt membrane IgD. Immunol Rev. 1977;37:210–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam F. W., Florent G., Paul C., Shinoda T., Shimizu A. Complete amino acid sequence of the Mu heavy chain of a human IgM immunoglobulin. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):287–291. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Early P., Carter C., Calame K., Bond M., Hood L., Wall R. Two mRNAs with different 3' ends encode membrane-bound and secreted forms of immunoglobulin mu chain. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverton E. W., Navia M. A., Davies D. R. Three-dimensional structure of an intact human immunoglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sire J., Collé A., Bourgois A. Identification of an IgD-like surface immunoglobulin on rabbit lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jan;9(1):13–16. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of the Fc fragment of IgD resembles IgE and IgG sequences. Nature. 1975 Apr 24;254(5502):723–725. doi: 10.1038/254723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Marcu K. B., Newell N., Richards J., Blattner F. R. Sequence of the cloned gene for the constant region of murine gamma 2b immunoglobulin heavy chain. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.117549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]