Abstract
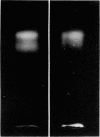
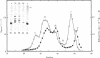
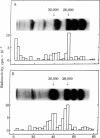
A protein polymer characteristically present in human cataract was shown to contain significant amounts of gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine isopeptides. It is proposed that these crosslinks are produced by the action of transglutaminase (R-glutaminyl-peptide:amine-gamma-glutamyl-yltransferase, EC 2.3.2.13), which is all the more plausible because lens contains the enzyme and endogenous protein substrates for it. The enzyme is similar to that obtained from liver and is Ca2+ dependent. Highest apparent activity is found in lens cortex. When cortex homogenate from the rabbit was incubated in the presence of Ca2+ with either [14C]putrescine or with dansylcadaverine, a a selective incorporation of the radioactive or fluorescent amine into the heavier subunits (Mr approximately 26,000 and 30,000) of beta-crystallins could be demonstrated. Possible modes of regulating the crosslinking activity of this enzyme in lens are discussed.
Full text
PDF
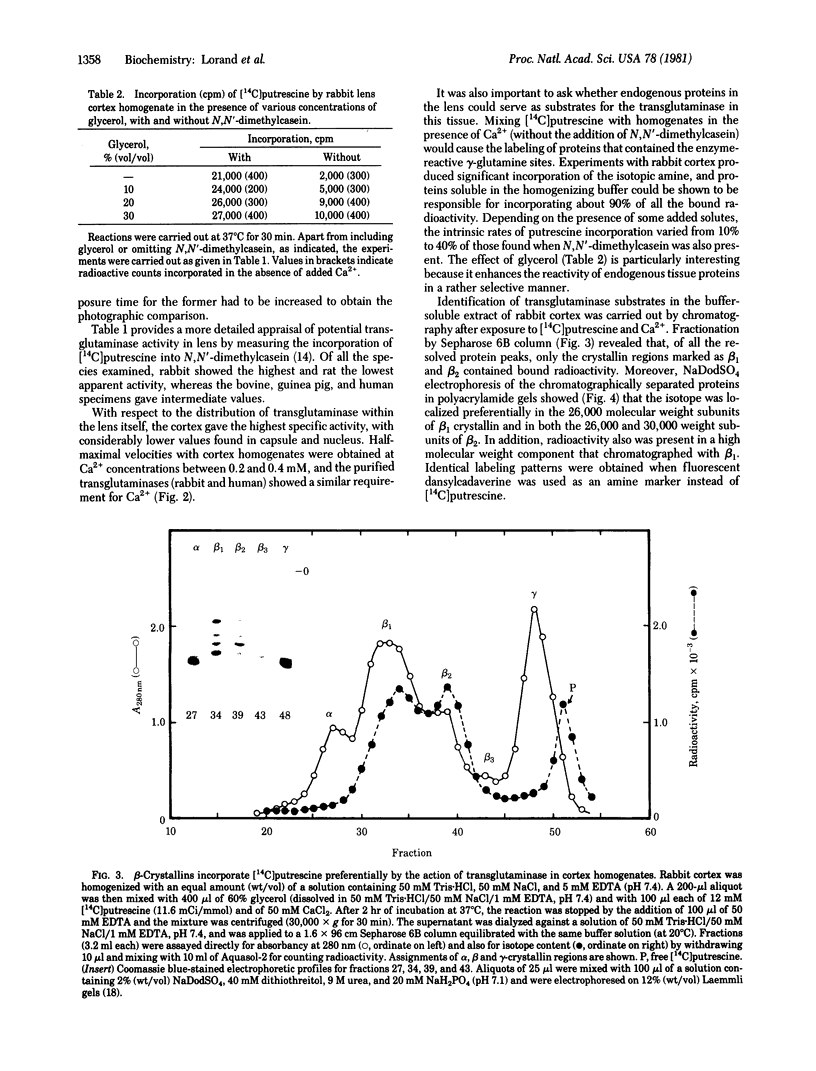
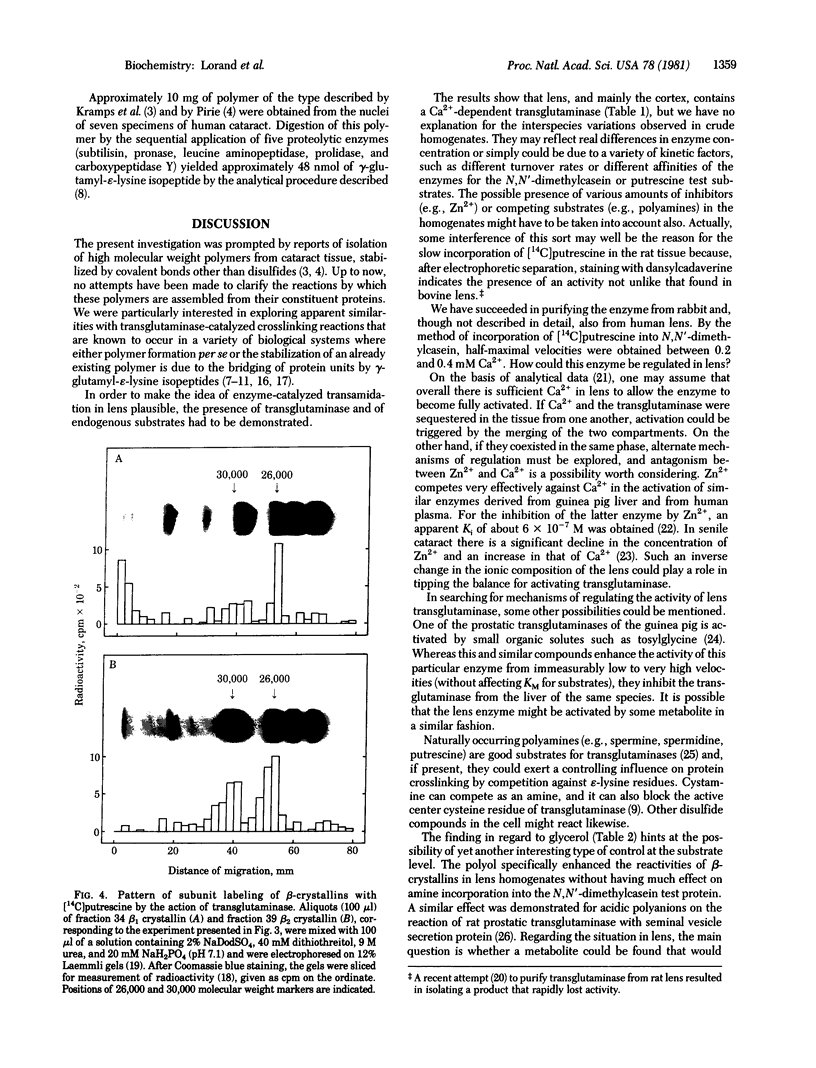

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloemendal H. The vertebrate eye lens. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):127–138. doi: 10.1126/science.877544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagerholm P. P. The influence of calcium on lens fibers. Exp Eye Res. 1979 Feb;28(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(79)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., Hoenders H. J., Wollensak J. Increase of non-disulphide cross-links during progress of nuclear cataract. Exp Eye Res. 1978 Dec;27(6):731–735. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(78)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Campbell-Wilkes L. K., Cooperstein L. A filter paper assay for transamidating enzymes using radioactive amine substrates. Anal Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(2):623–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Chenoweth D., Gray A. Titration of the acceptor cross-linking sites in fibrin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:155–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Chenoweth D. Intramolecular localization of the acceptor cross-linking sites in fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1247–1252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Downey J., Gotoh T., Jacobsen A., Tokura S. The transpeptidase system which crosslinks fibrin by gamma-glutamyle-episilon-lysine bonds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Apr 19;31(2):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90734-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L. Fibrinoligase: the fibrin-stabilizing factor system of blood plasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:6–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Parameswaran K. N., Stenberg P., Tong Y. S., Velasco P. T., Jönsson N. A., Mikiver L., Moses P. Specificity of guinea pig liver transglutaminase for amine substrates. Biochemistry. 1979 May 1;18(9):1756–1765. doi: 10.1021/bi00576a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Rule N. G., Ong H. H., Furlanetto R., Jacobsen A., Downey J., Oner N., Bruner-Lorand J. Amine specificity in transpeptidation. Inhibition of fibrin cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1968 Mar;7(3):1214–1223. doi: 10.1021/bi00843a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Siefring G. E., Jr, Lowe-Krentz L. Formation of gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine bridges between membrane proteins by a Ca2+-regulated enzyme in intact erythrocytes. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(3):427–440. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Siefring G. E., Jr, Tong Y. S., Bruner-Lorand J., Gray A. J., Jr Dansylcadaverine specific staining for transamidating enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):453–458. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Weissmann L. B., Epel D. L., Bruner-Lorand J. Role of the intrinsic transglutaminase in the Ca2+-mediated crosslinking of erythrocyte proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4479–4481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirie A. Color and solubility of the proteins of human cataracts. Invest Ophthalmol. 1968 Dec;7(6):634–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Green H. Presence in human epidermal cells of a soluble protein precursor of the cross-linked envelope: activation of the cross-linking by calcium ions. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Green H. The cornified envelope of terminally differentiated human epidermal keratinocytes consists of cross-linked protein. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siefring G. E., Jr, Apostol A. B., Velasco P. T., Lorand L. Enzymatic basis for the Ca2+-induced cross-linking of membrane proteins in intact human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2598–2604. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A., Roy D. Disulfide-linked high molecular weight protein associated with human cataract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3244–3248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. J., Rouzer C. A., Monnier V. M., Cerami A. Diabetic cataract formation: potential role of glycosylation of lens crystallins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams-Ashman H. G., Wilson J., Beil R. E., Lorand L. Transglutaminase reactions associated with the rat semen clotting system: modulation by macromolecular polyanions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 21;79(4):1192–1198. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]