Abstract
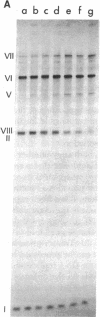
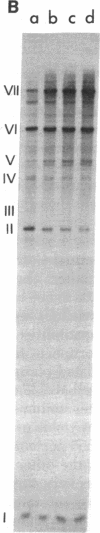
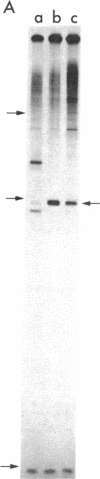
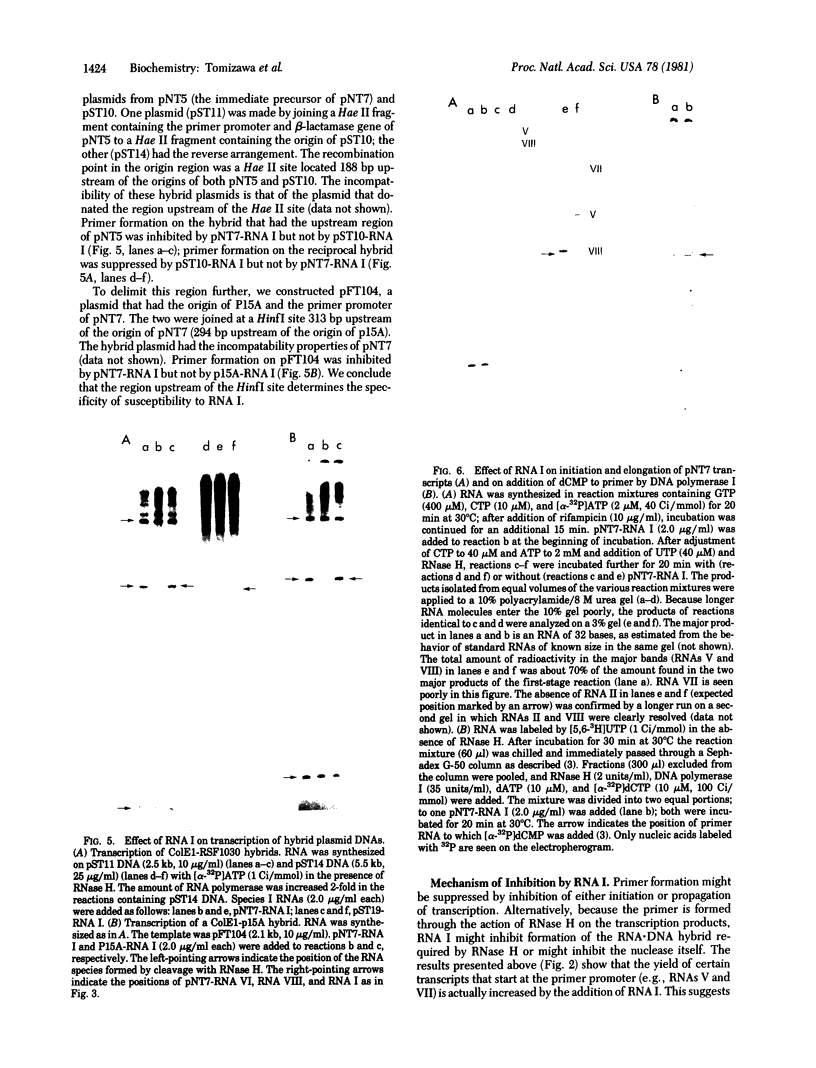
Transcription of ColE1 DNA by RNA polymerase in vitro starts at two sites in a region required for maintenance of the plasmid. Certain transcripts that start at one of the sites can be cleaved by RNase H and then act as primers for DNA replication. Transcription from the other site produces a RNA approximately 108 nucleotides long (species I or RNA I). Transcripts analogous to the primer and RNA I of ColE1 are produced when p15A or small derivatives of two other ColE1-compatible plasmids, CloDF13 and RSF1030, are used as template. If purified RNA I is added to the transcription reaction containing RNase H, formation of primer is inhibited. Each RNA I can inhibit primer formation by the plasmid that specifies it but has no effect on primer formation by heterologous templates. Thus, the inhibition of primer formation by RNA I is incompatibility specific. Because RNA I does not inhibit initiation or propagation of transcription or the processing of preformed precursors, the step that is sensitive to inhibition is probably formation of the hybrid between the primer precursor and the template. This hybrid is the required substrate for RNase H. Experiments with recombinant plasmids show the region that determines the specificity of response to RNA I to be greater than 300 base pairs upstream of the origin of DNA replication.
Full text
PDF
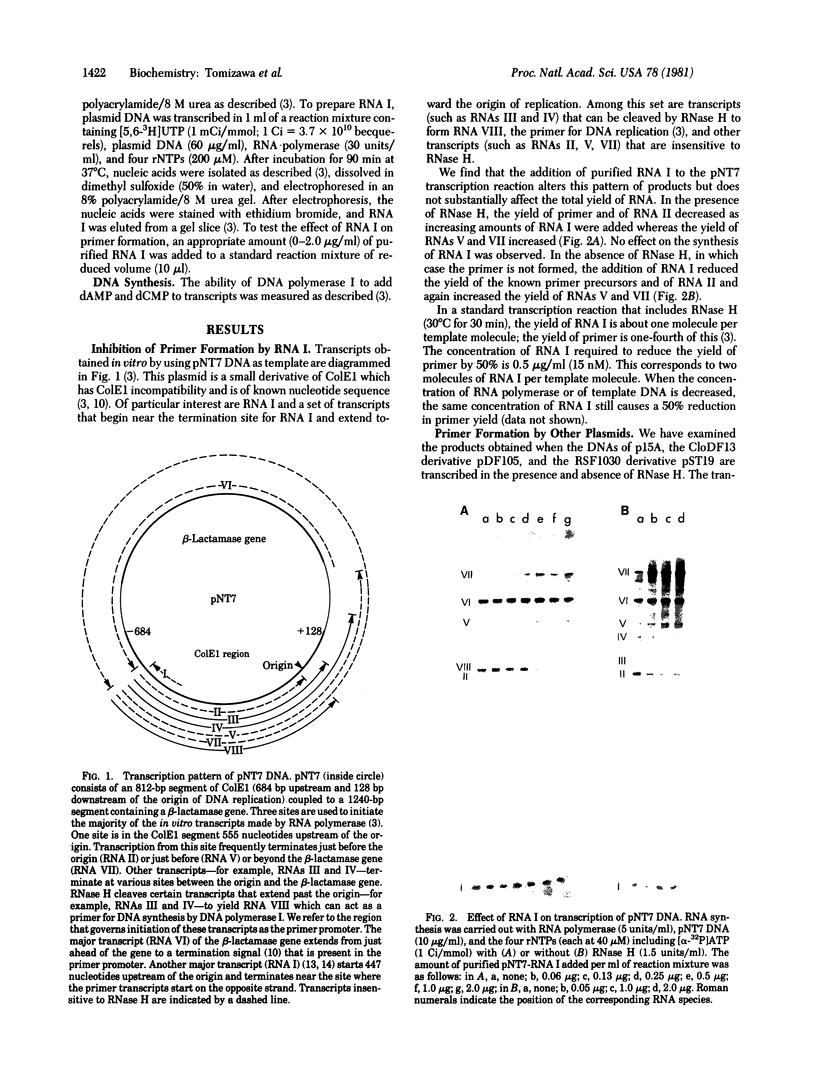
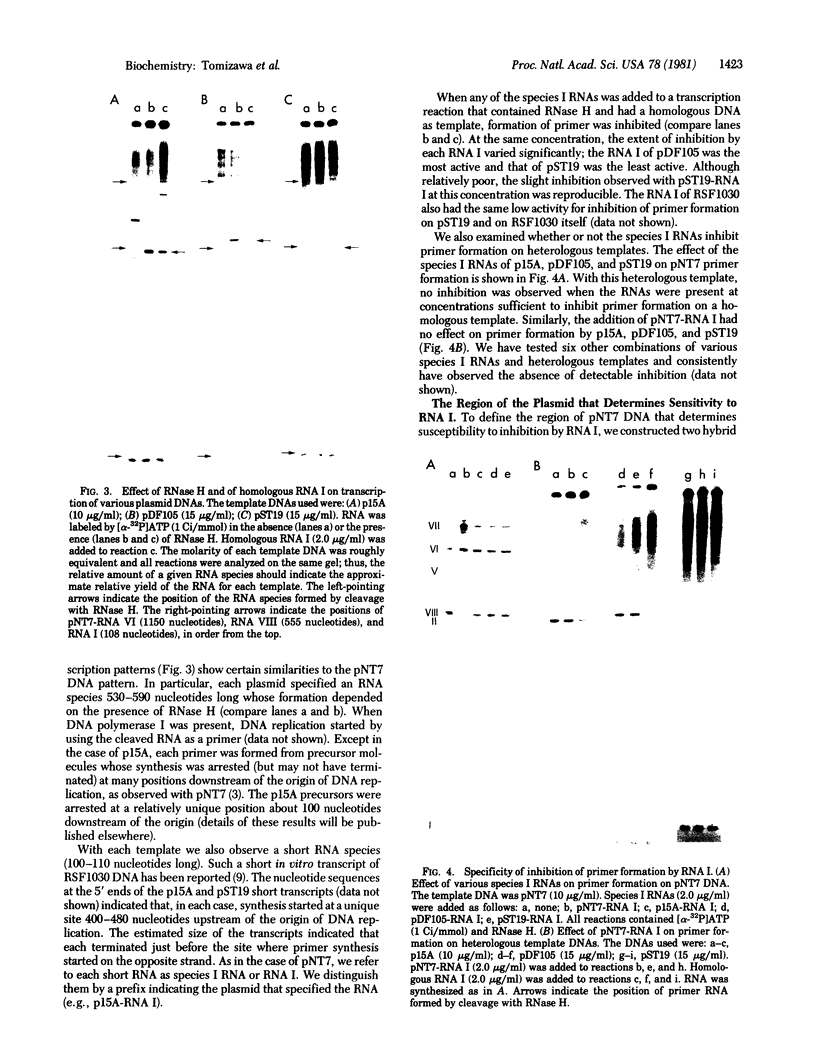

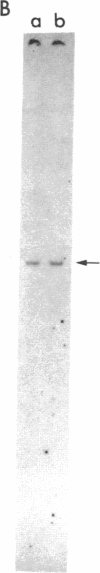
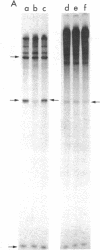
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conrad S. E., Campbell J. L. Role of plasmid-coded RNA and ribonuclease III in plasmid DNA replication. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad S. E., Wold M., Campbell J. L. Origin and direction of DNA replication of plasmid RSF1030. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):736–740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R., Kelly R. B., Kornberg A. A minute circular DNA from Escherichia coli 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):992–999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Luttropp L. K., Falkow S. Nature of R-factor replication in the presence of chloramphenicol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):654–658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto-Gotoh T., Inselburg J. ColE1 plasmid incompatibility: localization and analysis of mutations affecting incompatibility. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):608–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.608-619.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., So M., McCarthy B. J. In vitro mutagenesis of a circular DNA molecule by using synthetic restriction sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Formation of an RNA primer for initiation of replication of ColE1 DNA by ribonuclease H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2450–2454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita M., Oka A. The structure of a transcriptional unit on colicin E1 plasmid. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;97(2):435–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. Nucleotide sequence of the region required for maintenance of colicin E1 plasmid. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 3;176(2):161–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00273210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L. Structure and replication of the colicin E1 plasmid. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;83:93–156. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67087-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuitje A. R., Veltkamp E., Maat J., Heyneker H. L. The nucleotide sequence surrounding the replication origin of the cop3 mutant of the bacteriocinogenic plasmid Clo DF13. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1459–1473. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Shimada K., Oka A., Takagi Y. Location of a ColE1 deoxyribonucleic acid region that affects the plaque-forming ability of lambda-ColE1 hybrid bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):294–296. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.294-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tieze G. A., Stouthamer A. H., Jansz H. S., Zandberg J., van Bruggen E. F. A bacteriocinogenic factor of Enterobacter cloacae. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;106(1):48–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]