Abstract
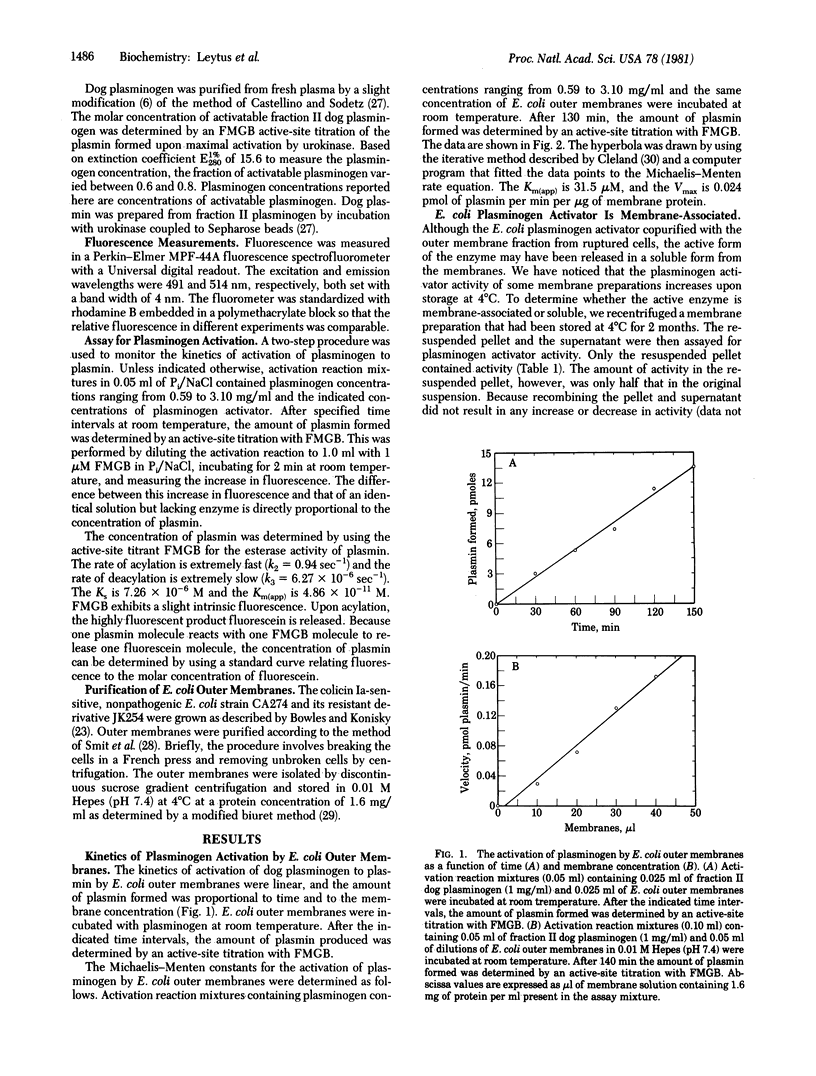
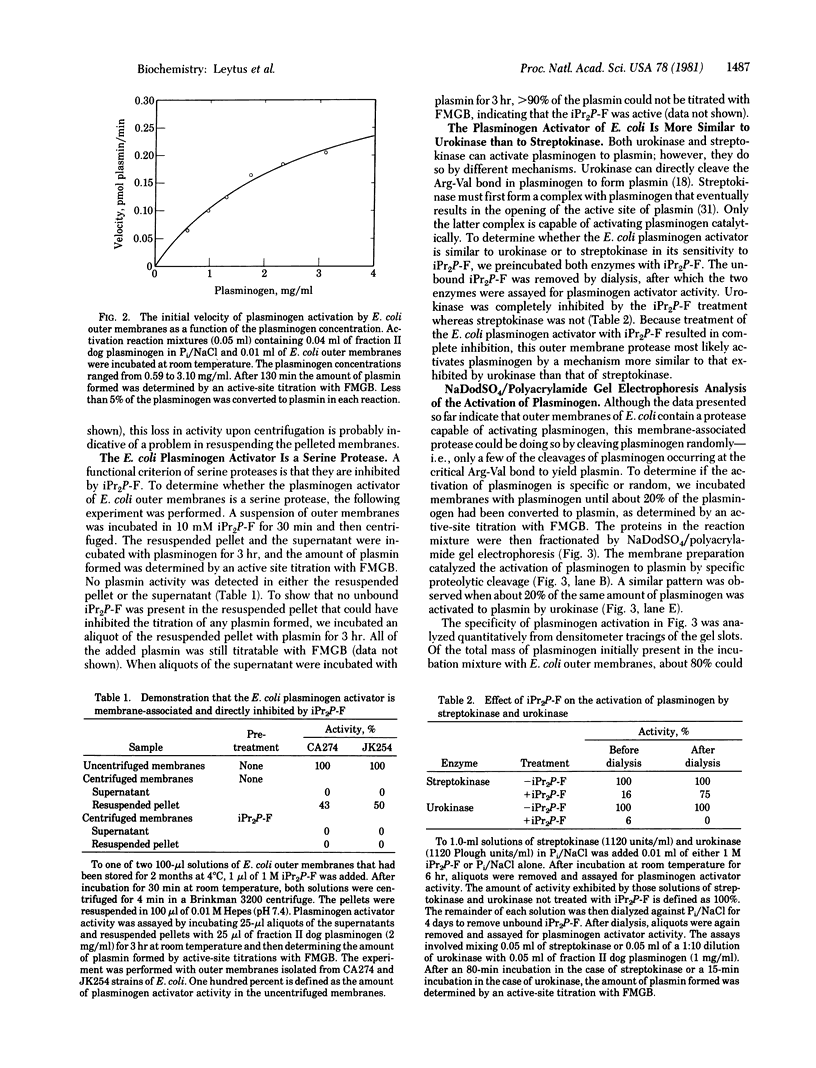
Preparations of outer membrane of two strains of Escherichia coli contain a protease that can activate the serum zymogen plasminogen to the active protease plasmin. The amount of plasmin formed is proportional to the membrane concentration. The kinetics of plasminogen activation are linear and obey the Michaelis--Menten rate equation. The Km(app) for the activation of dog plasminogen by E. coli outer membrane preparations is similar to the Km(app) for the activation of dog plasminogen by human urokinase. The E. coli enzyme is active in a membrane-associated form, as opposed to a secreted or soluble form, and is most likely a serine protease because it is inhibited by diisopropyl fluorophosphate. It is also inhibited from activating plasminogen by p-nitrophenyl-p-guanidinobenzoate and aprotinin. Analysis of the activation of plasminogen by the E. coli enzyme by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed that the cleavage of plasminogen to plasmin was as specific as that exhibited in the activation of plasminogen to plasmin by urokinase. Possible in vivo roles for this plasminogen activator in E. coli outer membranes are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. C., Crawford B. D., Grady D. L., Hester L. D., Jones P. A., Benedict W. F., Ts'o P. O. Temporal acquistion of enhanced fibrinolytic activity by syrian hamster embryo cells following treatment with benzo(a)pyrene. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3815–3823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles L. K., Konisky J. Cleavage of colicin Ia by the Escherichia coli K-12 outer membrane is not mediated by the colicin Ia receptor. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):668–671. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.668-671.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino F. J., Sodetz J. M. Rabbit plasminogen and plasmin isozymes. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:273–286. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Inouye H., Model P., Beckwith J. Processing of alkaline phosphatase precursor to the mature enzyme by an Escherichia coli inner membrane preparation. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):726–728. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.726-728.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Activation of plasminogen by human plasma kallikrein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith G. H., Jr, Saito H., Ratnoff O. S. The activation of plasminogen by Hageman factor (Factor XII) and Hageman factor fragments. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):54–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI109113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howett M. K., High C. S., Rapp F. Production of plasminogen activator by cells transformed by herpesviruses. Cancer Res. 1978 Apr;38(4):1075–1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye H., Beckwith J. Synthesis and processing of an Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase precursor in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1440–1444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaken S., Black P. H. Differences in intracellular distribution of plasminogen activator in growing, confluent, and transformed 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):246–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCHOLATY W., ELLIS W. W., JENSEN H. Activation of plasminogen by trypsin and plasmin. Blood. 1952 Sep;7(9):882–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Epidermal growth factor, like phorbol esters, induces plasminogen activator in HeLa cells. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):696–697. doi: 10.1038/274696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. Y., Peltz G. A., Leytus S. P., Livingston C., Brocklehurst J., Mangel W. F. Sensitive assay for plasminogen activator of transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3796–3800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNKRES K. D., RICHARDS F. M. THE PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF NEUROSPORA MALATE DEHYDROGENASE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Mar;109:466–479. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90391-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H., Bishop C. W., Blech J. E. Localization of proteolytic activity in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):574–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.574-583.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangel W. F., Livingston D. C., Brocklehurst J. R., Liu H. Y., Peltz G. A., Cannon J. F., Leytus S. P., Wehrly J. A., Salter B. L., Mosher J. L. New assay for the plasminogen activator activity of transformed cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):669–680. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock D. K., Bell P. H. The mechanism of activation of human plasminogen by streptokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):694–702. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90670-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Reich E. Plasminogen activator: induction of synthesis by DNA damage. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Voellmy R., Goldberg A. L. Protein degradation is stimulated by ATP in extracts of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8194–8200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein N. S., Dvorak H. F., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Nerve growth factor: a protease that can activate plasminogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5497–5500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Biegel D., Reich E. Mammary plasminogen activator: correlation with involution, hormonal modulation and comparison between normal and neoplastic tissue. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. II. Mammalian fibroblast cultures transformed by DNA and RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):112–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud M., Richaud C. Protease II from Escherichia coli. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7771–7779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud M., Uriel J. Isolation and some propeties of a proteolytic enzyme from Escherichia coli (protease I). Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 10;23(3):435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P., Ossowski L., Reich E. Plasminogen, the serum proenzyme activated by factors from cells transformed by oncogenic viruses. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4306–4311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Summaria L., Hsieh B., Shah R. J. The peptide chains of human plasmin. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen to plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2333–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. I., Strickland S., Reich E. Differentiation of early mouse embryonic and teratocarcinoma cells in vitro: plasminogen activator production. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4208–4216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Reich E., Sherman M. I. Plasminogen activator in early embryogenesis: enzyme production by trophoblast and parietal endoderm. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W., Hall J. D., Marsden M., Teresky A. K., Rifkin D., Levine A. J., Pollack R. In vitro differentiation of teratomas and the distribution of creatine phosphokinase and plasminogen activator in teratocarcinoma-derived cells. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4217–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Ossowski L., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. I. Chick embryo fibroblast cultures transformed by avian RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):85–111. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J., Dano K., Kellerman G. M., Reich E. Fibrinolysis associated with oncogenic transformation. Partial purification and characterization of the cell factor, a plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4295–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Violand B. N., Castellino F. J. Mechanism of the urokinase-catalyzed activation of human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3906–3912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Weinstein I. B. Tumour promotor induces plasminogen activator. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):232–233. doi: 10.1038/259232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohl R. C., Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Kinetics of activation of human plasminogen by different activator species at pH 7.4 and 37 degrees C. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]