Abstract
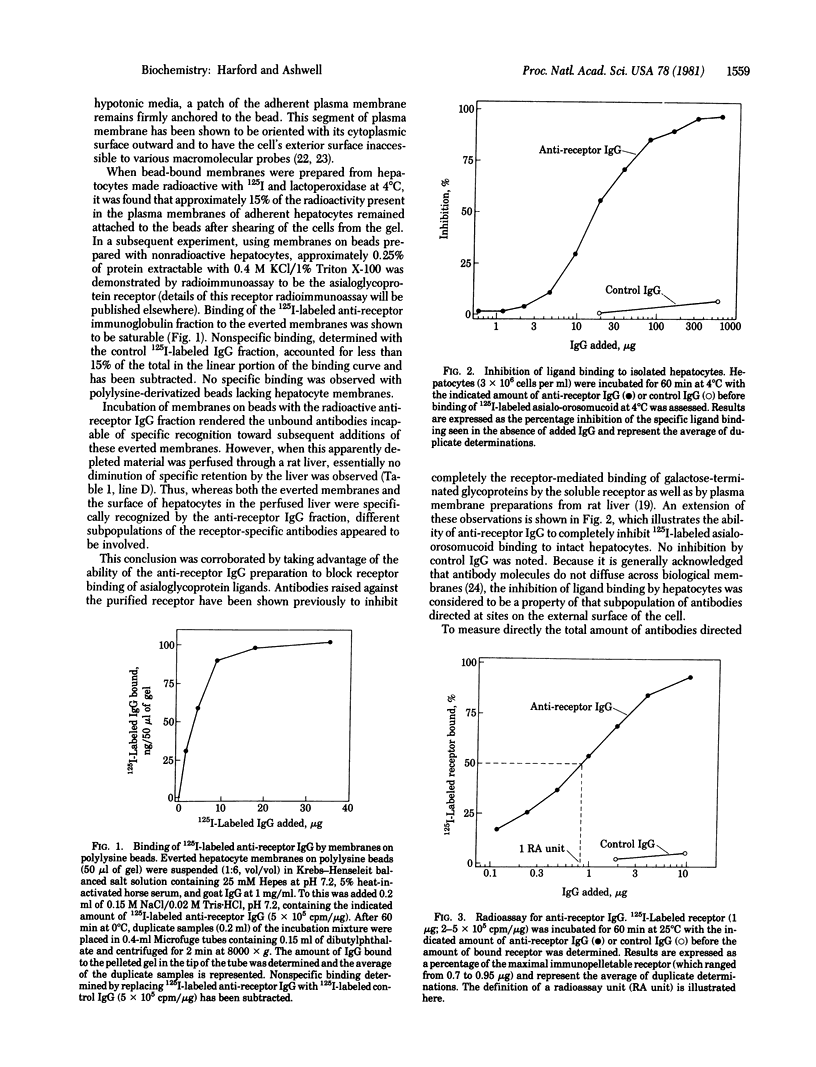
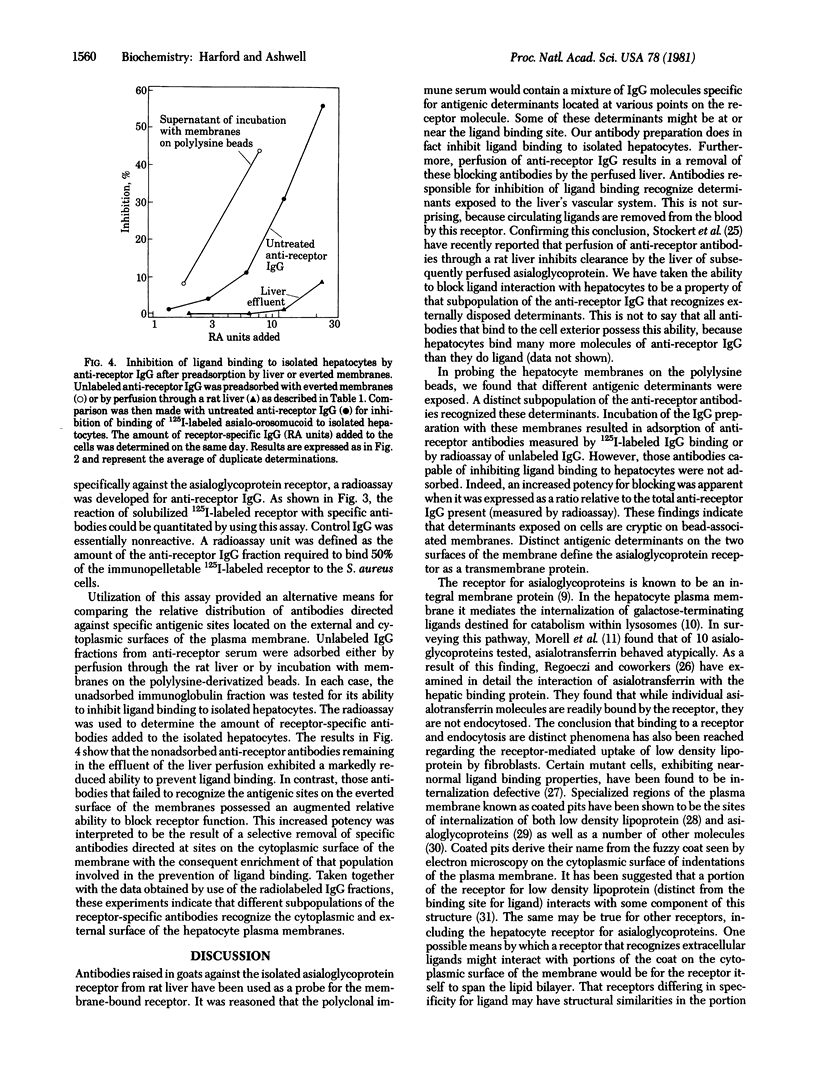
Antibodies raised in goats against the rat hepatic receptor for desialylated glycoproteins were perfused through a rat liver and were specifically retained by the liver. These antireceptor antibodies also bound specifically to hepatocyte plasma membranes oriented with their cytoplasmic surface outward on polylysine-derivatized beads. These two phenomena were judged to be properties of distinct subpopulations of the antibody preparation because: (i) maximal adsorption of antibodies with membranes on polylysine beads did not affect subsequent retention by the perfused liver, and (ii) whereas perfusion resulted in a depletion of antibodies capable of blocking ligand binding, adsorption by the everted membrane preparation led to a relative enrichment of blocking antibodies. These results are interpreted as indicative of distinct antigenic determinants of the receptor being present on the two faces of the membrane and demonstrate a transbilayer disposition of the asialoglycoprotein receptor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Role of the coated endocytic vesicle in the uptake of receptor-bound low density lipoprotein in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. A mutation that impairs the ability of lipoprotein receptors to localise in coated pits on the cell surface of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):695–699. doi: 10.1038/270695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Morell A. G. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):99–128. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Analysis of a mutant strain of human fibroblasts with a defect in the internalization of receptor-bound low density lipoprotein. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):663–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. H., Schatz G. Use of antibodies for studying the sidedness of membrane components. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:223–228. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M., Kalish D. I., Jacobson B. S., Branton D. Membrane isolation on polylysine-coated beads. Plasma membrane from HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Oct;75(1):119–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M., Kramer R. M., Branton D. Transbilayer mapping of membrane proteins using membranes isolated on polylysine-coated polyacrylamide beads. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 27;597(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Membrane receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):169–214. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G., Morell A. G., Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H. Catabolism of desialylated ceruloplasmin in the liver. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5833–5837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:731–752. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. Cancer Res. 1960 Nov;20:1495–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson B. S., Branton D. Plasma membrane: rapid isolation and exposure of the cytoplasmic surface by use of positively charged beads. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):302–304. doi: 10.1126/science.831278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalish D. I., Cohen C. M., Jacobson B. S., Branton D. Membrane isolation on polylysine-coated glass beads. Asymmetry of bound membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 4;506(1):97–110. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Isolation and characterization of an avian hepatic binding protein specific for N-acetylglucosamine-terminated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6536–6543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Furthmayr H., Tomita M. The red cell membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:667–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Gregoriadis G., Scheinberg I. H., Hickman J., Ashwell G. The role of sialic acid in determining the survival of glycoproteins in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1461–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. Subcellular distribution of a mammalian hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7539–7544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. The binding of desialylated glycoproteins by plasma membranes of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4825–4833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Taylor P., Hatton M. W., Wong K. L., Koj A. Distinction between binding and endocytosis of human asialo-transferrin by the rat liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj1740171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lenard J. Membrane asymmetry. Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):743–753. doi: 10.1126/science.402030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. Molecular biology of cellular membranes with applications to immunology. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):1–66. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer C. J., Ashwell G. Studies on a mammalian hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. Evidence for receptor recycling in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3008–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert R. J., Howard D. J., Morell A. G., Scheinberg I. H. Functional segregation of hepatic receptors for asialoglycoproteins during endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9028–9029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. Subcellular membrane topology and turnover of a rat hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1038–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Nilsson M., Norum K. R. Uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled asialo-fetuin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall D. A., Wilson G., Hubbard A. L. The galactose-specific recognition system of mammalian liver: the route of ligand internalization in rat hepatocytes. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel P. H. Characterization of the asialoglycoprotein receptor on isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6111–6120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


