Abstract
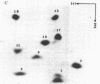
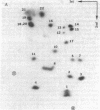
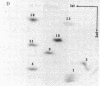
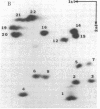
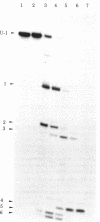
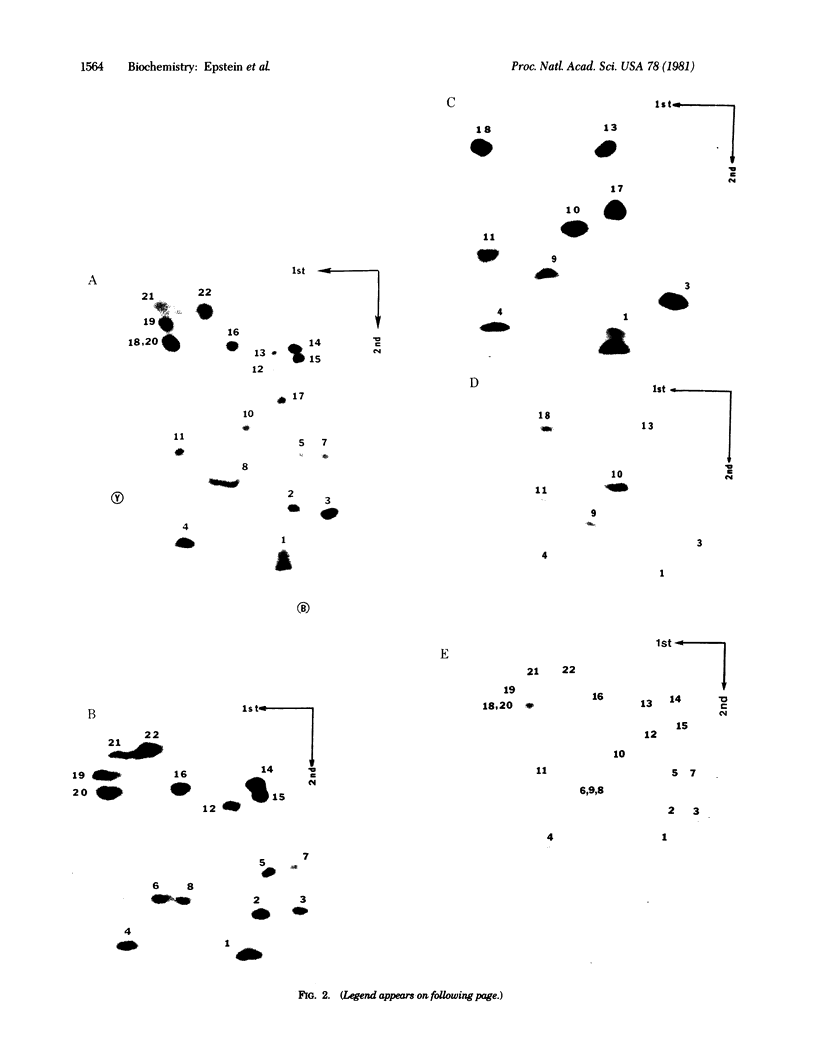
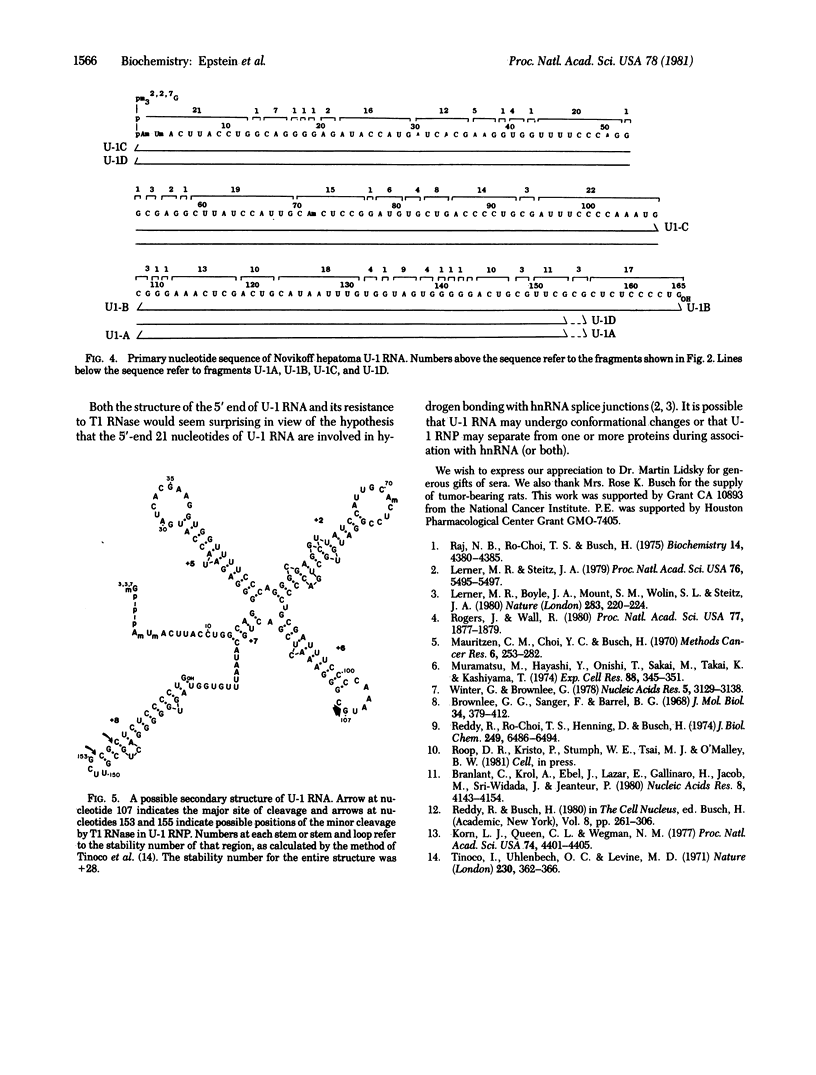
The structures and functions of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles have become of interest because of their suggested role in processing heterogeneous nuclear RNA [Lerner, M. R., Boyle, J. A., Mount, S. M., Wolin S. L. & Steitz, J. A. (1980) Nature (London) 283, 220-224]. To determine the conformation of U-1 RNA in U-1 ribonucleoprotein particles and whether proteins of these particles protect segments of U-1 RNA, intact particles and isolated U-1 RNA were digested with T1 RNase. The digested particles were immunoprecipitated with anti-Sm antibodies. A 5'-end fragment containing nucleotides 1-107 and 3'-end fragments containing nucleotides 108-165 and 108-153 were recovered in nearly quantitative yield from digestion of the particles, suggesting that position 107 is the principal cleavage site in them. At the same T1 RNase concentrations, deproteinized U-1 RNA was cleaved into many fragments. At low T1 RNase concentrations, major cleavage site of deproteinized U-1 RNA was at nucleotide 69. Comparison of the cleavage sites of free U-1 RNA and of U-1 RNA in U-1 ribonucleoprotein particles suggested similar secondary structures. The resistance of the 5' end of U-1 RNA to T1 RNase was unexpected inasmuch as this region has been implicated in hydrogen bonding with heterogeneous nuclear RNA splice junctions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Lazar E., Gallinaro H., Jacob M., Sri-Widada J., Jeanteur P. Nucleotide sequences of nuclear U1A RNAs from chicken, rat and man. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4143–4154. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F., Barrell B. G. The sequence of 5 s ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):379–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Queen C. L., Wegman M. N. Computer analysis of nucleic acid regulatory sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4401–4405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Ro-Choi T. S., Busch H. Nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes containing U1 and U2 RNA. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4380–4385. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Ro-Choi T. S., Henning D., Busch H. Primary sequence of U-1 nuclear ribonucleic acid of Novikoff hepatoma ascites cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6486–6494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C., Levine M. D. Estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nature. 1971 Apr 9;230(5293):362–367. doi: 10.1038/230362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Brownlee G. G. 3'End labelling of RNA with 32P suitable for rapid gel sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3129–3139. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]