Abstract
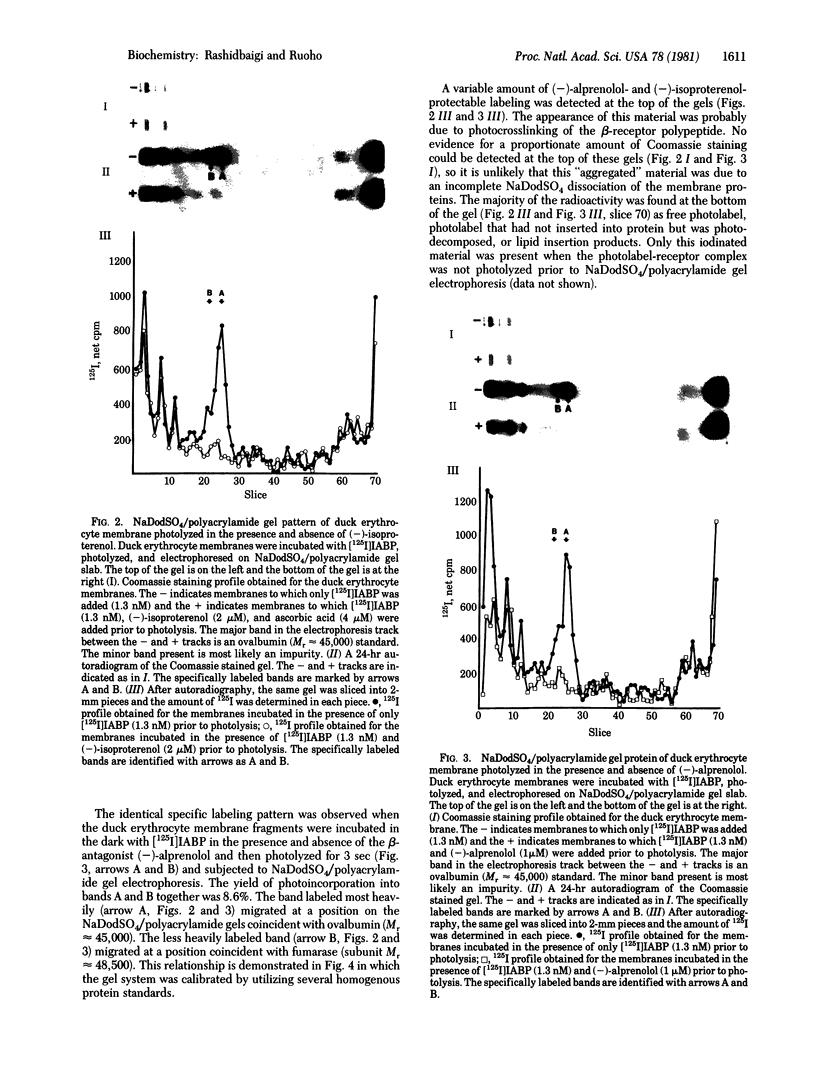
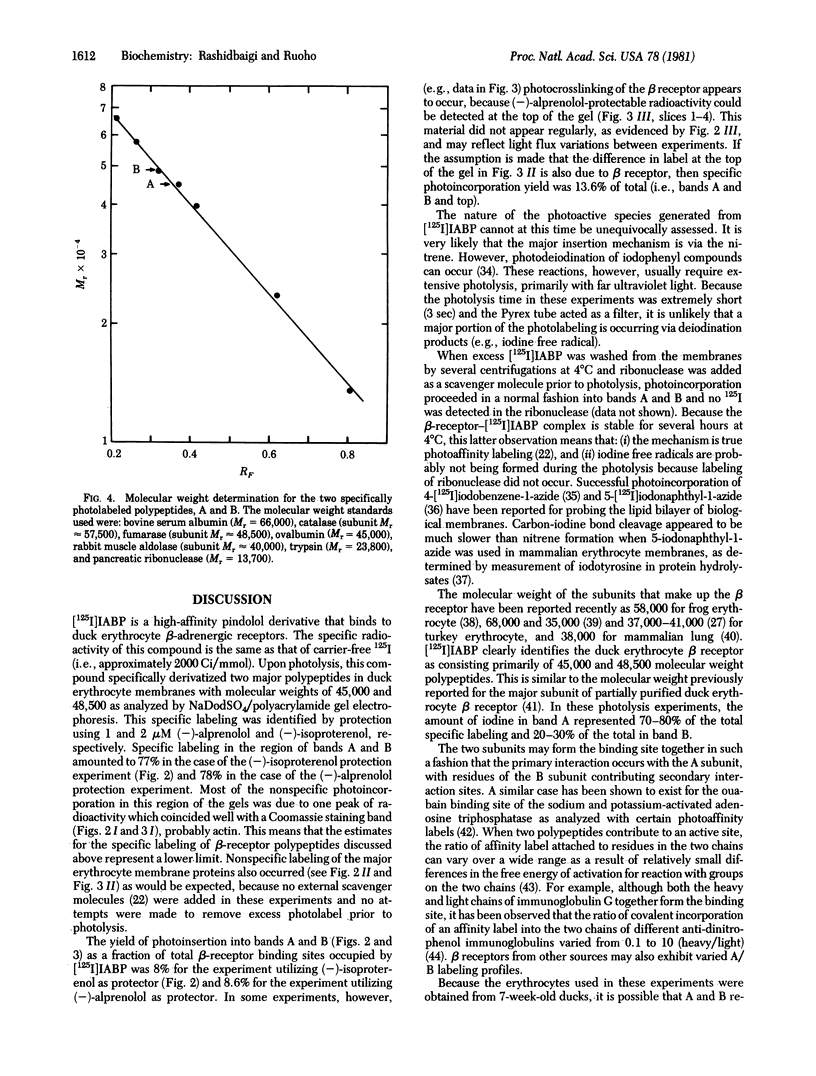
A high-affinity pindolol derivative, (+/-)-1-(indol-4-yloxy)-3-[1-(p-azido-m-iodophenyl)-2-isobutylamine]-2-propanol (IABP), has been prepared; it contains an iodide and an azide functional group and acts as a photoaffinity label for the beta-adrenergic receptor. When [125I]IABP (specific activity 1300 Ci/mmol) was photolyzed with crude duck erythrocyte membrane preparations, which contain beta-adrenergic receptor binding sites highly specific labeling of two polypeptides was observed upon electrophoresis on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels. These two polypeptides, A (Mr approximately 45,000) and B (Mr approximately 48,500), and B (Mr approximately 48,500), were photolabeled in a ratio of approximately 4:1 A/B. Binding of [125I]IABP and covalent derivatization of the beta receptor was at least 70% specific. The data indicate that [125I]IABP is a very effective compound for identification of polypeptides containing the beta-receptor binding site even in crude membrane preparations. The beta receptor of the duck erythrocyte plasma membrane may be composed of more than one subunit.
Full text
PDF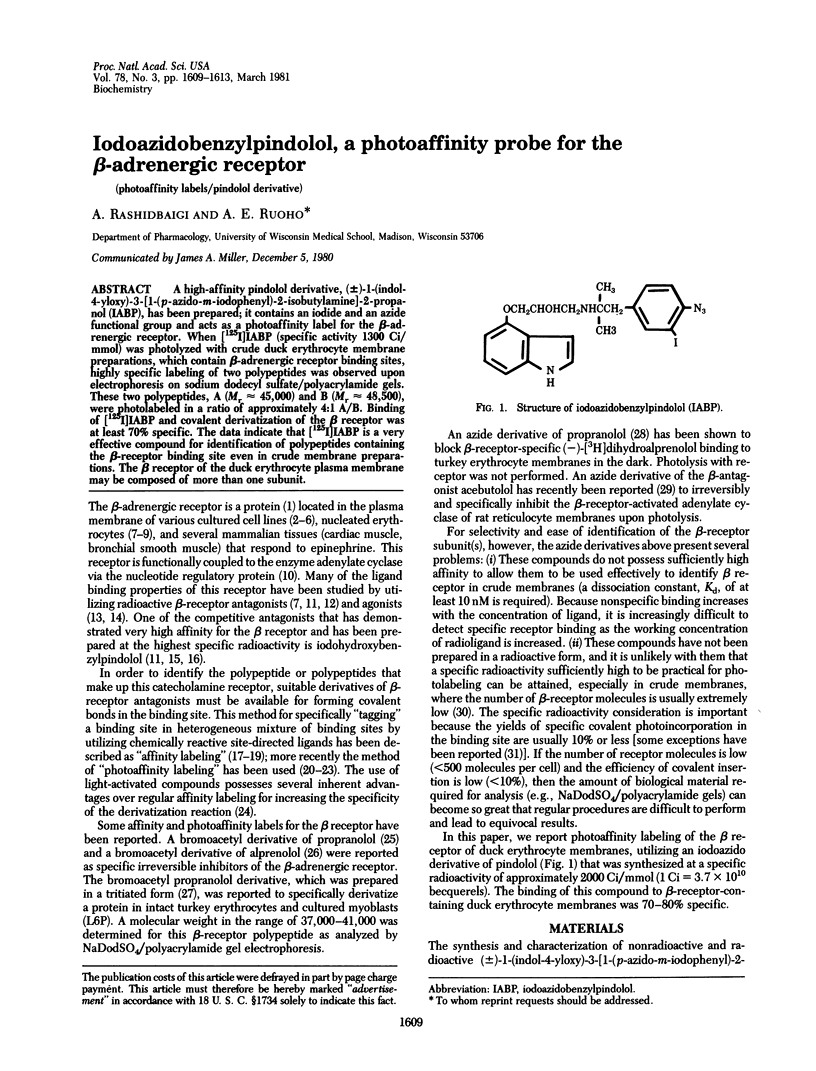


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas D., Levitzki A. An irreversible blocker for the beta-adrenergic receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas D., Levitzki A. Tentative identification of beta-adrenoreceptor subunts. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):370–371. doi: 10.1038/272370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurbach G. D., Fedak S. A., Woodard C. J., Palmer J. S., Hauser D., Troxler F. Beta-adrenergic receptor: stereospecific interaction of iodinated beta-blocking agent with high affinity site. Science. 1974 Dec 27;186(4170):1223–1224. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4170.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley H., Knowles J. R. Photoaffinity labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:69–114. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearer C. F., Knapp R. D., Kaumann A. J., Swartz T. L., Birnbaumer L. Iodohydroxybenzylpindolol: preparation, purification, localization of its iodine to the indole ring, and characterization as a partial agonist. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 May;17(3):328–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercovici T., Gitler C. 5-[125I]Iodonaphthyl azide, a reagent to determine the penetration of proteins into the lipid bilayer of biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1484–1489. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. M., Aurbach G. D. Beta-Adrenergic receptor interactions. Characterization of iodohydroxybenzylpindolol as a specific ligand. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1232–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhry V., Westheimer F. H. Photoaffinity labeling of biological systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:293–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri Y., Schramm M. Resolution, reconstitution and kinetics of the primary action of a hormone receptor. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):297–300. doi: 10.1038/287297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbush B., 3rd, Kaplan J. H., Hoffman J. F. Characterization of a new photoaffinity derivative of ouabain: labeling of the large polypeptide and of a proteolipid component of the Na, K-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3667–3676. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C., Ruoho A. Ouabain-binding-site photoaffinity probes that label both subunits of Na+,K+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4529–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer H., Lindstrom J., Lennox E. S., Singer S. J. Photo-affinity labeling of specific acetylcholine-binding sites on membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1688–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Gitler C. Photoactive covalent labeling of membrane components from within the lipid core. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Atlas D., Steer M. L. The binding characteristics and number of beta-adrenergic receptors on the turkey erythrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2773–2776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Sevilia N., Atlas D., Steer M. L. Ligand specificity and characteristics of the beta-adrenergic receptor in turkey erythrocyte plasma membranes. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 5;97(1):35–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Adenylate cyclase-coupled beta adrenergic receptors effect of membrane lipid-perturbing agents on receptor binding and enzyme stimulation by catecholamines. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;12(4):559–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M., Bockaert J. Use of (-)-[3H]dihydroalprenolol to study beta adrenergic receptor-adenylate cyclase coupling in C6 glioma cells: role of 5'-guanylylimidodiphosphate. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;13(2):314–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Wiklund R. A., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Binding of (125I)iodohydroxybenzylpindolol to putative beta-adrenergic receptors of rat glioma cells and other cell clones. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1221–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchoff C. D., Marinetti G. V. Hormone action at the membrane level. V. Binding of (+/-)-[3H]isoproterenol to intact chicken erythrocytes and erythrocyte ghosts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 4;436(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N., Warner N. L., Roeder P. E., Singer S. J. Affinity labeling of a mouse IgG2a myeloma protein with binding affinity for nitrophenyl ligands. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4999–5005. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier K. E., Ruoho A. E. An avidin-biotinyl-propranolol complex for beta-adrenergic receptor characterization. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(2):243–252. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee C., Caron M. G., Coverstone M., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification of adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptors in frog erythrocytes with (minus)-[3-H] alprenolol. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4869–4876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoho A. E., Kiefer H., Roeder P. E., Singer S. J. The mechanism of photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2567–2571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear M., Insel P. A., Melmon K. L., Coffino P. Agonist-specific refractoriness induced by isoproterenol. Studies with mutant cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7572–7576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard J. R. Catecholamine hormone receptor differences identified on 3T3 and simian virus-transformed 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1091–1094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. Covalent labeling of active sites. Adv Protein Chem. 1967;22:1–54. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Martin N., Thorpe N. O. Affinity labeling of the active sites of antibodies and myeloma proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:342–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Smith C. C., Henneberry R. C. Induction of functional beta-adrenergic receptors in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):873–877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOFSY L., METZGER H., SINGER S. J. Affinity labeling-a general method for labeling the active sites of antibody and enzyme molecules. Biochemistry. 1962 Nov;1:1031–1039. doi: 10.1021/bi00912a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Lefkowitz R. J. Slowly reversible binding of catecholamine to a nucleotide-sensitive state of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7207–7213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn S. M., Jr, Homcy C. J. Photoaffinity label for the beta-adrenergic receptor: synthesis and effects on isoproterenol-stimulated adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4449–4453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





