Abstract
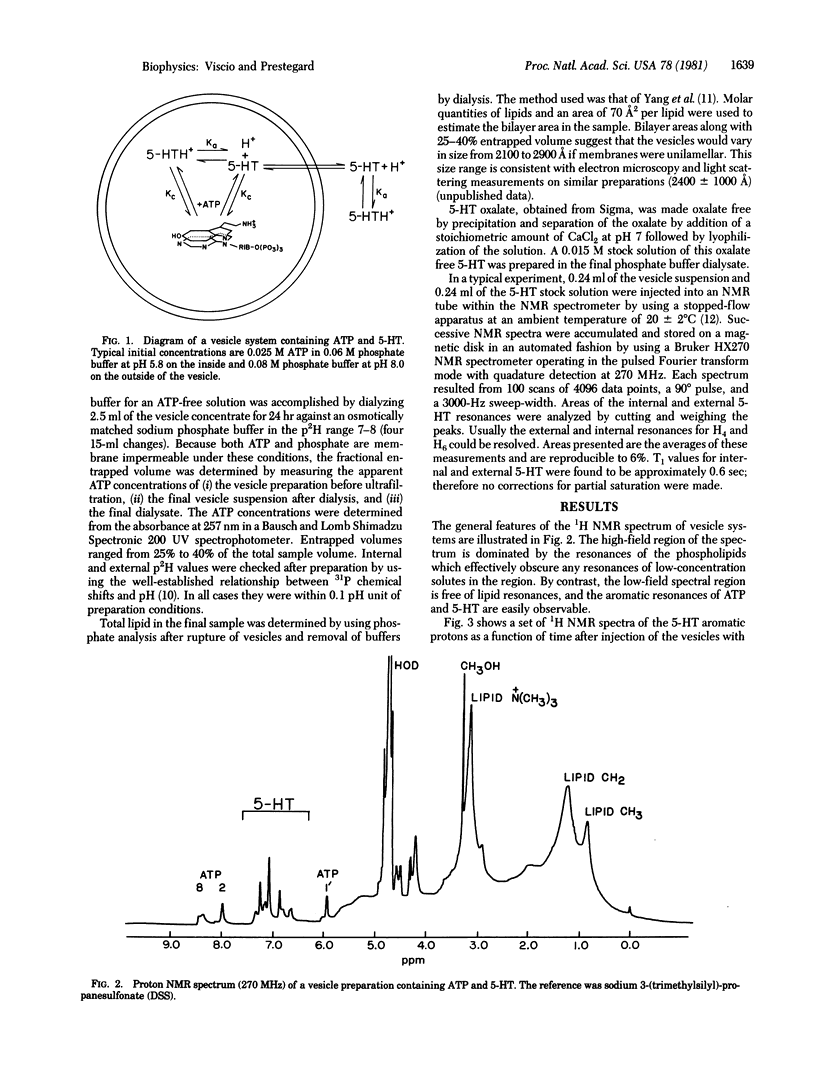
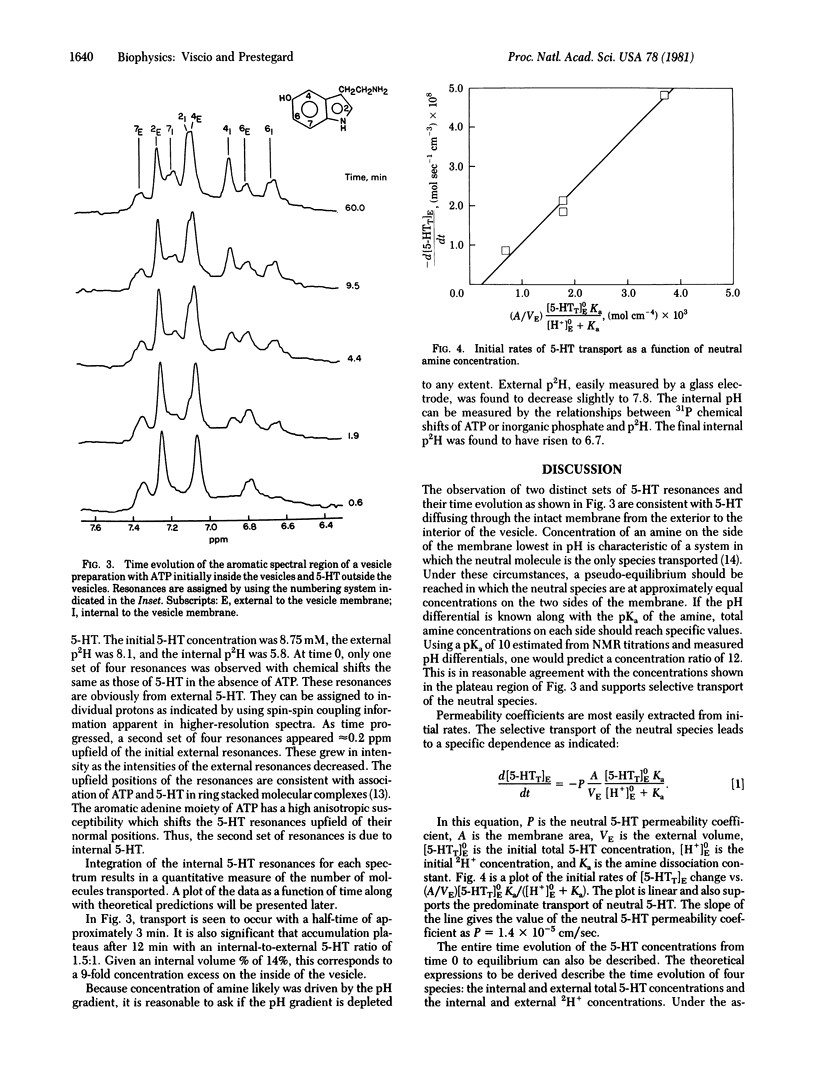
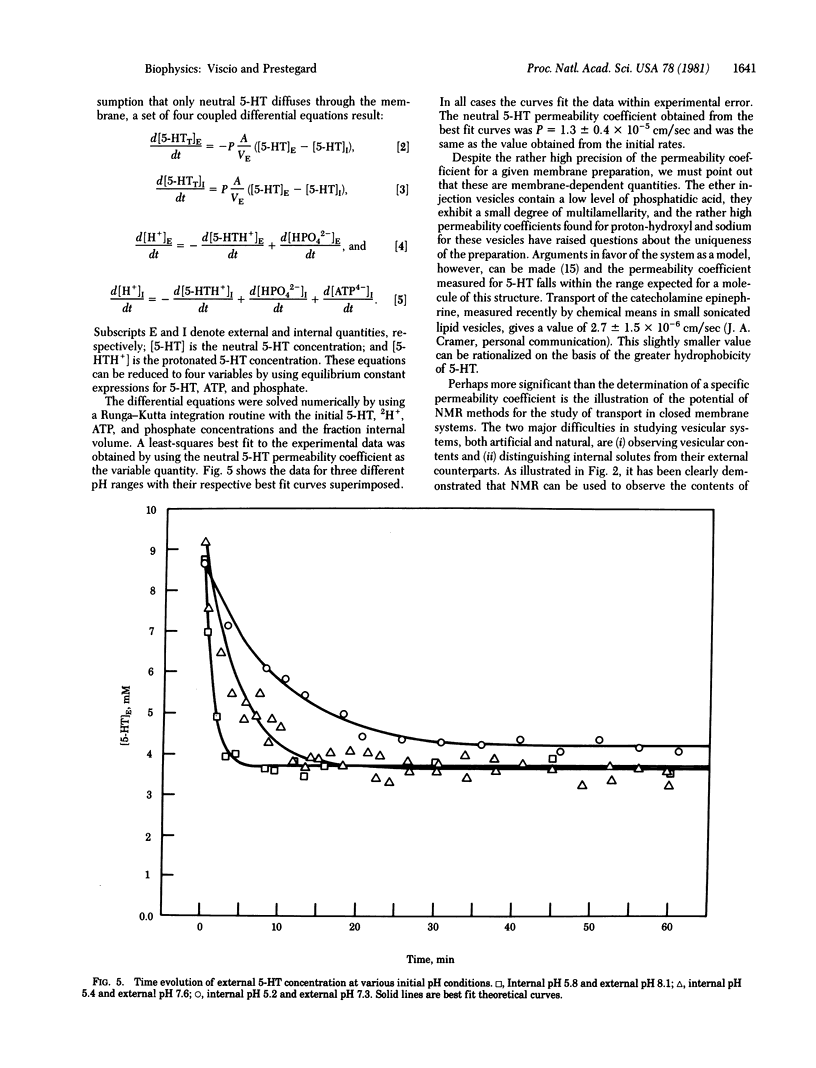
Nuclear magnetic resonance techniques developed to study membrane permeability in closed membrane systems have been used to investigate transport of 5-hydroxytryptamine across the phospholipid membranes of large unilamellar vesicles. The vesicles, modeling the 5-hydroxytryptamine storage organelles of blood platelets, contained a high internal level of ATP buffered at a pH low relative to the external solution. The resultant pH gradient drove accumulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine to a level consistent with selective transport of the neutral amine. The upfield shifts of the 5-hydroxytryptamine resonances resulting from complexation with internally confined ATP were utilized to resolve and, simultaneously, to observe the internal and external amine. Simulation of the time evolution of the 5-hydroxytryptamine concentration allowed measurement of a permeability coefficient of 1.4 +/- 0.5 X 10(-5) cm/sec for the neutral amine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berneis K. H., Da Prada M., Pletscher A. Micelle formation between 5-hydroxytryptamine and adenosine triphosphate in platelet storage organelles. Science. 1969 Aug 29;165(3896):913–914. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3896.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R. P., Njus D., Radda G. K., Sehr P. A. Active proton uptake by chromaffin granules: observation by amine distribution and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):972–977. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D., Bangham A. D. Large volume liposomes by an ether vaporization method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 7;443(3):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Pfister D., Carty S. E., Scarpa A. Biological amine transport in chromaffin ghosts. Coupling to the transmembrane proton and potential gradients. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10963–10972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Scarpa A., Salganicoff L. The internal pH of isolated serotonin containing granules of pig platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):7061–7068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao M. J., Prestegard J. H. Fusion kinetics of phosphatidylcholine-phosphatidic acid mixed lipids vesicles: a proton nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 20;599(1):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Deamer D. W. Net proton-hydroxyl permeability of large unilamellar liposomes measured by an acid-base titration technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2038–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogrady T., Hrdina P. D., Ling G. M. Investigation into the association between serotonin and adenosine triphosphate in vitro by nuclear magnetic resonance and ultraviolet spectroscopy. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Sep;8(5):565–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestegard J. H., Cramer J. A., Viscio D. B. Nuclear magnetic resonance determinations of permeation coefficients for maleic acid in phospholipid vesicles. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):575–584. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85272-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. A., Greenawalt J. W., Huang L. Transport of 5-hydroxytryptamine by dense granules from porcine platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6260–6265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. F., Freer S., Benson A. A. Transphosphatidylation by phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


