Abstract
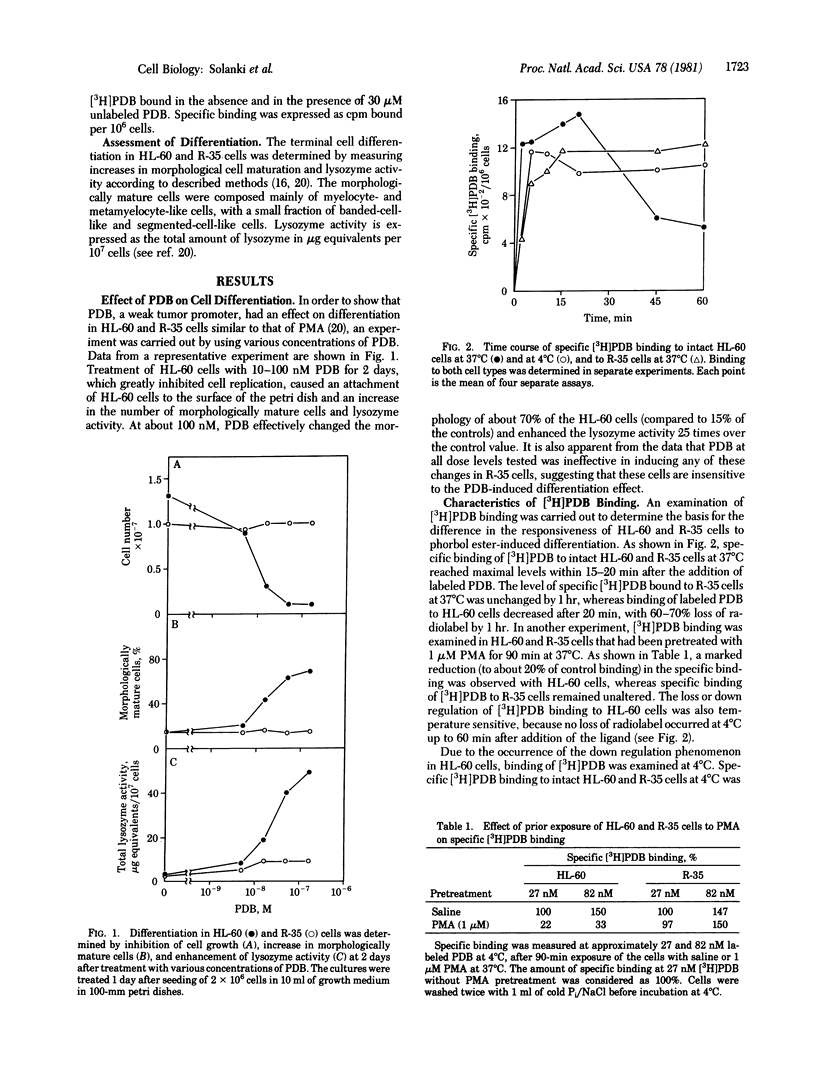
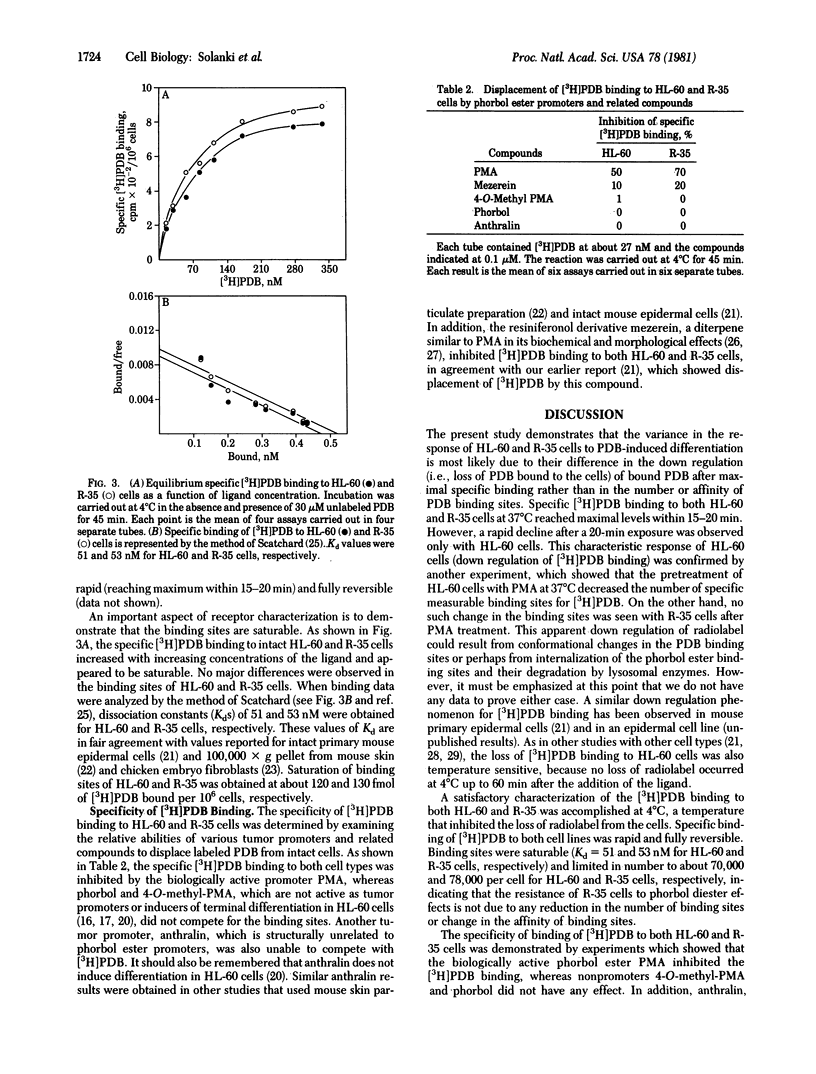
Binding of [20-3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate ([3H]PDB) to intact human promyelocytic leukemia cells susceptible (HL-60) or resistant (R-35) to phorbol ester-induced differentiation was characterized. Specific binding of [3H]PDB to both HL-60 and R-35 cells at 37 degrees C reached a maximum within 15-20 min. Maximal specific [3H]PDB binding to HL-60 cells was followed by a decline (down regulation) of radioactivity. This down regulation was temperature dependent, because no loss of radiolabel occurred by 1 hr at 4 degrees C. The down regulation of bound [3H]PDB seen in HL-60 cells at 37 degrees C was not observed with R-35 cells. Prior exposure of the HL-60 cells but not of R-35 cells to 1 microM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate for 90 min at 37 degrees C caused a marked reduction in the specific binding of [3H]PDB. When [3H]PDB binding was carried out at 4 degrees C, [3H]PDB bound to both cell types in a rapid, specific, and reversible manner. At equilibrium, HL-60 and R-35 cells were found to contain almost the same number of binding sites, which had dissociation constants of about 50 nM, indicating that the failure of R-35 cells to undergo PDB-induced differentiation was not associated with any change in the affinity or in the number of [3H]PDB binding sites. These results indicate that the down regulation of specific [3H]PDB binding may be a crucial early event in the control of phorbol ester-induced terminal differentiation in HL-60 cells. Furthermore, we suggest that such down regulation may be involved in other cellular and biochemical effects of phorbol diester tumor promoters.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boutwell R. K. The function and mechanism of promoters of carcinogenesis. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1974 Jan;2(4):419–443. doi: 10.3109/10408447309025704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to surface receptors by tumor promotors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. Y., Maxfield F. R., Robbins J., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Receptor-mediated uptake of 3,3',5-triiodo-L-thyronine by cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3425–3429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R., Pacifici M., Rubinstein N., Biehl J., Holtzer H. Effect of a tumour promoter on myogenesis. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):538–540. doi: 10.1038/266538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2458–2462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delclos K. B., Nagle D. S., Blumberg P. M. Specific binding of phorbol ester tumor promoters to mouse skin. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driedger P. E., Blumberg P. M. Specific binding of phorbol ester tumor promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):567–571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Callaham M. F. Induction of terminal differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells by tumor-promoting agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Weeks C., Herrmann A., Callaham M., Slaga T. Alterations in polyamine levels induced by phorbol diesters and other agents that promote differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1062–1066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N., Fibach E., Yamasaki H., Weinstein I. B. Tumor promoters inhibit morphological differentiation in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):556–559. doi: 10.1126/science.644318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasukabe T., Honma Y., Hozumi M. Inhibition of functional and morphological differentiation of cultured mouse myeloid leukemia cells by tumor promoters. Gan. 1979 Feb;70(1):119–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Regulation of normal differentiation in mouse and human myeloid leukemic cells by phorbol esters and the mechanism of tumor promotion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5158–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R. M., Filedsteel A. H., Fodge D. W. Opposing effects of tumor promoters on erythroid differentiation. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):271–272. doi: 10.1038/274271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson R. A., Fischer S. M., Verma A. K., Gleason G. L., Slaga T. J., Boutwell R. K. Effects of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and mezerein on epidermal ornithine decarboxylase activity, isoproterenol-stimulated levels of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate, and induction of mouse skin tumors in vivo. Cancer Res. 1979 Dec;39(12):4791–4795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa K., Mak T. W. Phorbol esters induce differentiation in human malignant T lymphoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacifici M., Holtzer H. Effects of a tumor-promoting agent on chondrogenesis. Am J Anat. 1977 Sep;150(1):207–212. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001500116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raick A. N. Cell differentiation and tumor-promoting action in skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1974 Nov;34(11):2915–2925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., O'Brien T. G., Diamond L. Induction of differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells by tumor promoters. Science. 1979 May 25;204(4395):868–870. doi: 10.1126/science.286421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., O'Brien T. G., Diamond L. Tumor promoters inhibit spontaneous differentiation of Friend erythroleukemia cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2894–2898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Santoli D., Damsky C. Human promyelocytic leukemia cells in culture differentiate into macrophage-like cells when treated with a phorbol diester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. Control of normal cell differentiation and the phenotypic reversion of malignancy in myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):535–539. doi: 10.1038/274535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivak A. Cocarcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 4;560(1):67–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaga T. J., Fischer S. M., Nelson K., Gleason G. L. Studies on the mechanism of skin tumor promotion: evidence for several stages in promotion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart R. K., Hamilton J. A. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters stimulate hematopoietic colony formation in vitro. Science. 1980 Apr 25;208(4442):402–404. doi: 10.1126/science.6245446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Fibach E., Nudel U., Weinstein I. B., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Tumor promoters inhibit spontaneous and induced differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3451–3455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



