Abstract
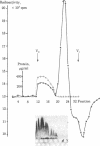
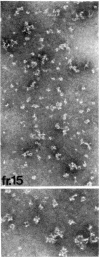
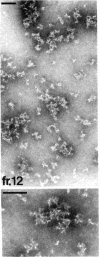
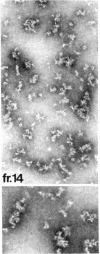
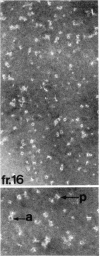
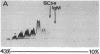
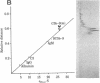
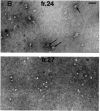
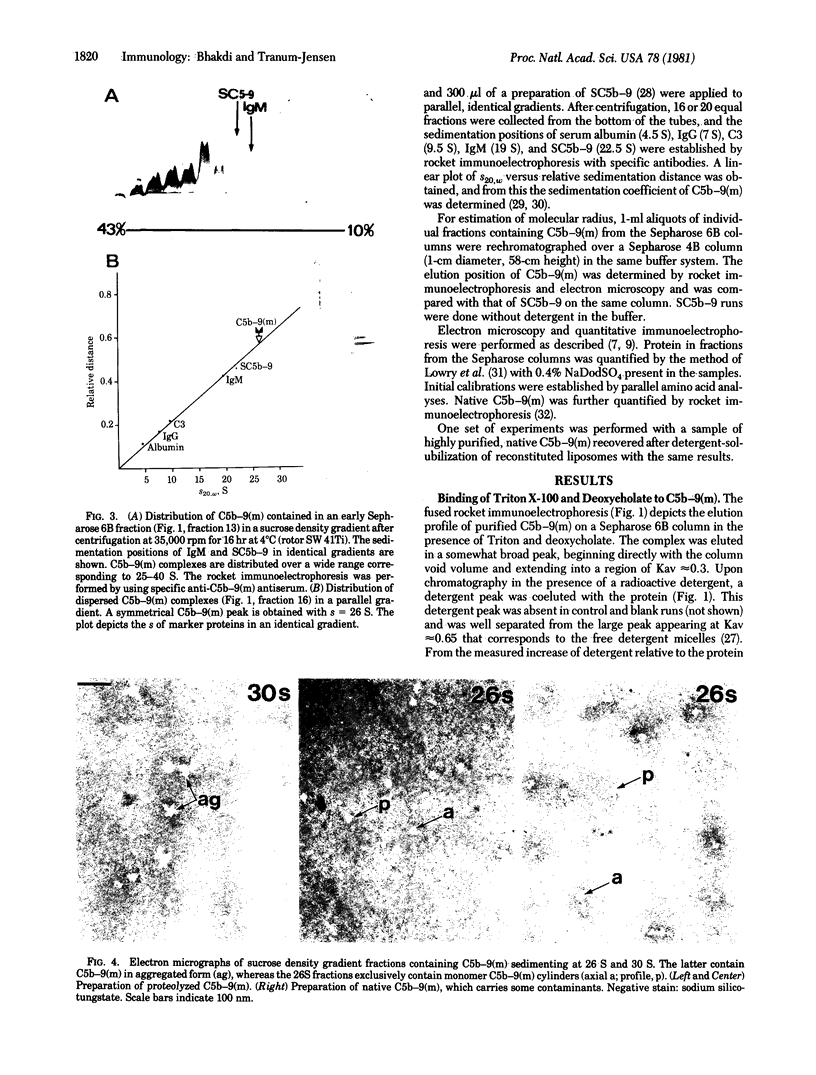
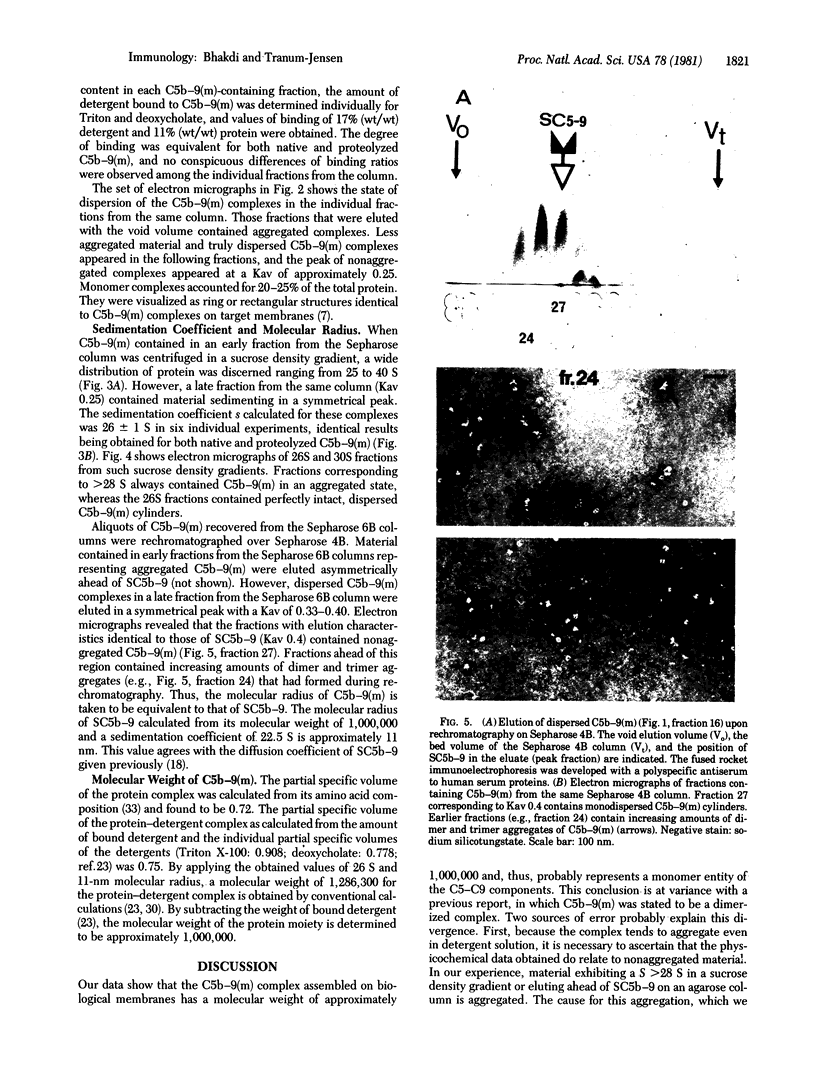
The hydrodynamic properties of the detergent-solubilized, terminal membrane complex of serum complement components C5-C9 [C5b-9(m)] were studied to obtain an estimate of its molecular weight. In a solution of Triton X-100/deoxycholate, the protein complex binds 17% Triton X-100 and 11% deoxycholate by weight. The sedimentation coefficient of the protein-detergent complex is 26 S as determined by sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation, and gel filtration indicated a molecular radius of 11 nm. It was ascertained by electron microscopy that these hydrodynamic parameters apply to mono-dispersed C5b-9(m) complexes, which were observed as nonaggregated, hollow protein cylinders and were identical to the complement "lesions" formed on target membranes. The calculated molecular weight of the protein-detergent complex is approximately 1,286,300 to which the protein moiety contributes approximately 1,000,000. The results indicate that the C5b-9(m) complex formed on biological membranes is a monomer entity of the C5-C9 complement components.
Full text
PDF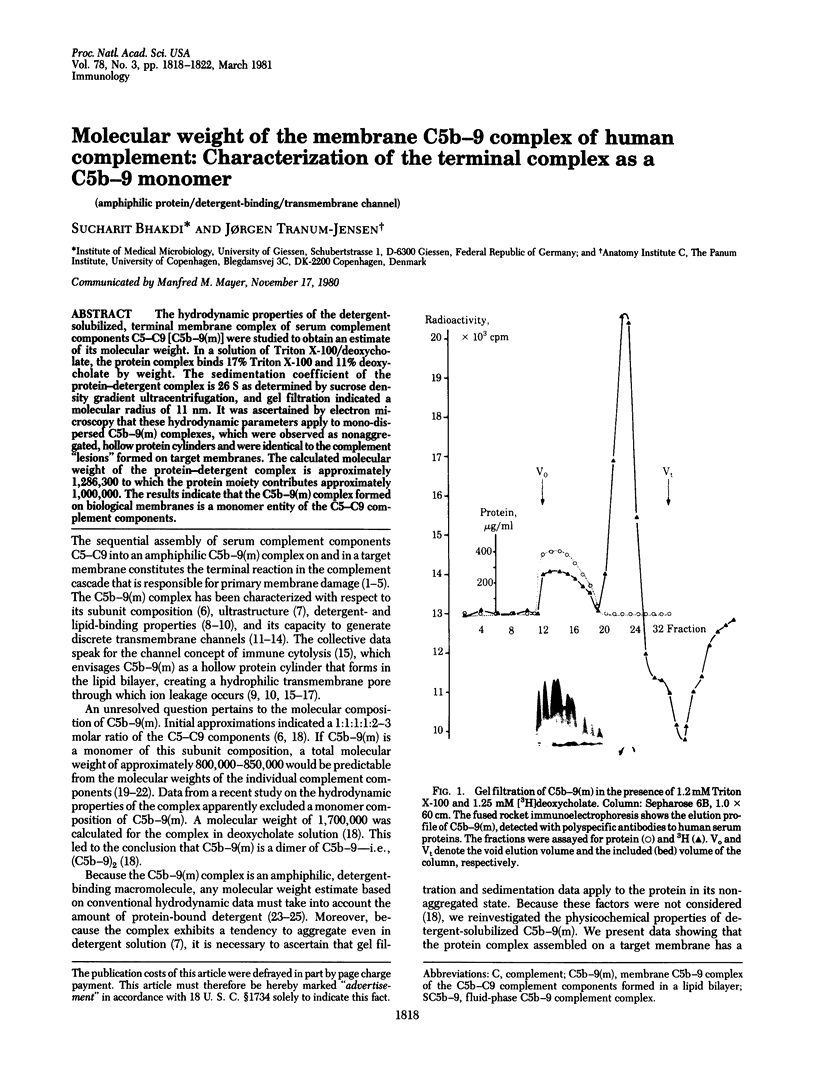

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J., Tranum-Jensen J. Difference in antigenic reactivity and ultrastructure between fluid-phase C5b-9 and the C5b-9 membrane attack complex of human complement. FEBS Lett. 1979 Mar 1;99(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Bjerrum O. J., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Tranum-Jensen J. Complement lysis: evidence for an amphiphilic nature of the terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2526–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Ey P., Bhakdi-Lehnen B. Isolation of the terminal complement complex from target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 6;419(3):445–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Evidence for a two-domain structure of the terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5872–5876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J., Klump O. The terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement. Evidence for the existence of multiple protease-resistant polypeptides that form the trans-membrane complement channel. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2451–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular nature of the complement lesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Re-incorporation of the terminal C5b-9 complement complex into lipid bilayers: formation and stability of reconstituted liposomes. Immunology. 1980 Nov;41(3):737–742. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Podack E. R., Halverson C. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C5b-9 dimer: isolation from complement lysed cells and ultrastructural identification with complement-dependent membrane lesions. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):448–458. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giavedoni E. B., Chow Y. M., Dalmasso A. P. The functional size of the primary complement lesion in resealed erythrocyte membrane ghosts. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadding U., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The ninth component of human complement: isolation, description and mode of action. Immunology. 1969 Jun;16(6):719–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. The binding of detergents to lipophilic and hydrophilic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3656–3661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klob W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: the three polypeptide chain structure of the eigth component (C8). J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1131–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Verification of a stable C5-9 complex in free solution. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):438–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Bowyer D. E., Nicol P., Dawson R. M., Munn E. A. Studies on the terminal stages of complement lysis. Immunology. 1973 Jan;24(1):135–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thompson R. A. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. II. The characterization of activated reactor as C56 and the participation of C8 and C9. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):643–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M., Hammer C. H., Michaels D. W., Shin M. L. Immunologically mediated membrane damage: the mechanism of complement action and the similarity of lymphocyte-mediated cytoxicity. Immunochemistry. 1978 Nov;15(10-11):813–831. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Mechanism of cytolysis by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2954–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels D. W., Abramovitz A. S., Hammer C. H., Mayer M. M. Increased ion permeability of planar lipid bilayer membranes after treatment with the C5b-9 cytolytic attack mechanism of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2852–2856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Purification of the sixth and seventh component of human complement without loss of hemolytic activity. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Binding of desoxycholate, phosphatidylcholine vesicles, lipoprotein and of the S-protein to complexes of terminal complement components. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1025–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Mayer M. M. Life-span and size of the trans-membrane channel formed by large doses of complement. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2281–2287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Lauf P. K. Steady-state analysis of tracer exchange across the C5b-9 complement lesion in a biological membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5669–5673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F., Morris S. C., Prahl J. W. Fifth component of human complement: purification from plasma and polypeptide chain structure. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1490–1497. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Nozaki Y., Reynolds J. A., Makino S. Molecular characterization of proteins in detergent solutions. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2369–2376. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Characterization of membrane proteins in detergent solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):133–170. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranum-Jensen J., Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J., Speth V. Complement lysis: the ultrastructure and orientation of the C5b-9 complex on target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(1):45–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]