Abstract
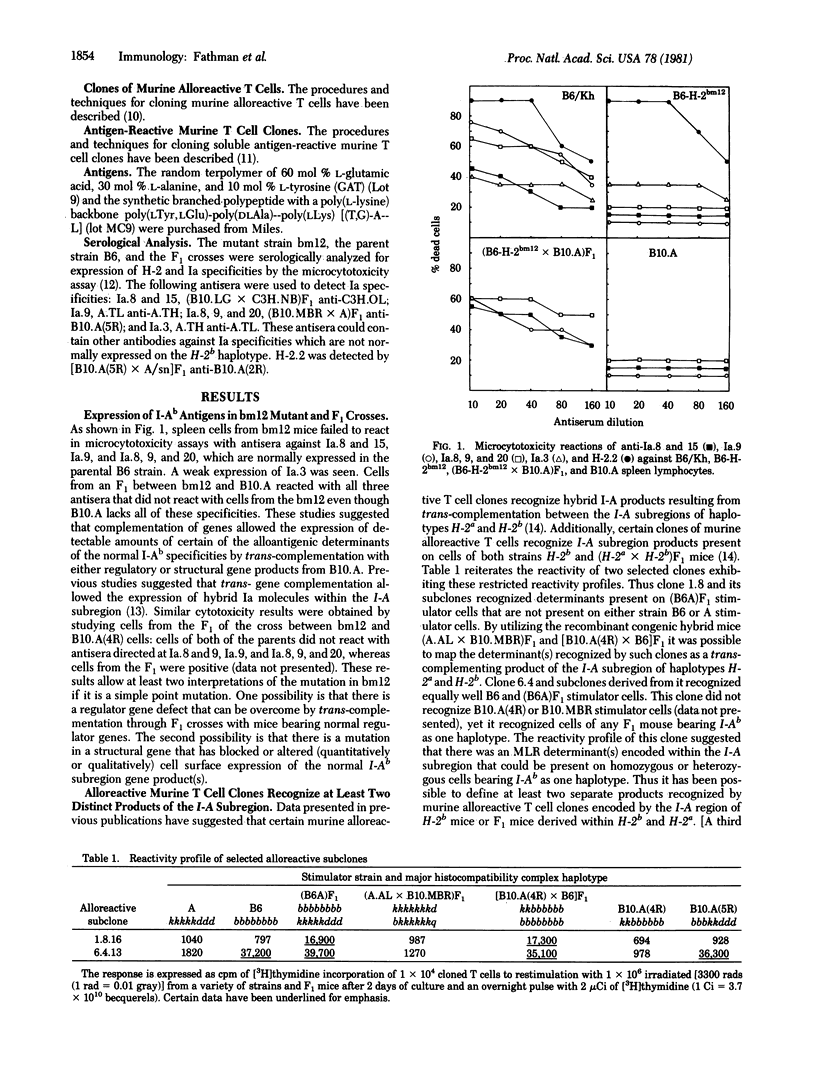
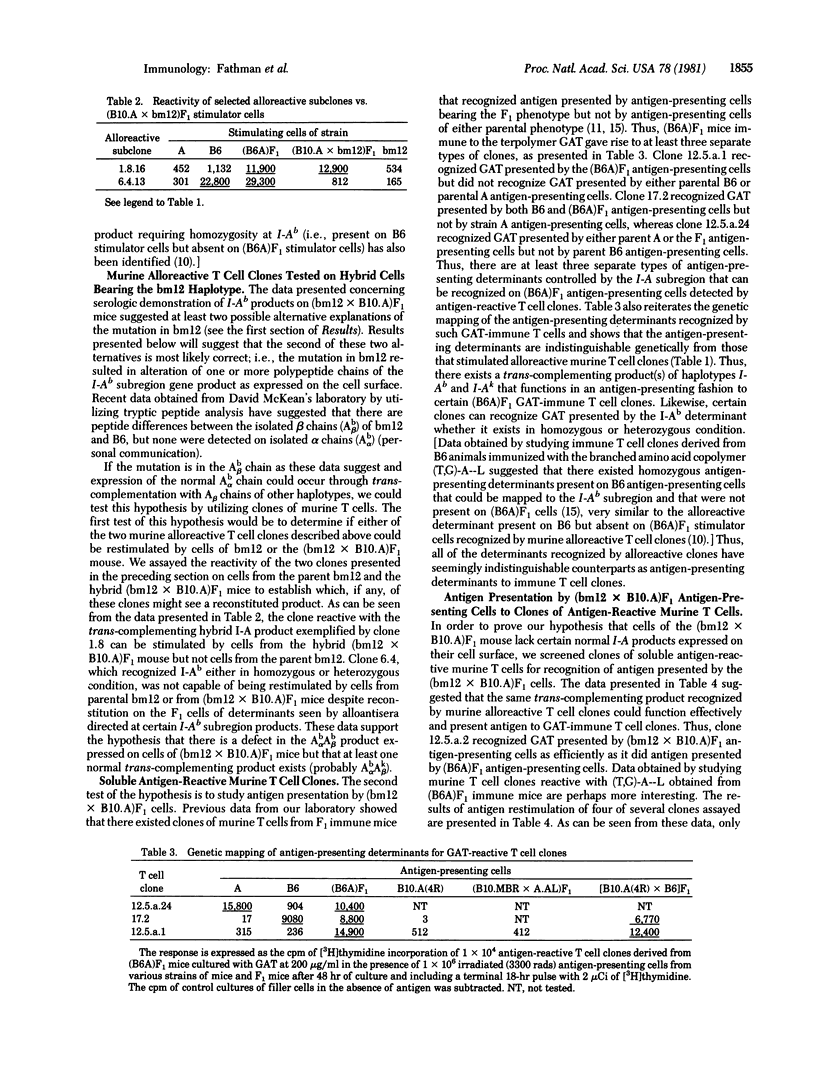
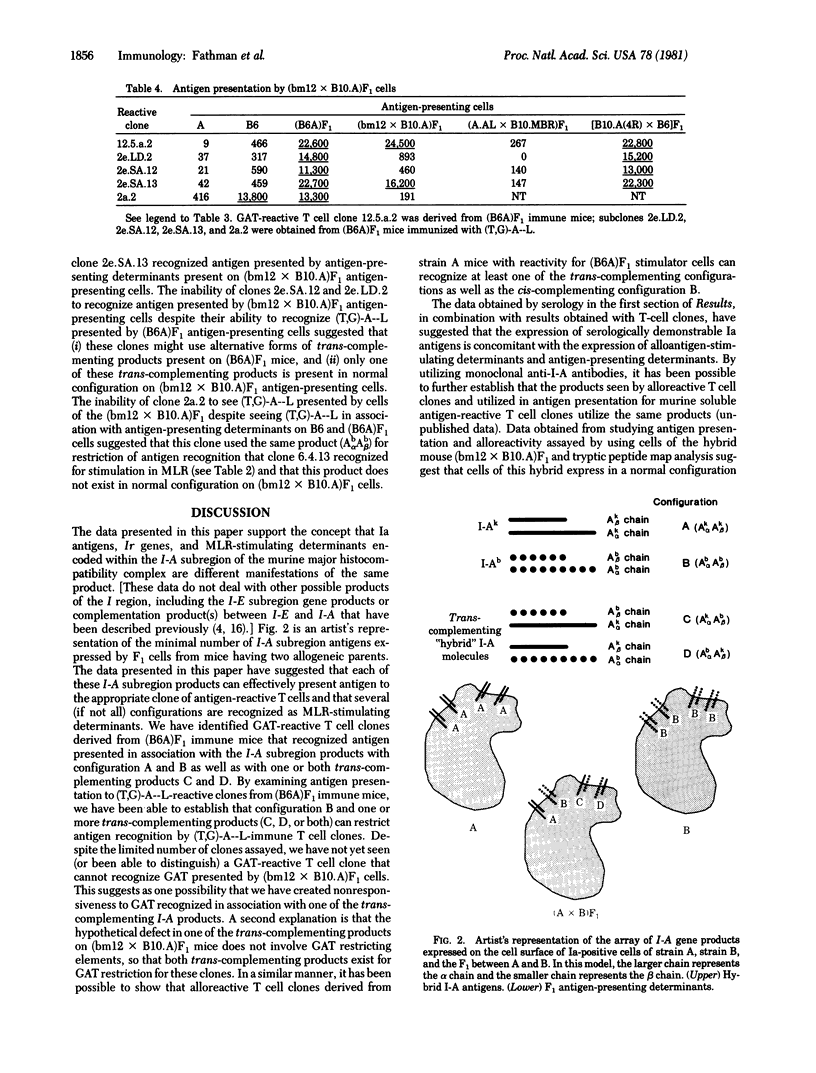
By using clones of murine T cells reactive with alloantigens as well as soluble antigens, it has been possible to demonstrate that Ia antigens, Ir gene phenomena (defined as the ability of immune T cells to recognize antigen), and mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR)-stimulating determinants encoded within the I-A subregion are different manifestations associated with same product. These studies utilized the I-Ab mutant mouse B6.C-H-2bm (bm12), whose defect in the normal expression of the cell surface products of the I-Ab subregion can be partially circumvented through trans-complementation by deriving hybrids between bm12 and mice expressing normal I-A subregion products. Such mice [e.g., (bm12 X B10.A)F1] express several serologically normal I-Ab products but have defects in certain I-A subregion gene products normally expressed on cells of H-2a X H-2b heterozygote mice that are used as restricting elements for antigen recognition by antigen-reactive T cell clones or recognized as alloantigens by alloreactive T cell clones. This defect in cell surface expression of certain normal I-Ab products on the mutant bm12 cells has allowed us to suggest that there exist trans-complementing products on H-2a X H-2b heterozygote mice consisting of Ab alpha Ak beta and Ak alpha Ab beta that restrict antigen recognition by cloned T cells, stimulate MLR responses by cloned T cells, and react with certain anti-Ia antisera.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B., Germain R. N. The immune response genes of the major histocompatibility complex. Immunol Rev. 1978;38:70–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathman C. G., Hengartner H. Crossreactive mixed lymphocyte reaction determinants recognized by cloned alloreactive T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5863–5866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelinger J. A., Neiderhuber J. E., David C. S., Shreffler D. C. Evidence for the expression of Ia (H-2-associated) antigens on thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1273–1284. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Melvold R. W., Arn J. S., Sachs D. H. Evidence for mutation in an I-A gene. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):340–341. doi: 10.1038/285340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner H., Fathman C. G. Clones of alloreactive T cells. I. A. unique homozygous MLR-stimulating determinant present on B6 stimulators. Immunogenetics. 1980;10(2):175–184. doi: 10.1007/BF01561566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., McDevitt H. O. Two-gene control of the expression of a murine Ia antigen. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):925–939. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto M., Fathman C. G. Antigen-reactive T cell clones. I. Transcomplementing hybrid I-A-region gene products function effectively in antigen presentation. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):759–770. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Hauptfeld V. Ia antigens: their serology, molecular relationships, and their role in allograft reactions. Transplant Rev. 1976;30:83–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafuse W. P., McCormick J. F., David C. S. Serological and biochemical identification of hybrid Ia antigens. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):709–715. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Matis L. A., Janeway C. A., Jr, Jones P. P., Schwartz R. H., Murphy D. B. Monoclonal antibody against an Ir gene product? J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1085–1101. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie I. F., Morgan G. M., Sandrin M. S., Michaelides M. M., Melvold R. W., Kohn H. I. B6.C-H-2bm12. A new H-2 mutation in the I region in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1323–1338. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie I. F., Sandrin M. S., Morgan G. M., Henning M. M., Melvold R. W. Mutation in the IA subregion of the murine H-2 complex. Immunogenetics. 1980 Jul;11(1):103–106. doi: 10.1007/BF01567775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., David C. S., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B., Paul W. E. Inhibition of dual Ir gene-controlled T-lymphocyte proliferative response to poly (Glu56Lys35Phe9)n with anti-Ia antisera directed against products of either I-A or I-C subregion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2387–2391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., David C. S., Sachs D. H., Paul W. E. T lymphocyte-enriched murine peritoneal exudate cells. III. Inhibition of antigen-induced T lymphocyte Proliferation with anti-Ia antisera. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):531–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Yano A., Stimpfling J. H., Paul W. E. Gene complementation in the T-lymphocyte proliferative response to poly (Glu55Lys36Phe9)n. A demonstration that both immune response gene products must be expressed in the same antigen-presenting cell. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):40–57. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Swain S. L., Hubert J. J. Small subunit of I-A subregion antigens determines the allospecificity recognized by a monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):272–274. doi: 10.1038/286272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]