Abstract
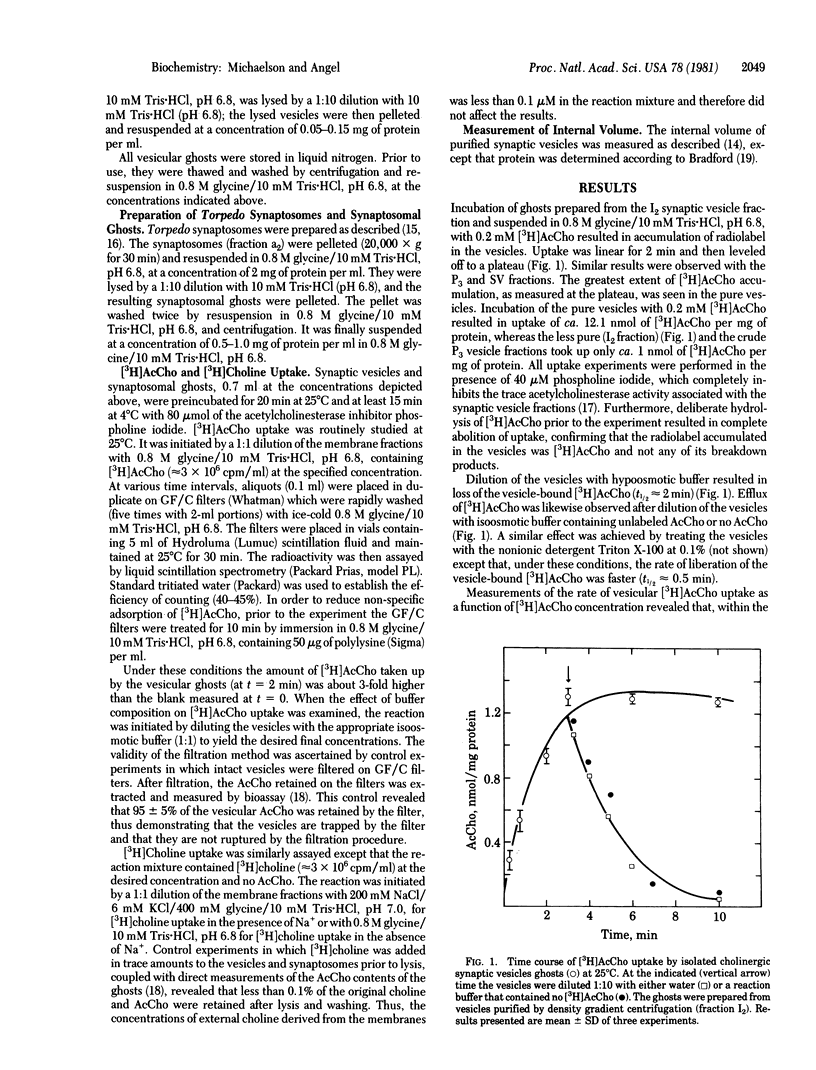
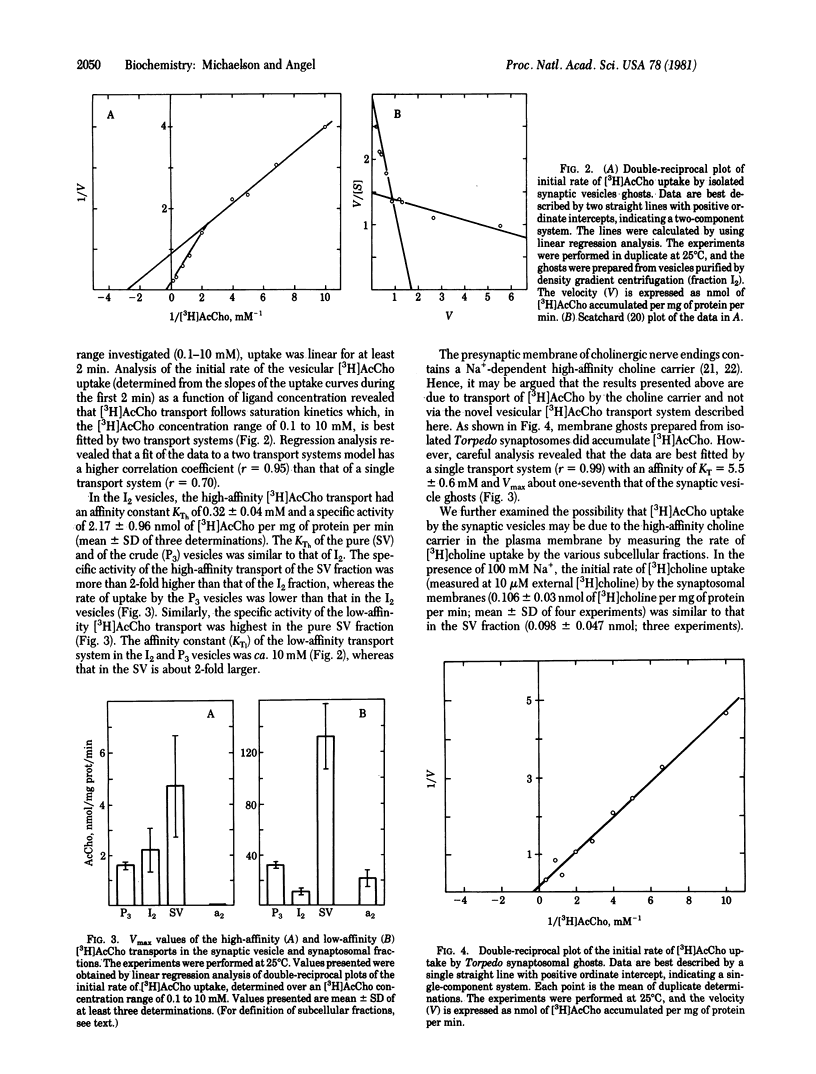
The uptake of [3H[acetylcholine ([3H]AcCho) into cholinergic synaptic vesicle ghosts purified from Torpedo electric organ was studied at concentration of [3H]AcCho ranging from 0.1 to 10 mM. The accumulated [3H]AcCho can be released either by hypoosmotic buffer or by low levels of the detergent Triton X-100. Kinetic analysis of the initial rate of [3H]AcCho uptake reveals temperature-dependent saturation kinetics which are best fitted by high-affinity (KTh approximately 0.3 mM) and low-affinity (KT) approximately 10 mM) vesicular [3H]AcCho transport systems. Several lines of evidence suggest that [3H]AcCho transport is mediated by vesicle-associated transport systems and not by a contaminant of other subcellular moieties such as the plasma membrane choline transport system. (i) The specific activity of the [3H]AcCho transport systems is higher in the purest vesicular fraction than in the less-pure fractions. (ii) Ghosts prepared from isolated synaptosomes manifest only low levels of low-affinity [3H]AcCho transport and no high-affinity [3H]AcCho transport. (iii) The vesicular AcCho transport systems lack some of the typical characteristics of synaptosomal choline transport, such as Na+ activation. (iv) The ratio of uptakes of [3H]AcCho and [3H]choline (10 microM) is about 5-fold higher in the pure vesicles than in isolated synaptosomal membranes. Addition of Mg2+-ATP decreases the rate of vesicular [3H]AcCho uptake by about 50%. The simultaneous addition of NaHCO3 and Mg2+-ATP results in activation of [3H]AcCho uptake to about 125% (relative to control), which is a 2.5-fold enhancement relative to the rate observed with Mg2+-ATP. The present findings demonstrate the presence of novel vesicle-associated AcCho transport systems. Their physiological role in the life cycle of the cholinergic synaptic vesicle and nerve terminal are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breer H., Morris S. J., Whittaker V. P. A structural model of cholinergic synaptic vesicles from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata deduced from density measurements at different osmotic pressures. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 3;87(3):453–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breer H., Morris S. J., Whittaker V. P. Adenosine triphosphatase activity associated with purified cholinergic synaptic vesicles of Torpedo marmorata. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):313–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter R. S., Parsons S. M. Electrogenic behavior of synaptic vesicles from Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):326–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdall M. J., Simon E. J. Comparative studies on synaptosomes: uptake of (N-Me-3H)choline by synaptosomes from squid optic lobes. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):969–982. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Choline acetyltransferase binding to and release from membranes. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):389–398. doi: 10.1042/bj1090389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. The 'compartmentation' of choline acetyltransferase within the synaptosome. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):262–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1030262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M., Dunant Y., Manaranche R. The present status of the vesicular hypothesis. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;13(3):237–275. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël M., Manaranche R., Mastour-Frachon P., Morel N. Isolation of pure cholinergic nerve endings from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 15;160(1):113–115. doi: 10.1042/bj1600113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jope R. S. High affinity choline transport and acetylCoA production in brain and their roles in the regulation of acetylcholine synthesis. Brain Res. 1979 Dec;180(3):313–344. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(79)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsberger R., Parsons S. M. Bicarbonate and magnesium ion-ATP dependent stimulation of acetylcholine uptake by Torpedo electric organ synaptic vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):305–312. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Simon J. R. Acetylcholine uptake: lack of association with cholinergic neurons. J Neurochem. 1974 Jun;22(6):1135–1137. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchbanks R. M. Exchangeability of radioactive acetylcholine with the bound acetylcholine of synaptosomes and synaptic vesicles. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):87–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1060087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Angel I. Determination of delta pH in cholinergic synaptic vesicles: its effect on storage and release of acetylcholine. Life Sci. 1980 Jul 7;27(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Bilen J., Volsky D. Torpedo synaptosomes: evidence for synaptic vesicle fusion accompanying Ca2+-induced ionophore (A23187)-mediated acetylcholine release. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 13;154(2):409–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90715-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Ophir I. Sidedness of (calcium, magnesium) adenosine triphosphatase of purified Torpedo synaptic vesicles. J Neurochem. 1980 Jun;34(6):1483–1490. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Sokolovsky M. Induced acetylcholine release from active purely cholinergic Torpedo synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1978 Jan;30(1):217–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Sokolovsky M. Neurotransmitter release from viable purely cholinergic Torpedo synaptosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 8;73(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90492-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel N., Israel M., Manaranche R. Determination of ACh concentration in torpedo synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1978 Jun;30(6):1553–1557. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Njus D., Radda G. K. Bioenergetic processes in chromaffin granules a new perspective on some old problems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 10;463(3-4):219–244. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa K., Dowe G. H., Morris S. J., Whittaker V. P. The lipid and protein content of cholinergic synaptic vesicles from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata purified to constant composition: implications for vesicle structure. Brain Res. 1979 Feb 9;161(3):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein J. E., Parsons S. M. Specificity of association of a Ca2+/Mg2+ ATPase with cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo electric organ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 13;88(3):1069–1076. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91517-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suszkiw J. B. Acetylcholine translocation in synaptic vesicle ghosts in vitro. J Neurochem. 1976 Oct;27(4):853–857. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb05146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suszkiw J. B., Zimmermann H., Whittaker V. P. Vesicular storage and release of acetylcholine in Torpedo electroplaque synapses. J Neurochem. 1978 Jun;30(6):1269–1280. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER V. P., SHERIDAN M. N. THE MORPHOLOGY AND ACETYLCHOLINE CONTENT OF ISOLATED CEREBRAL CORTICAL SYNAPTIC VESICLES. J Neurochem. 1965 May;12:363–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler D. D. A model of high affinity choline transport in rat cortical synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1979 Apr;32(4):1197–1213. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. The biogenesis of adrenal chromaffin granules. Neuroscience. 1977;2(5):657–683. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. High affinity transport of choline into synaptosomes of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Dec;21(6):1355–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H., Denston C. R. Separation of synaptic vesicles of different functional states from the cholinergic synapses of the Torpedo electric organ. Neuroscience. 1977;2(5):715–730. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



