Abstract
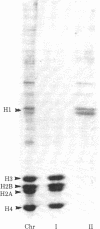
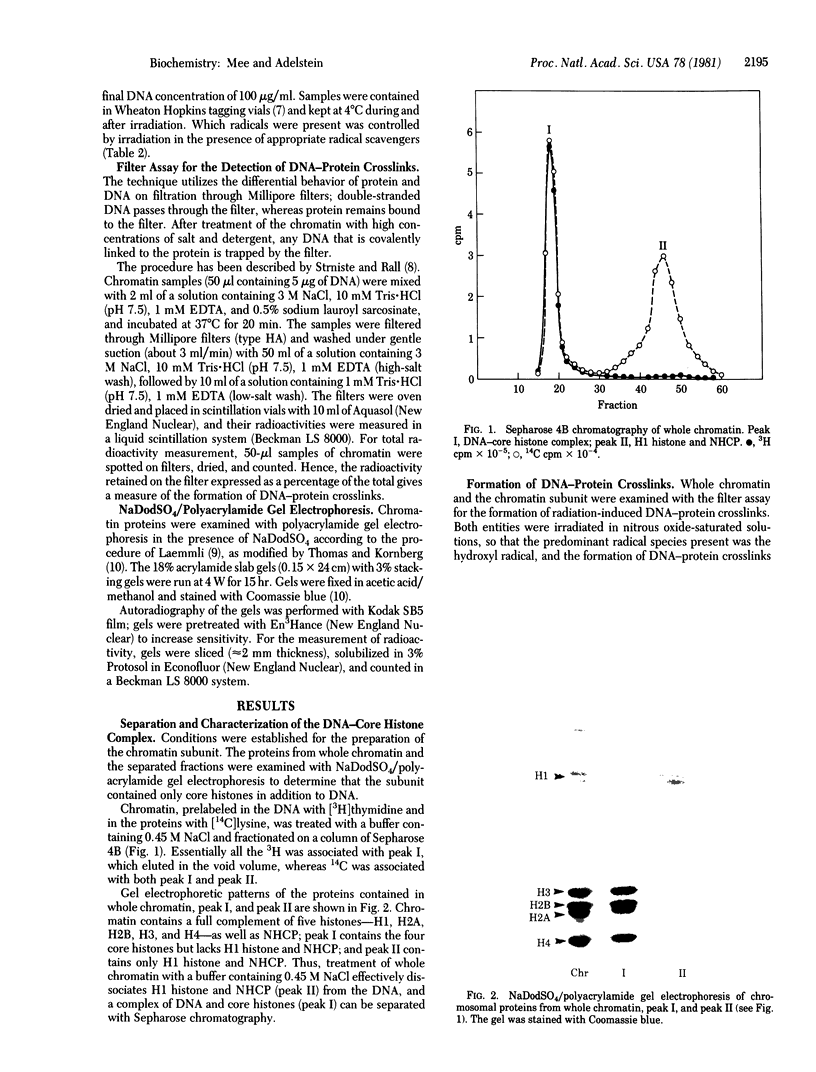
Chromatin and a subunit of chromatin containing a complex of DNA and the core histones--H2A, H2B, H3, and H4--have been prepared from cultured Chinese hamster cells. Comparison of the formation of radiation-induced DNA--protein crosslinks in whole chromatin with that in the DNA--core histone complex has demonstrated that the core histones are the specific proteins involved in crosslinking. gamma irradiation of the chromatin subunit in the presence of radical scavengers has shown the hydroxyl radical to be the most effective aqueous radical intermediate for the promotion of crosslinking and the solvated electron and superoxide radical to be essentially ineffective.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achey P., Duryea H. Production of DNA strand breaks by the hydroxyl radical. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1974 Jun;25(6):595–601. doi: 10.1080/09553007414550791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoku S. DNA single-strand breaks of preheated cultured mammalian cells irradiated under nitrogen- and nitrous oxide-saturated conditions. Radiat Res. 1977 Sep;71(3):678–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok J., Loman H. The effects of gamma-radiation in DNA. Curr Top Radiat Res Q. 1973 Dec;9(2):165–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Little J. B. DNA crosslinking induced by x-rays and chemical agents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 16;477(4):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYMER W. C., KUFF E. L. ISOLATION OF NUCLEI FROM MAMMALIAN TISSUES THROUGH THE USE OF TRITON X-100. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 May;12:359–363. doi: 10.1177/12.5.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helene C. Specific recognition of guanine bases in protein-nucleic acid complexes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 15;74(1):10–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80740-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. C., Huang P. C. Effect of protein-bound RNA associated with chick embryo chromatin on template specificity of the chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan;39(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Martinson H. G. Histone-DNA interactions within chromatin. Isolation of histones from DNA-histone adducts induced in nuclei by UV light. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4263–4272. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M., Yoshii G. Electron transfer between protein and DNA in gamma-irradiated deoxyribonucleoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 19;432(3):292–299. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillicrap S. C., Fielden E. M. Energy transfer between protein and DNA in nucleoprotein. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1972 Feb;21(2):137–144. doi: 10.1080/09553007214550161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel R., Kolomijtseva G., Brahms J. G. DNA-protein interactions in nucleosomes and in chromatin. Structural studies of chromatin stabilized by ultraviolet-light induced crosslinking. Eur J Biochem. 1979 May 15;96(2):257–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee L. K., Adelstein S. J. Radiolysis of chromatin extracted from cultured mammalian cells: formation of DNA-protein cross links. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1979 Oct;36(4):359–366. doi: 10.1080/09553007914551141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee L. K., Adelstein S. J., Stein G. Inactivation of ribonuclease by the primary aqueous radicals. Radiat Res. 1972 Dec;52(3):588–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee L. K., Adelstein S. J., Stein G. Radiolysis of chromatin extracted from cultured mammalian cells: production of alkali-labile strand damage in DNA. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1978 May;33(5):443–455. doi: 10.1080/09553007814550361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan N., Patil M. S., Pradhan D. S. Effect of gamma irradiation on chromosomal proteins from Yoshida ascites tumour chromatin. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1979 Apr;35(4):365–371. doi: 10.1080/09553007914550441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roots R., Okada S. Protection of DNA molecules of cultured mammalian cells from radiation-induced single-strand scissions by various alcohols and SH compounds. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1972 Apr;21(4):329–342. doi: 10.1080/09553007214550401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling J., Sperling R. Photochemical cross-linking of histones to DNA nucleosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2755–2773. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strniste G. F., Rall S. C. Induction of stable protein-deoxyribonucleic acid adducts in Chinese hamster cell chromatin by ultraviolet light. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1712–1719. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]