Abstract
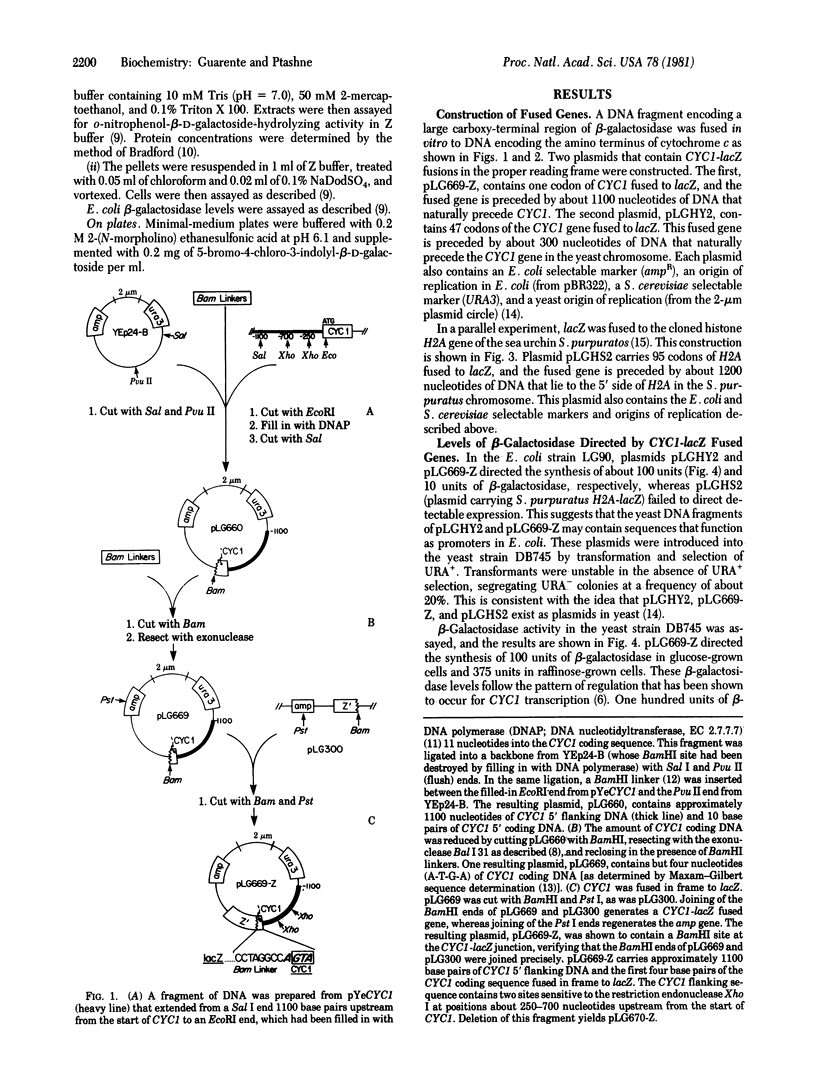
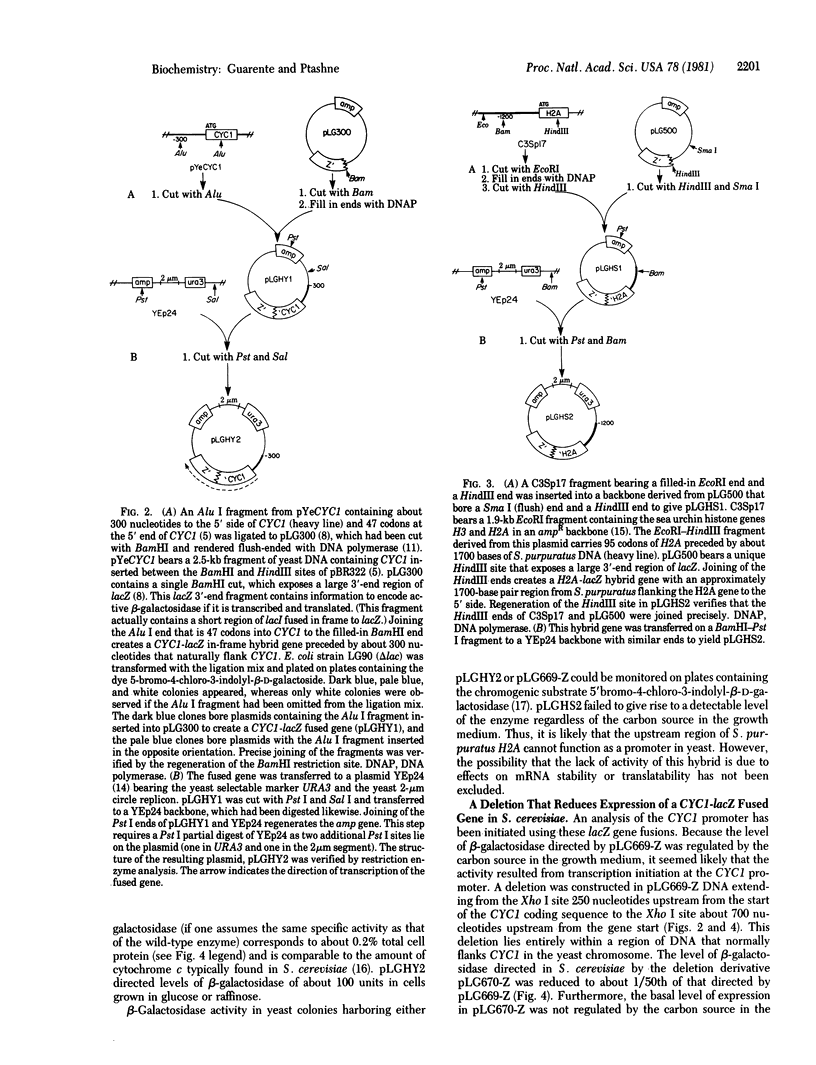
Hybrid genes between the Escherichia coli lacZ gene and the iso-1-cytochrome c (CYC1) gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae were constructed by recombination in vitro. Each of the hybrid genes encodes a chimeric protein with a cytochrome c moiety at the amino terminus and an active beta-galactosidase (beta-D-galactoside galactohydrolase, EC 3.2.1.23) moiety at the carboxy terminus. When these hybrids are introduced into S. cerevisiae on plasmid vectors, they direct synthesis of beta-galactosidase. beta-Galactosidase levels directed by one such plasmid display the pattern of regulation normally seen for cytochrome c (i.e., a reduction of synthesis in cells grown in glucose). This plasmid contains one codon of CYC1 fused to lacZ, and the fused gene is preceded by the 1100 nucleotides that lie upstream from CYC1. An analysis of deletions in the upstream DNA suggests that sequences required for efficient transcription initiation of CYC1 lie within the DNA segment 250--700 base pairs upstream from the start of the CYC1 coding sequence. This region is at least 130 base pairs upstream from the "Hogness box" sequence that precedes the CYC1 coding sequence.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backman K., Ptashne M., Gilbert W. Construction of plasmids carrying the cI gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4174–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M. L., Beckwith J. Use of gene fusions to isolate promoter mutants in the transfer RNA gene tyrT of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 25;130(3):303–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Jacob F. Genetic mapping of the regulator and operator genes of the lac operon. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Leung D. W., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Smith M. Deletion mapping of sequences essential for in vivo transcription of the iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lauer G., Roberts T. M., Ptashne M. Improved methods for maximizing expression of a cloned gene: a bacterium that synthesizes rabbit beta-globin. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90640-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Jeffrey A., Johnson A. D., Maurer R., Meyer B. J., Pabo C. O., Roberts T. M., Sauer R. T. How the lambda repressor and cro work. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Casadaban M. J., Botstein D. Yeast genes fused to beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli can be expressed normally in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2460–2464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., Dickerson R. E., Boyer H. W., Riggs A. D., Itakura K. Chemical synthesis of restriction enzyme recognition sites useful for cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.847463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F., Stewart J. W. Genetics and biosynthesis of cytochrome c. Annu Rev Genet. 1971;5:257–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.05.120171.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F., Stewart J. W., Schweingruber A. M. Mutants of yeast initiating translation of iso-1-cytochrome c within a region spanning 37 nucleotides. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Leung D. W., Gillam S., Astell C. R., Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D. Sequence of the gene for iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Lowry J., Kedes L. H. The DNA sequence of sea urchin (S. purpuratus) H2A, H2B and H3 histone coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitomer R. S., Montgomery D. L., Nichols D. L., Hall B. D. Transcriptional regulation of the yeast cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3627–3631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


