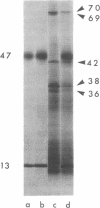
Abstract
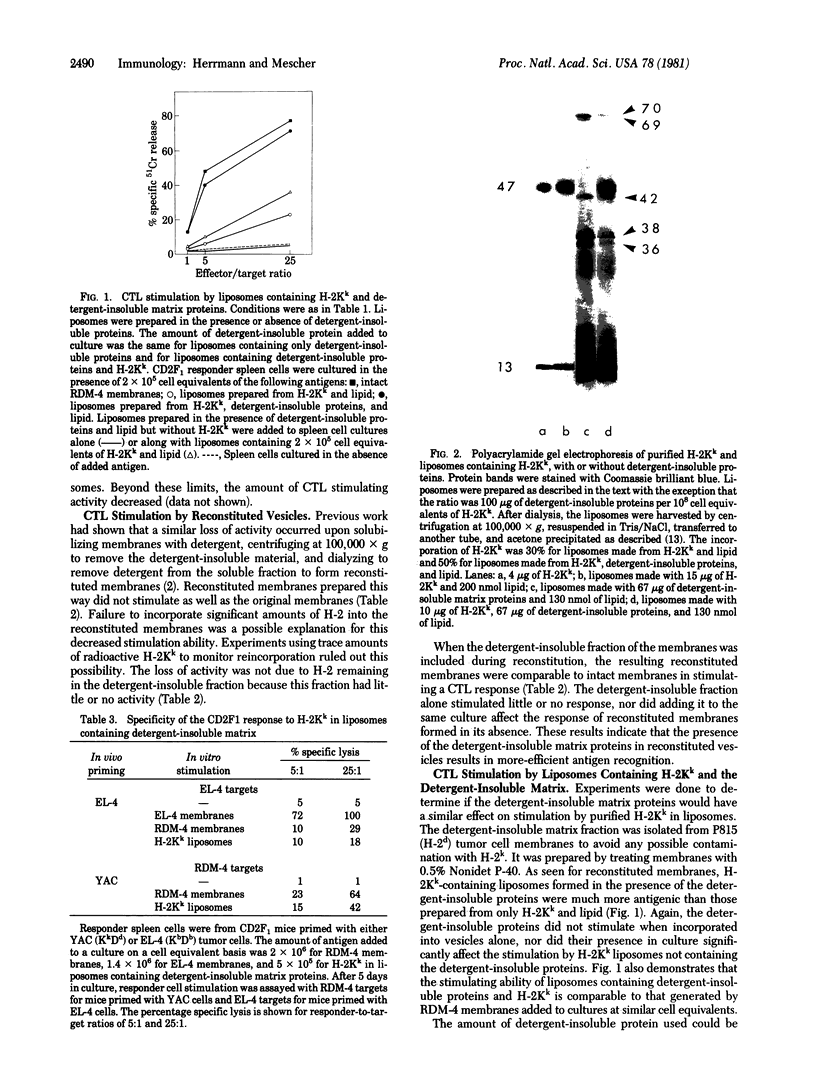
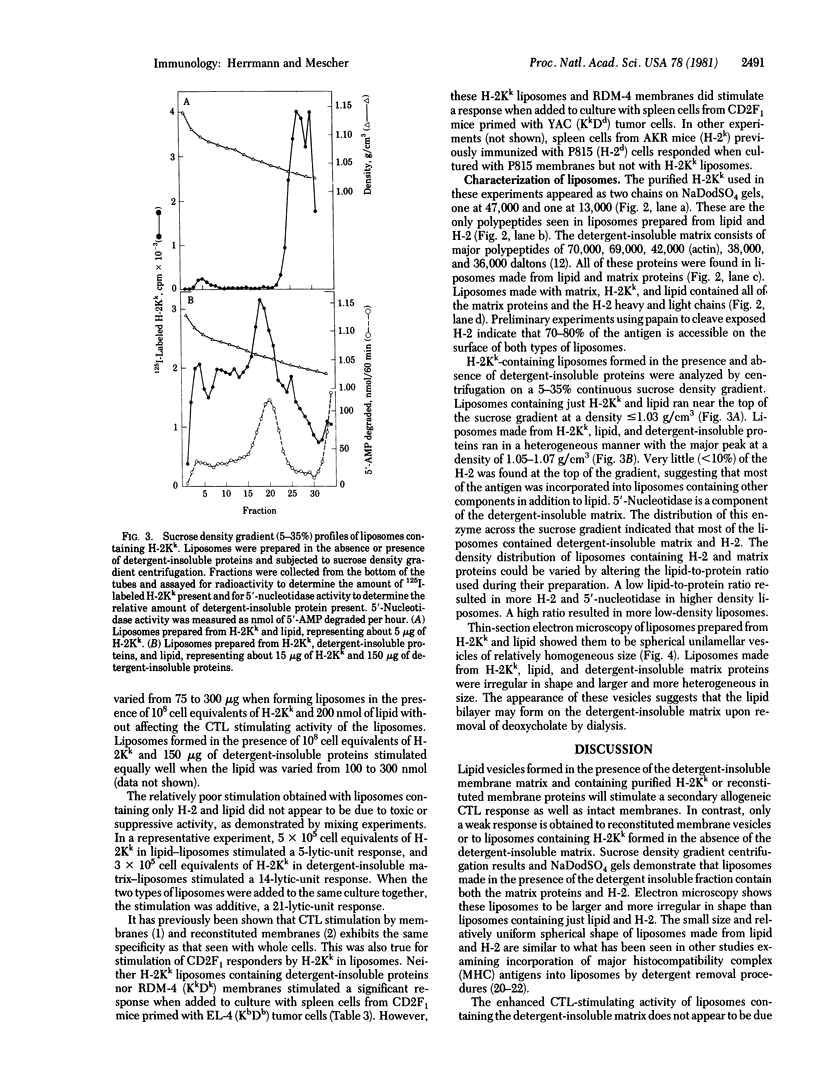
Purified H-2Kk incorporated into lipid vesicles induced a secondary allogeneic cytolytic T lymphocyte response. However, the level of the response was much less than that generated by using purified plasma membranes containing an equivalent amount of antigen. Similarly, reconstituted membranes stimulated less effectively than did intact plasma membranes. In both cases the stimulating activity of the antigen was increased by including a detergent-insoluble membrane matrix fraction during formation of the liposomes or reconstructed vesicles. Liposomes formed in the presence of the matrix were larger, were more irregular in shape, and had a higher density than those formed in its absence. Both the H-2 antigen and matrix proteins were incorporated into the same vesicles. The greater antigenicity of H-2 in vesicles containing the matrix protein might be due to either the larger size of the liposomes or interaction of the antigen with a component(s) of the matrix.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alaba O., Law L. W. Secondary induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes with solubilized syngeneic tumor cell plasma membranes. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1435–1439. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alaba O., Law L. W. Specific induction of syngeneic cytotoxic T lymphocytes by solubilized tumor antigen: fractionation of the specific R-MuLV-induced leukemia antigen. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):414–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burakoff S. J., Germain R. N., Dorf M. E., Benacerrah B. Inhibition of cell-mediated cytolysis of trinitrophenyl-derivatized target cells by alloantisera directed to the products of the K and D loci of the H-2 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):625–629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Lowry O. H. Measurement of nanogram quantities of protein by hydrolysis followed by reaction with orthophthalaldehyde or determination of glutamate. Anal Biochem. 1976 Dec;76(2):502–523. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciavarra R. P., Kang C. Y., Forman J. Vesicular stomatitis antigens recognized by cytotoxic cells: analysis with defective interfering particles and reconstituted membrane vesicles. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):336–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curman B., Klareskog L., Peterson P. A. On the mode of incorporation of human transplantation antigens into lipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7820–7826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard V. H., Guild B. C., Helenius A., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Reconstitution of purified detergent-soluble HLA-A and HLA-B antigens into phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3230–3234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard V. H., Strominger J. L., Mescher M., Burakoff S. Induction of secondary cytotoxic T lymphocytes by purified HLA-A and HLA-B antigens reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5688–5691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast L. D., Fan D. P. Dissociated and reconstituted subcellular alloantigen capable of stimulating mouse cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1092–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg R., Mescher M., Burakoff S. J. The induction of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes with solubilized viral and membrane proteins. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1620–1627. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale A. H., Lyles D. S., Fan D. P. Elicitation of anti-Sendai virus cytotoxic T lymphocytes by viral and H-2 antigens incorporated into the same lipid bilayer by membrane fusion and by reconstitution into liposomes. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):724–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann S. H., Mescher M. F. Purification of the H-2Kk molecule of the murine major histocompatibility complex. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8713–8716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander N., Mehdi S. Q., Weissman I. L., McConnell H. M., Kriss J. P. Allogeneic cytolysis of reconstituted membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4042–4045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. L., Smith M. J. An association between actin and the major histocompatibility antigen H-2. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):274–278. doi: 10.1038/273274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemonnier F., Mescher T. M., sherman L., Burakoff S. The induction of cytolytic T lymphocytes with purified plasma membranes. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1114–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R., Cullen S. E., Schwartz B. D. Insertion of Ia and H-2 alloantigens into model membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):902–906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh D., Ross A. H., Hale A. H., Baltimore D., Eisen H. N. Synthetic phospholipid vesicles containing a purified viral antigen and cell membrane proteins stimulate the development of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1067–1074. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mescher M. F., Jose M. J., Balk S. P. Actin-containing matrix associated with the plasma membrane of murine tumour and lymphoid cells. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):139–144. doi: 10.1038/289139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mescher M., Sherman L., Lemonnier F., Burakoff S. The induction of secondary cytolytic T lymphocytes by solubilized membrane proteins. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):946–951. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Burakoff S. J., Mescher M. F. Induction of allogeneic cytolytic T lymphocytes by partially purified membrane glycoproteins. Cell Immunol. 1980 Apr;51(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90244-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. J., Sanderson A. R. The preparation of liposomes bearing human (HLA) transplantation antigens. Biochem J. 1978 May 1;171(2):505–508. doi: 10.1042/bj1710505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger O., Herrmann S. H., Mescher M. F., Benacerraf B., Burakoff S. J. Cellular interactions in the generation of cytolytic T lymphocyte responses: role of Ia-positive splenic adherent cells in presentation in H-2 antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6091–6095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby E. M., Turner M. J., Sanderson A. R. Incorporation of rat histocompatibility (AgB) antigens into liposomes, and their susceptibility to immune lysis. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Sep;8(9):628–634. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]