Abstract
Herniation of bladder in inguinal hernia is rare, with most cases diagnosed intraoperatively. Preoperative diagnosis is even rarer. We report a case of bladder as content of inguinal hernia diagnosed using multidetector computed tomography.
Keywords: Bladder, CT, hernia
INTRODUCTION
Involvement of bladder in inguinal hernia is rare, with reported incidence of about 1 to 4% cases of inguinal hernia.[1] The incidence of bladder hernias increases in men aged 50 to 70 years. Only 10% of hernias involving the bladder are diagnosed preoperatively, rest are diagnosed intraoperatively.
CASE REPORT
A 54-year-old man presented to hospital with 1-month history of right groin pain, intermittent dysuria, and swelling. No gastrointestinal complaints or hematuria was present. Patient gave history of incomplete bladder evacuation, which relieved on manual compression of the hernia. No significant past or family history was present. On examination, right direct inguinal hernia was present, which reduced on manipulation. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a right inguinal hernia with fluid density lesion continuous with right lateral bladder wall [Figure 1a and b]. Herniation of the bladder and continuity of the lesion with bladder wall was better demonstrated on sagittal and coronal reformatted images [Figure 2]. No bowel/omentum was contained in the hernia. Bilateral kidneys were normal. Diagnosis of right inguinal hernia with bladder as content was made.
Figure 1.
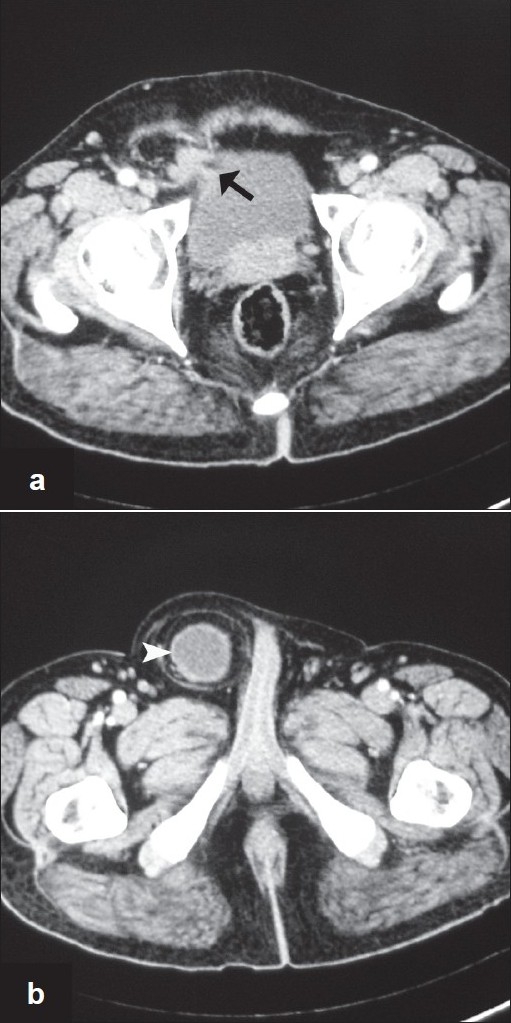
Axial CT scan (a, b) shows lateral deviation of the right lateral wall of the urinary bladder (arrow), which is pointing towards inguinal canal. At a caudal level, fluid intensity mass is seen in the right inguinal canal (arrowhead)
Figure 2.
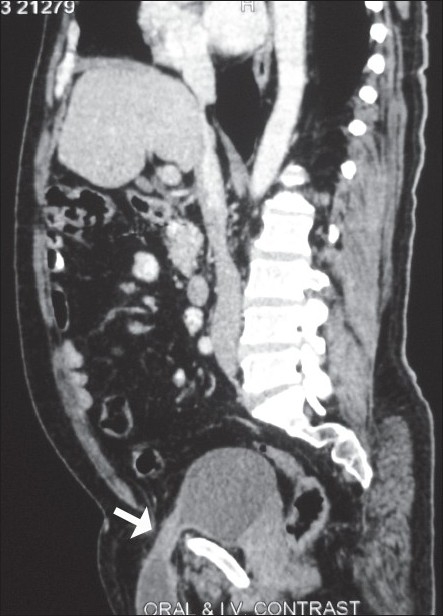
Sagittal reconstructed images better demonstrates the herniation of the bladder into the inguinal canal (arrow)
DISCUSSION
Majority of bladder hernia are asymptomatic, infrequently nonspecific symptoms such as frequency, hematuria, and nocturia can occur. In severe cases, the classic complaint of double voiding (need to compress the scrotum to complete voiding) and decrease in hernia size postvoiding can be present.[2] In suspected cases, imaging helps in confirmation of diagnosis, to look for potential complications (strangulation) and planning surgery. Retrograde and voiding cystourethrogram, USG, multidetector computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging are equally successful in establishing the diagnosis.[3–5] However, CT is the most important diagnostic modality, as it can identify the content of hernia (bowel/omentum) and rule out associated complications like strangulation and hydronephrosis. Imaging is not indicated in all cases of the inguinal hernia, and majority of bladder hernia are diagnosed incidentally during imaging done for other indications. Some authors recommend that if there is a strong clinical suspicion of the bladder hernia, imaging (Cystography/CT) should be performed as preoperative delineation of the anatomy of the sac and its content helps in reducing the risk of serious injury during herniorraphy.[4,6] Surgical repair is the standard treatment for inguinal hernias involving the bladder.[4]
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Madden JL, Hakim S, Agorogiannis AB. The anatomy and repair of inguinal hernias. Surg Clin North Am. 1971;51:1269–92. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)39582-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Catalano O. Computed tomography findings in scrotal cystocele. Eur J Radiol. 1995;21:126–7. doi: 10.1016/0720-048x(95)00715-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shelef I, Farber B, Hertzanu Y. Massive bladder hernia: Ultrasonographic imaging in two cases. Br J Urol. 1998;81:492–3. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.1998.00611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Andac N, Baltacioğlu F, Tüney D, Cimsşit NC, Ekinci G, Biren T. Inguinoscrotal bladder herniation: Is CT a useful tool in diagnosis? Clin Imaging. 2002;26:347–8. doi: 10.1016/s0899-7071(02)00447-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bernaerts A, de Beeck BO, Hoekx L, Parizel PM. Paraperitoneal indirect inguinal bladder hernia: MR demonstration. Abdom Imaging. 2005;30:685–8. doi: 10.1007/s00261-005-0316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Casas JD, Mariscal A, Barluenga E. Scrotal cystocele: US and CT Wndings in two cases. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 1998;22:53–6. doi: 10.1016/s0895-6111(98)00007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


