Abstract
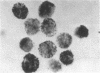
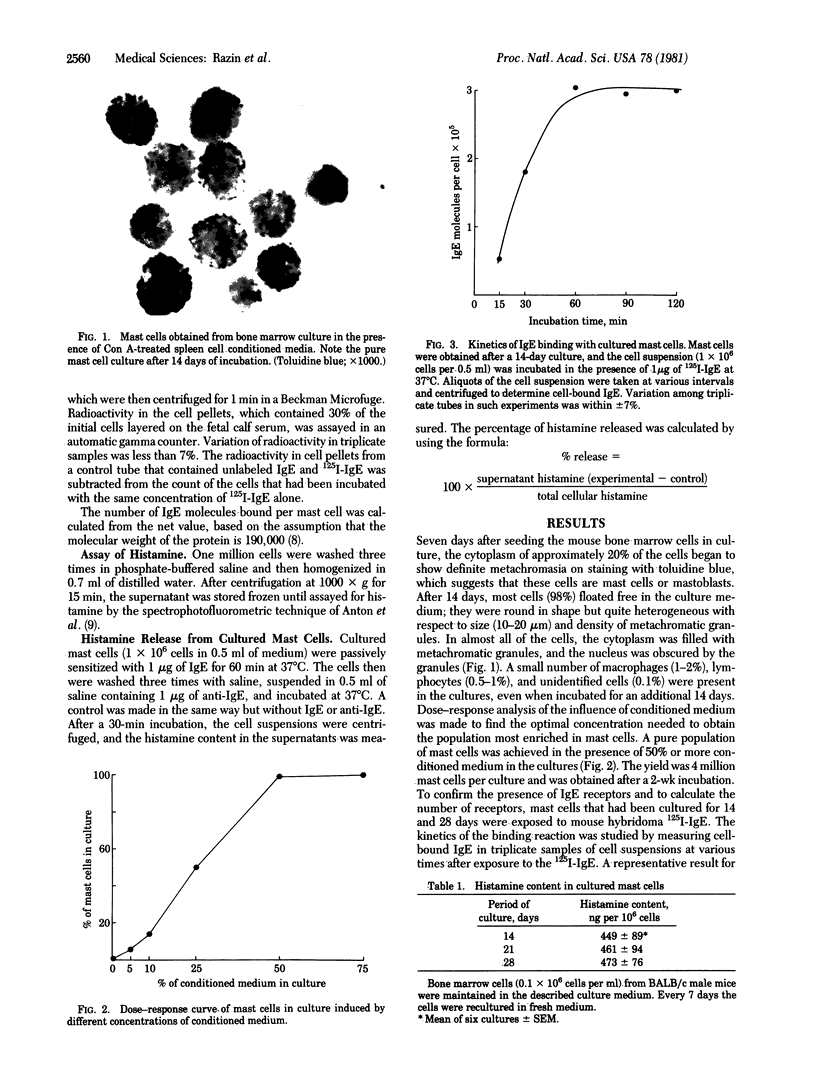
A pure population of mast cells was obtained after 14 days of culturing mouse bone marrow cells in the presence of medium derived from concanavalin A-stimulated mouse spleen cells. The cells were characterized as mast cells by their morphologic appearance and histologic staining, by their histamine content (450 ng per 10(6) cells) and by the demonstration of IgE receptors on their surface (150,000--440,000 receptor sites per cell). The histamine content and the number of IgE receptors remained constant for at least 7 wk of culture. These mast cells could be passively sensitized to mice hybridoma IgE. They then released 43% of their histamine content upon incubation with anti-mouse hybridoma IgE.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton A. H., Sayre D. F. A modified fluorometric procedure for tissue histamine and its distribution in various animals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Apr;166(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., Beckers A., Querinjean P. Three classes and four (sub)classes of rat immunoglobulins: IgM, IgA, IgE and IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG2c. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jan;4(1):44–48. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnet F. M. The probable relationship of some or all mast cells to the T-cell system. Cell Immunol. 1977 May;30(2):358–360. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad D. H., Bazin H., Sehon A. H., Froese A. Binding parameters of the interaction between rat IgE and rat mast cell receptors. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1688–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG H., SACHS L. FORMATION OF PURE SUSPENSIONS OF MAST CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE BY DIFFERENTIATION OF LYMPHOID CELLS FROM THE MOUSE THYMUS. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1963 Jul;31:1–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Lagunoff D. The in vitro differentiation of mast cells. Cultures of cells from immunized mouse lymph nodes and thoracic duct lymph on fibroblast monolayers. J Cell Biol. 1967 Dec;35(3):685–697. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Nir I., Hammel I., Eren R., Weissman B. A., Naot Y. Differentiation and activity of mast cells following immunization in cultures of lymph-node cells. Immunology. 1978 Sep;35(3):485–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Adachi T., Chang T-H, Ishizaka K. Development of mast cells in vitro. II. Biologic function of cultured mast cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Okudaira H., Mauser L. E., Ishizaka K. Development of rat mast cells in vitro. I. Differentiation of mast cells from thymus cells. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):747–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Go S. Decreased production of mast cells in S1/S1d anemic mice. Blood. 1979 Mar;53(3):492–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Hatanaka K., Murakami M., Shibata H. Presence of mast cell precursors in peripheral blood of mice demonstrated by parabiosis. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1085–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Shimada M., Go S., Matsuda H., Hatanaka K., Seki M. Distribution of mast-cell precursors in hematopoeitic and lymphopoietic tissues of mice. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):482–490. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Shimada M., Go S. Presence of mast cell precursors in fetal liver of mice. Dev Biol. 1979 Jun;70(2):510–514. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Shimada M., Hatanaka K., Miyano Y. Development of mast cells from grafted bone marrow cells in irradiated mice. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):442–443. doi: 10.1038/268442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki A., Jr, Metzger H. The interaction of IgE with rat basophilic leukemia cells. II. Quantitative aspects of the binding reaction. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1676–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian P. A., Siraganian R. P. Basophil activation by concanavalin A: characteristics of the reaction. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2117–2125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]