Abstract
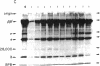
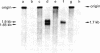
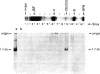
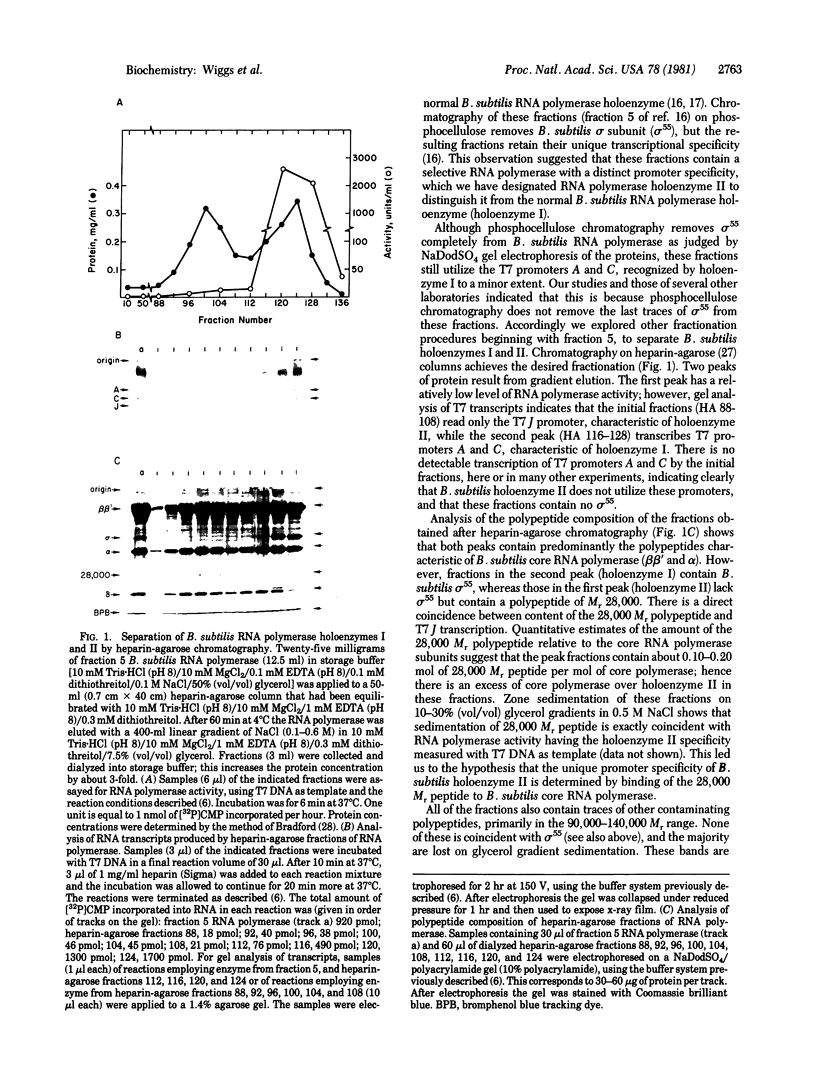
Preparations of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase (nucleosidetriphosphate:RNA nucleotidyltransferase, EC 2.7.7.6) from vegetatively growing cells contain small amounts of an activity (B. subtilis RNA polymerase holoenzyme II) that shows a unique promoter specificity with T7 bacteriophage DNA as compared with the normal B. subtilis holoenzyme (holoenzyme I) and lacks the normal sigma subunit [Jaehning, J. A., Wiggs, J. L. & Chamberlin, M. J. (1979) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 5470-5474]. By heparin-agarose chromatography we have obtained holoenzyme II fractions that have no detectable holoenzyme I activity as judged by their failure to utilize promoter sites for holoenzyme I on any template we have tested. These fractions are far more active with B. subtilis DNA than with T7 DNA or other heterologous templates. This high degree of specificity has allowed identification of plasmids containing cloned fragments of B. subtilis DNA that bear strong promoter sites for holoenzyme II. These promoter sites are not used at all by B. subtilis RNA polymerase holoenzyme I. The specificity of holoenzyme II is dictated by a peptide of Mr 28,000 as judged by copurification of the peptide with specific holoenzyme II activity and by reconstitution of the holoenzyme II promoter specificity when the isolated peptide is added to B. subtilis core polymerase. Hence the 28,000 Mr peptide appears to be a sigma factor that determines a promoter specificity distinct from that of RNA polymerase holoenzyme I and all other known bacterial RNA polymerases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W. M. Plasmid detection and sizing in single colony lysates. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):393–394. doi: 10.1126/science.318764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G. Isolation of bacterial and phage proteins by homopolymer RNA-cellulose chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J., Nierman W. C., Wiggs J., Neff N. A quantitative assay for bacterial RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10061–10069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. The selectivity of transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):721–775. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Leighton T., Rabinowitz J. C. Purification of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase with heparin-agarose. In vitro transcription of phi 29 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9220–9226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Specificity of promoter site utilization in vitro by bacterial RNA polymerases on Bacillus phage phi 29 DNA. Transcription mapping with exonuclease III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8819–8830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H. Role of ribonucleic acid polymerase in gene selection in procaryotes. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):568–594. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.568-594.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Geiduschek E. P. RNA polymerase from phage SP01-infected and uninfected Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4530–4541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Petrusek R. L., Geiduschek E. P. Conversion of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase activity in vitro by a protein induced by phage SP01. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2366–2370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich S. D. DNA cloning in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1433–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda R., Doi R. H. Two polypeptides associated with the ribonucleic acid polymerase core of Bacillus subtilis during sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):422–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.422-432.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Linn T. G., Losick R. Isolation of a new RNA polymerase-binding protein from sporulating Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):490–494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Lang N., Losick R. A sporulation-induced sigma-like regulatory protein from B. subtilis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. A modified RNA polymerase transcribes a cloned gene under sporulation control in Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):256–260. doi: 10.1038/282256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. Novel RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7000–7004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillel Z., Wu C. W. Photochemical cross-linking studies on the interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with T7 DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):2954–2961. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Whiteley H. R. A new polypeptide associated with RNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis during late stages of vegetative growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):462–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaehning J. A., Wiggs J. L., Chamberlin M. J. Altered promoter selection by a novel form of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klier A. F., Lecadet M. M., Dedonder R. Sequential modifications of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase during sporogenesis in Bacillus thuringiensis. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):317–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T., Greenleaf A. L., Losick R. RNA polymerase from sporulating Bacillus subtilis. Purification and properties of a modified form of the enzyme containing two sporulation polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9256–9261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Shorenstein R. G., Sonenshein A. L. Structural alteration of RNA polymerase during sporulation. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):910–913. doi: 10.1038/227910a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Chamberlin M. J. Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in vitro is affected by ribonucleoside triphosphate base analogs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2455–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Chamberlin M. J. Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase in vitro. Effect of altered reaction conditions and mutations in the enzyme protein on termination with T7 and T3 deoxyribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):3005–3015. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. B. The molecular topography of RNA polymerase-promoter interaction. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington C., Pero J. Distinctive nucleotide sequences of promoters recognized by RNA polymerase containing a phage-coded "sigma-like" protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5465–5469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talkington C., Pero J. Promoter recognition by phage SP01-modified RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1185–1189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Losick R., Pero J., Hinnebush A. Purification and comparative properties of the delta and sigma subunits of RNA polymerase from Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 15;74(1):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A., Buckland R. Heterogeneity of E. coli RNA polymerase. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 27;243(130):257–260. doi: 10.1038/newbio243257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. RNA polymerase specificity and the control of growth. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):641–646. doi: 10.1038/263641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley H. R., Hemphill H. E. The interchangeability of stimulatory factors isolated from three microbial RNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 9;41(3):647–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggs J. L., Bush J. W., Chamberlin M. J. Utilization of promoter and terminator sites on bacteriophage T7 DNA by RNA polymerases from a variety of bacterial orders. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson V. M., Doi R. H. Delta factor can displace sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase holoenzyme and regulate its initiation activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 May 3;161(2):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00274183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]