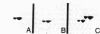Abstract
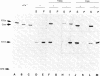
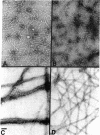
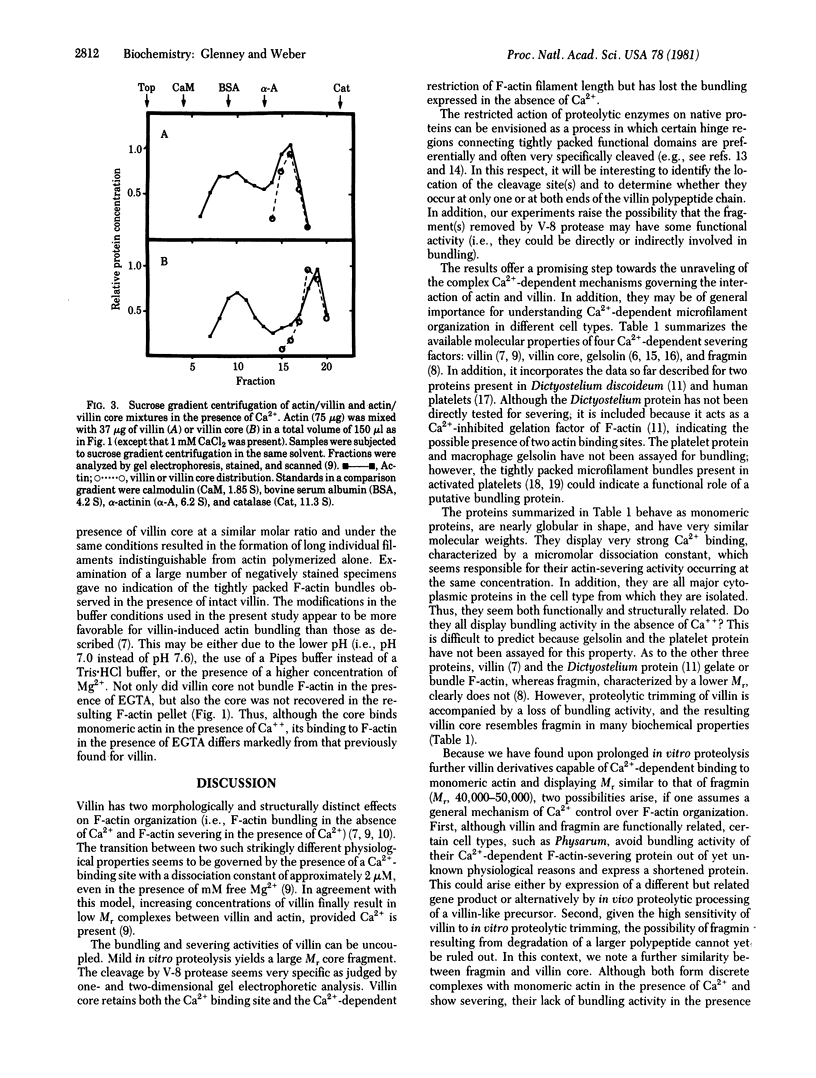
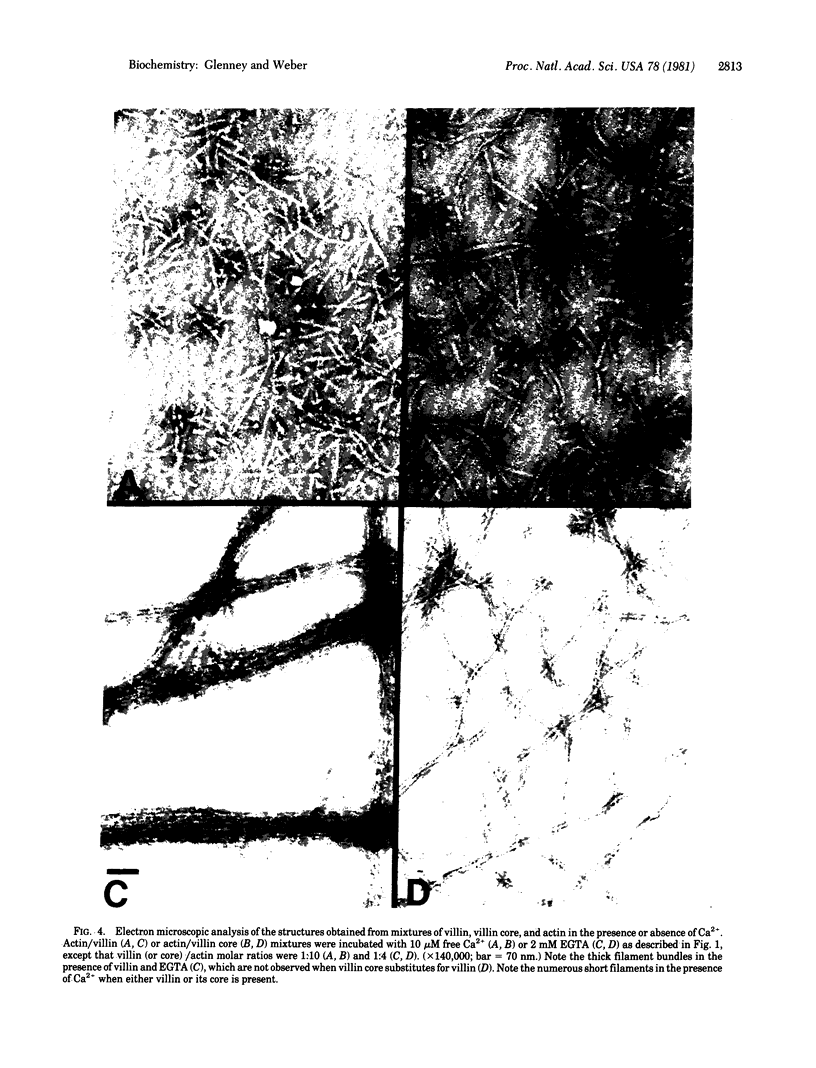
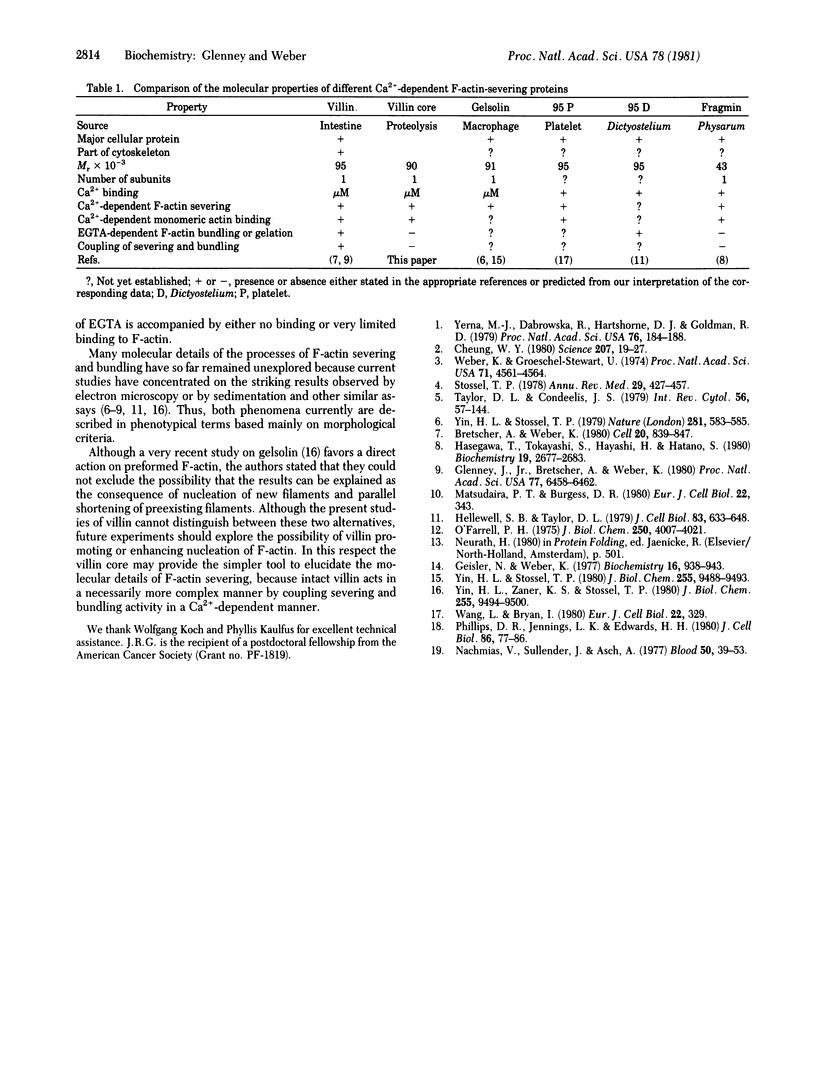
Villin is a major F-actin-bundling protein present in the microfilament bundle underlying the plasma membrane of the microvilli present on intestinal epithelial cells. Mild in vitro proteolysis converts villin (Mr, 95,000) into a large fragment, the villin core (apparent Mr, 90,000). Villin core has lost the F-actin-bundling activity expressed by villin in the absence of calcium but retains the micromolar Kd calcium-binding site and the calcium-dependent restriction of actin filament length (F-actin severing) of intact villin. This finding suggests a common structural and functional relatedness between the known calcium-dependent F-actin-severing proteins from different cell types, even though not all of them reveal F-actin-bundling activity.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Isolation of amino-terminal fragment of lactose repressor necessary for DNA binding. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):938–943. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Bretscher A., Weber K. Calcium control of the intestinal microvillus cytoskeleton: its implications for the regulation of microfilament organizations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6458–6462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa T., Takahashi S., Hayashi H., Hatano S. Fragmin: a calcium ion sensitive regulatory factor on the formation of actin filaments. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2677–2683. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellewell S. B., Taylor D. L. The contractile basis of ameboid movement. VI. The solation-contraction coupling hypothesis. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):633–648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V., Sullender J., Asch A. Shape and cytoplasmic filaments in control and lidocaine-treated human platelets. Blood. 1977 Jul;50(1):39–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K., Edwards H. H. Identification of membrane proteins mediating the interaction of human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):77–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Contractile proteins in cell structure and function. Annu Rev Med. 1978;29:427–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.29.020178.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. L., Condeelis J. S. Cytoplasmic structure and contractility in amoeboid cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;56:57–144. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61821-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Groeschel-Stewart U. Antibody to myosin: the specific visualization of myosin-containing filaments in nonmuscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4561–4564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yerna M. J., Dabrowska R., Hartshorne D. J., Goldman R. D. Calcium-sensitive regulation of actin-myosin interactions in baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):184–188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium-dependent regulatory protein. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):583–586. doi: 10.1038/281583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Purification and structural properties of gelsolin, a Ca2+-activated regulatory protein of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9490–9493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Zaner K. S., Stossel T. P. Ca2+ control of actin gelation. Interaction of gelsolin with actin filaments and regulation of actin gelation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9494–9500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]