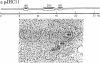
Abstract
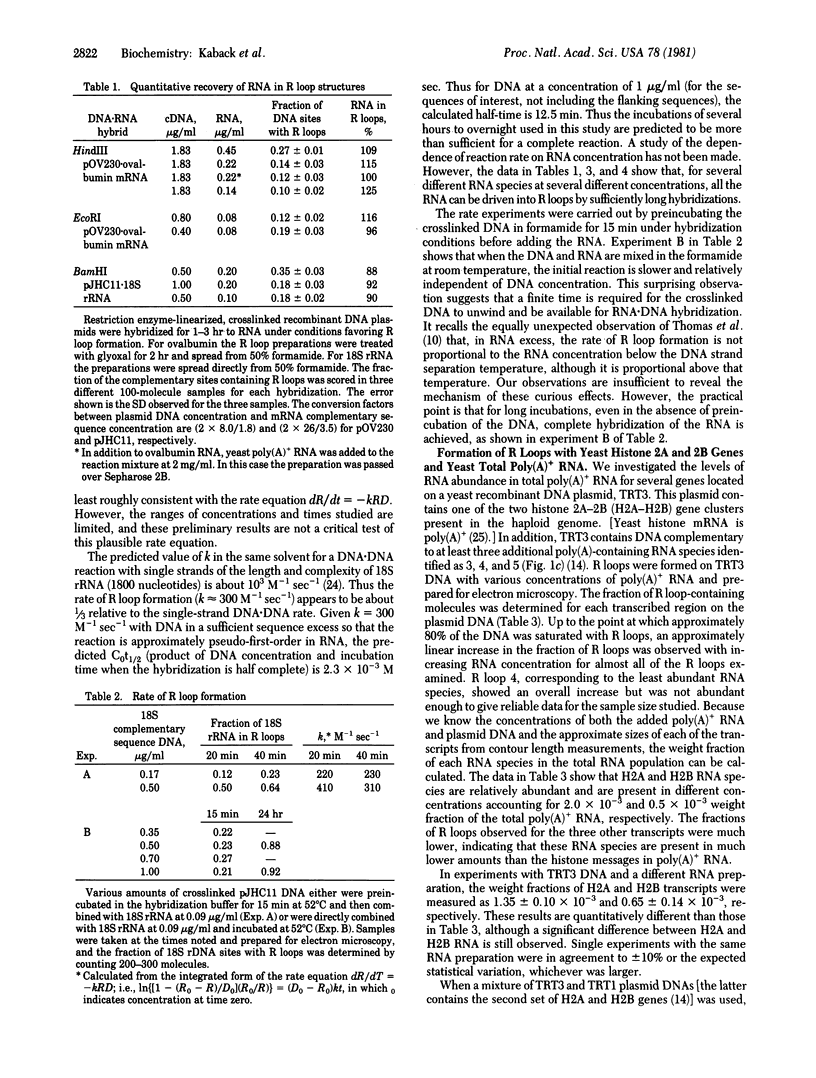
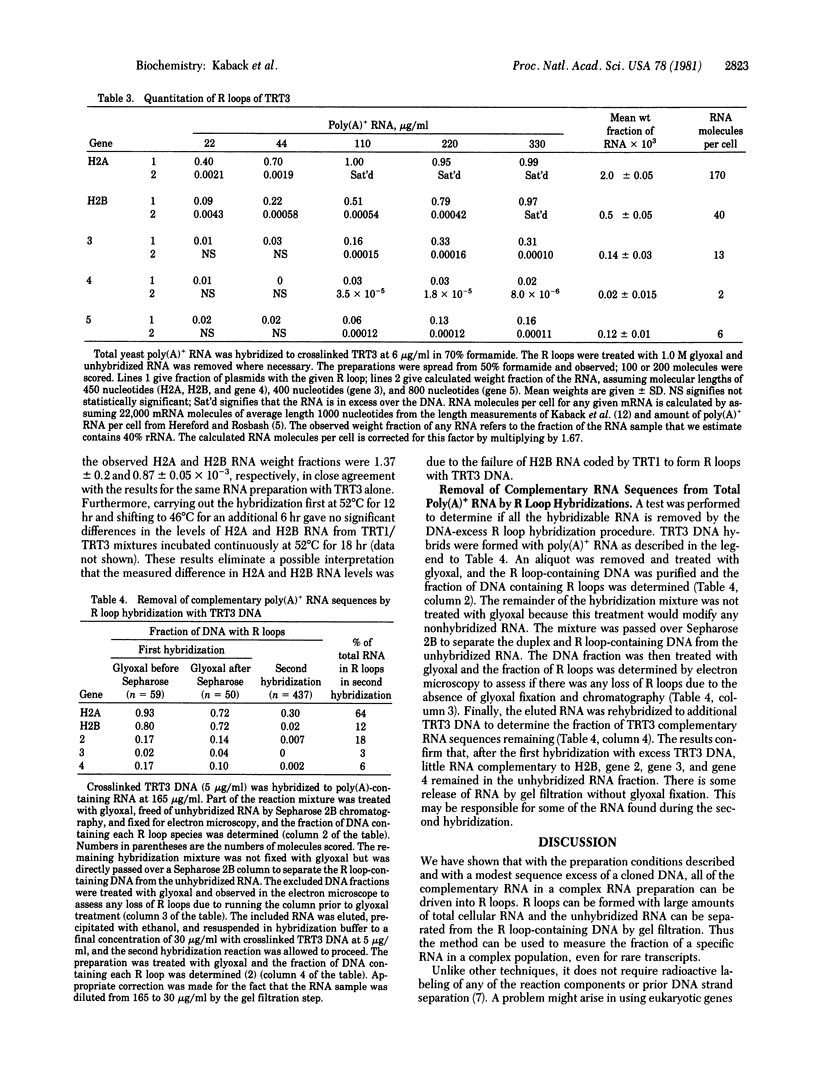
R loop hybridizations and electron microscopy have been used to determine cellular RNA concentrations for cloned genes. In plasmid DNA sequence excess, all the complementary RNA is driven into R loop structures that can be assayed by electron microscopy. To determine the concentration of a particular poly(A)+ RNA, plasmid DNA crosslinked once every 2000-5000 base pairs with trioxsalen and UV light is hybridized in DNA sequence excess to various known amounts of total poly(A)+ RNA, and the R loops are stabilized by treatment with glyoxal. If necessary, excess nonhybridized RNA is removed by Sepharose 2B chromatography, which enables the visualization of less abundant transcripts. Reconstruction experiments demonstrated that electron microscopic determination of the fraction of plasmid DNA molecules containing specific RNA loops gives accurate values of specific RNA weight fractions or concentrations in the total poly(A)+ RNA populations. These methods were also used to determine the concentrations of five RNA species complementary to sequences on TRT3, a recombinant DNA plasmid containing yeast histone 2A and 2B genes and three other nonhistone genes. The methods described allow one to visualize the R loop structures for both abundant and nonabundant transcripts and to estimate concentrations of these RNA species simply by determining the fraction of DNA containing R loops.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R., Feigelson P., Schutz G. Analysis of the complexity and diversity of mRNA from chicken liver and oviduct. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Morton J. G., Rosbash M., Richardson M. Three abundance classes in HeLa cell messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):199–204. doi: 10.1038/250199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J., Davidson N. Rates of formation and thermal stabilities of RNA:DNA and DNA:DNA duplexes at high concentrations of formamide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1539–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Gelinas R. E., Broker T. R., Roberts R. J. An amazing sequence arrangement at the 5' ends of adenovirus 2 messenger RNA. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer J. H., Farrelly F. W., Barnitz J. T., Rownd R. H. Construction and restriction endonuclease mapping of hybrid plasmids containing Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 16;151(3):229–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00268786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P. W., Davis M. M., Kaback D. B., Davidson N., Hood L. Immunoglobulin heavy chain gene organization in mice: analysis of a myeloma genomic clone containing variable and alpha constant regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):857–861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrner K., Yarger J., Hereford L. Yeast histone mRNA is polyadenylated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5725–5737. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Klein W. H., Davis M. M., Wold B. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Structural gene sets active in embryos and adult tissues of the sea urchin. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover D. M., Hogness D. S. A novel arrangement of the 18S and 28S sequences in a repeating unit of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn W. E., Van Ness J., Maxwell I. H. Complex population of mRNA sequences in large polyadenylylated nuclear RNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5544–5547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Rosbash M. Number and distribution of polyadenylated RNA sequences in yeast. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Fahrner K., Woolford J., Jr, Rosbash M., Kaback D. B. Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback D. B., Angerer L. M., Davidson N. Improved methods for the formation and stabilization of R-loops. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2499–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Lev Z., Xin J. H., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Messenger RNA prevalence in sea urchin embryos measured with cloned cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5317–5321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L., Nozick N. D., Tobin A. J. Few transcribed RNAs are translated in avian erythroid cells. Dev Biol. 1978 Nov;67(1):23–39. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev Z., Thomas T. L., Lee A. S., Angerer R. C., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Developmental expression of two cloned sequences coding for rare sea urchin embryo messages. Dev Biol. 1980 May;76(2):322–340. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90382-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P., Rosenthal N., Efstratidadis A., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Tizard R. The structure and evolution of the two nonallelic rat preproinsulin genes. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Wintersberger E. Synthesis of yeast histones in the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1863–1867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Coulson A. R., Fiddes C. A., Hutchison C. A., Slocombe P. M., Smith M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):687–695. doi: 10.1038/265687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., White R. L., Davis R. W. Hybridization of RNA to double-stranded DNA: formation of R-loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink P. C., Finnegan D. J., Donelson J. E., Hogness D. S. A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford J. L., Jr, Hereford L. M., Rosbash M. Isolation of cloned DNA sequences containing ribosomal protein genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1247–1259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford J. L., Jr, Rosbash M. The use of R-looping for structural gene identification and mRNA purification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2483–2497. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]