Abstract
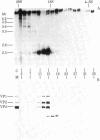
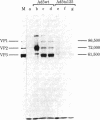
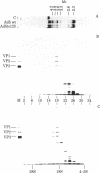
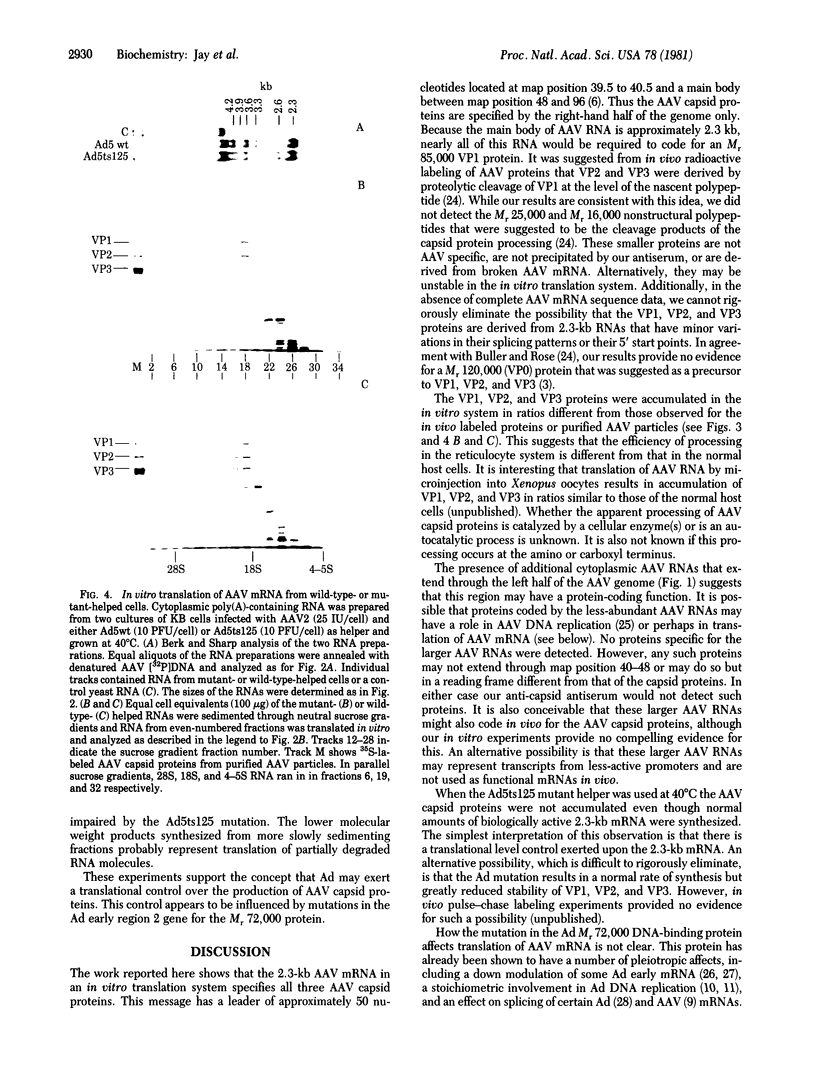
Growth of adeno-associated virus (AAV) requires expression of certain adenovirus (Ad) genes in the same cell. AAV particles contain three proteins, VP1 (Mr 85,700), VP2 (Mr 72,000), and VP3 (Mr 61,500). These proteins have overlapping peptide maps. We recently reported that AAV RNAs make up a 3'-coterminal family of overlapping molecules. We report here that the most abundant AAV mRNA, a 2.3-kilobase spliced RNA, codes for all three proteins--VP1, VP2, and VP3--when translated in an in vitro reticulocyte lysate. This shows that the AAV capsid proteins are coded by the genome sequence between map positions 48.0 and 96.0 (1 map unit is 1% of the genome or 47 base pairs). When AAV was grown in human KB cells with the Ad temperature-sensitive mutant Ad5ts125 at the nonpermissive temperature (40 degrees C), the accumulation in vivo of AAV capsid proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3 was decreased to less than 1/50th. However, normal amounts of the 2.3-kilobase mRNA were accumulated, and this RNA could be efficiently translated in an in vitro reticulocyte lysate system to yield VP1, VP2, and VP3. These experiments suggest that in infected cells control is exerted upon the AAV 2.3-kilobase mRNA at the translational level and that this control can be influenced by mutations in Ad. These Ad mutations map in the region 2 early gene for the Ad DNA-binding protein. The temperature-sensitive system that we have studied may be useful for analysis of translational control of a eukaryotic mRNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Rose J. A. Characterization of adenovirus-associated virus-induced polypeptides in KB cells. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):331–338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.331-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Straus S. E., Rose J. A. Mechanism of host restriction of adenovirus-associated virus replication in African green monkey kidney cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):663–672. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. H., Blanton R. A. Possible role of the 72,000 dalton DNA-binding protein in regulation of adenovirus type 5 early gene expression. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):664–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.664-674.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinger M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Selection and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of type 5 adenovirus. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):328–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.328-339.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron L. Post-transcriptional restriction of human adenovirus expression in monkey cells. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1256–1261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1256-1261.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber M. S., Baum S. G. Transcription of adenovirus RNA in permissive and nonpermissive infections. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):136–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.136-148.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Straus S. E., Roeder R. G. Transcripts of the adenovirus-associated virus genome: multiple polyadenylated RNAs including a potential primary transcript. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):560–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.560-565.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay F. T., de la Maza L. M., Carter B. J. Parvovirus RNA transcripts containing sequences not present in mature mRNA: a method for isolation of putative mRNA precursor sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):625–629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Jay F. T., Friedman R. M., Levine A. S. Biosynthesis, immunological specificity, and intracellular distribution of the simian virus 40-specific protein induced by the nondefective hybrid Ad2+ND1. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.411-419.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Jay F. T., Friedman R. M., Levine A. S. Simian virus 40-specific ribosome-binding proteins induced by a nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):692–699. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.692-699.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Blacklow N. R., Hoggan M. D. Immunological reactivity of antisera prepared against the sodium dodecyl sulfate-treated structural polypeptides of adenovirus-associated virus. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):1017–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.1017-1026.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. B., Thomson T. A., Taylor P. A., Vlazny D. A. Molecular similarities among the adenovirus-associated virus polypeptides and evidence for a precursor protein. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Structure-function relationships of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11051–11060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Anderson C. W. Block to multiplication of adenovirus serotype 2 in monkey cells. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1650–1668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1650-1668.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Chow L. T. Incomplete splicing and deficient accumulation of the fiber messenger RNA in monkey cells infected by human adenovirus type 2. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 15;139(2):221–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Grodzicker T. Mutations that allow human Ad2 and Ad5 to express late genes in monkey cells map in the viral gene encoding the 72K DNA binding protein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F. Isolation of a variant of human adenovirus serotype 2 that multiplies efficiently on monkey cells. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1243–1246. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1243-1246.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin C. A., Myers M. W., Risin D. L., Carter B. J. Defective-interfering particles of the human parvovirus adeno-associated virus. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):162–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin C. A., Westphal H., Carter B. J. Spliced adenovirus-associated virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5567–5571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubeck M. D., Lee H. M., Hoggan M. D., Johnson F. B. Adenovirus-associated virus structural protein sequence homology. J Gen Virol. 1979 Oct;45(1):209–216. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-1-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. W., Laughlin C. A., Jay F. T., Carter B. J. Adenovirus helper function for growth of adeno-associated virus: effect of temperature-sensitive mutations in adenovirus early gene region 2. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):65–75. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.65-75.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Winkler J. J. Regulation of early adenovirus transcription: a protein product of early region 2 specifically represses region 4 transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1893–1897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Gold L. M., Huang W. M. The identification of prereplicative bacteriophage T4 proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5499–5501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L. Adenovirus proteins and their messenger RNAs. Adv Virus Res. 1979;25:357–405. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60573-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABSON A. S., O'CONOR G. T., BEREZESKY I. K., PAUL F. J. ENHANCEMENT OF ADENOVIRUS GROWTH IN AFRICAN GREEN MONKEY KIDNEY CELL CULTURES BY SV40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 May;116:187–190. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Carter B. J., Westphal H. Vero cells injected with adenovirus type 2 mRNA produce authentic viral polypeptide patterns: early mRNA promotes growth of adenovirus-associated virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Inman J. K., Shatkin A. J. Structural proteins of adenovirus-associated viruses. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):766–770. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.766-770.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter N. M., Davies W., Anderson C. W. Adenovirus coded deoxyribonucleic acid binding protein. Isolation, physical properties, and effects of proteolytic digestion. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2802–2810. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Vliet P. C., Levine A. J., Ensinger M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Thermolabile DNA binding proteins from cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of adenovrius defective in viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):348–354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.348-354.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]