Abstract
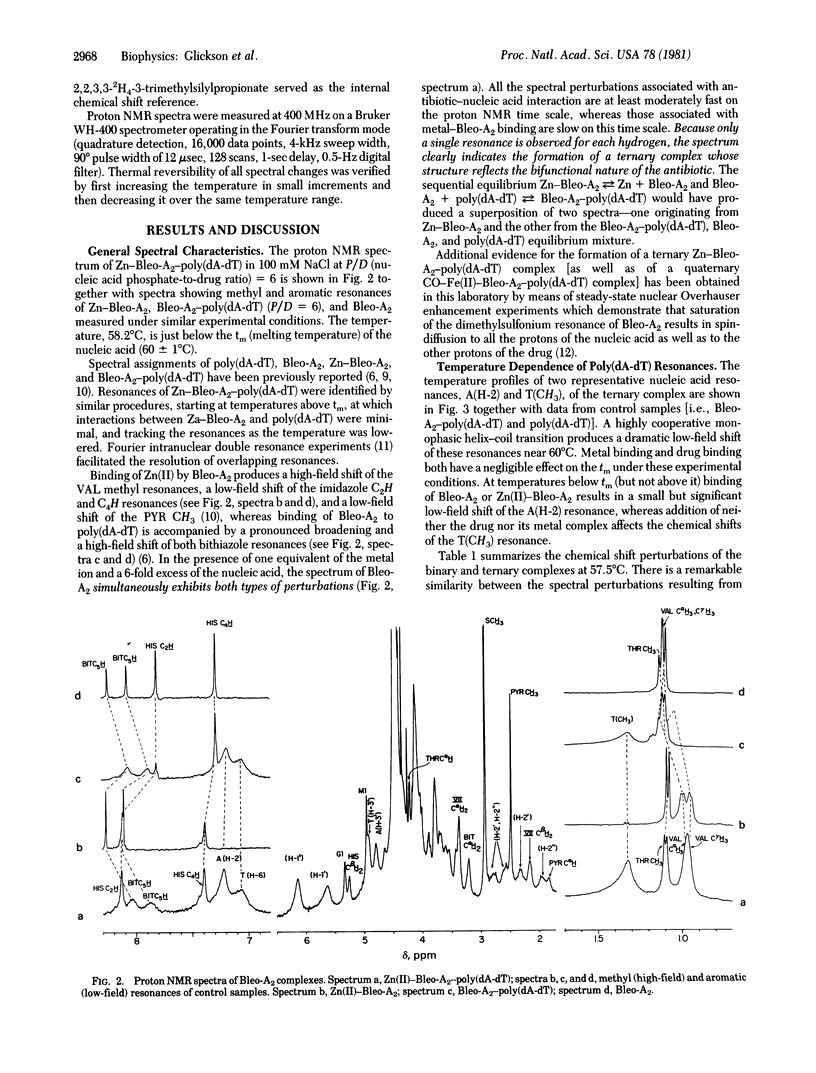
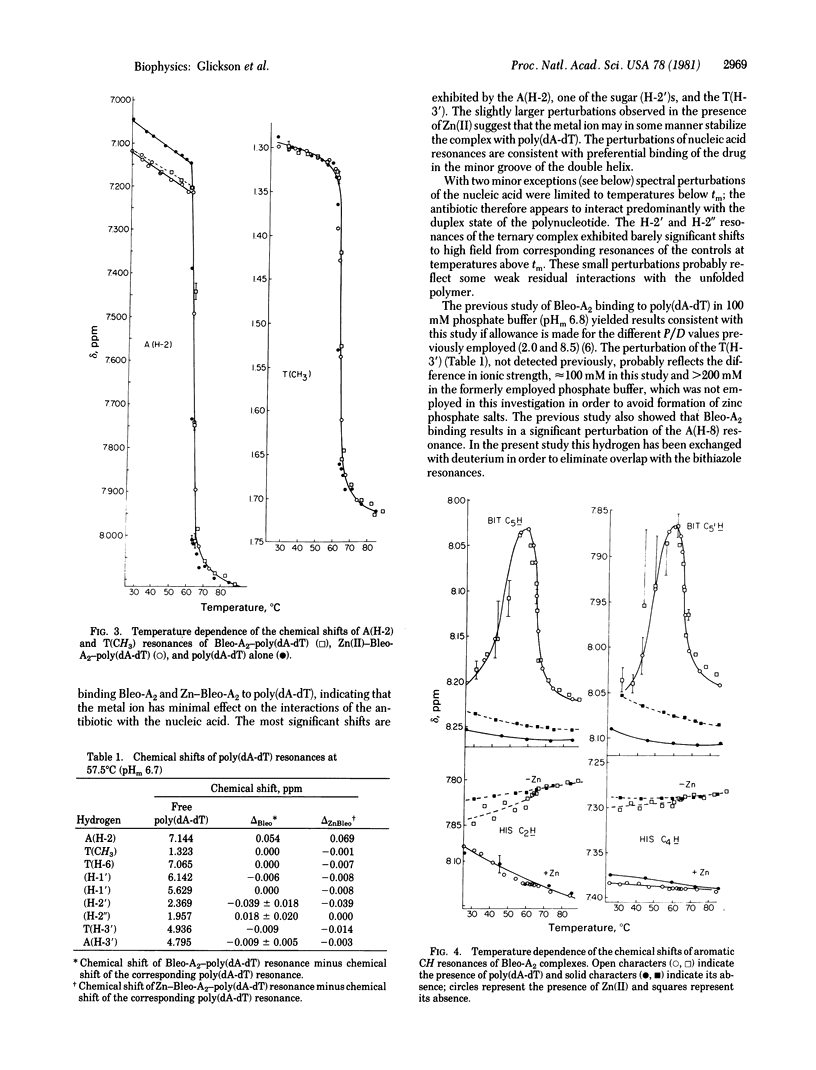
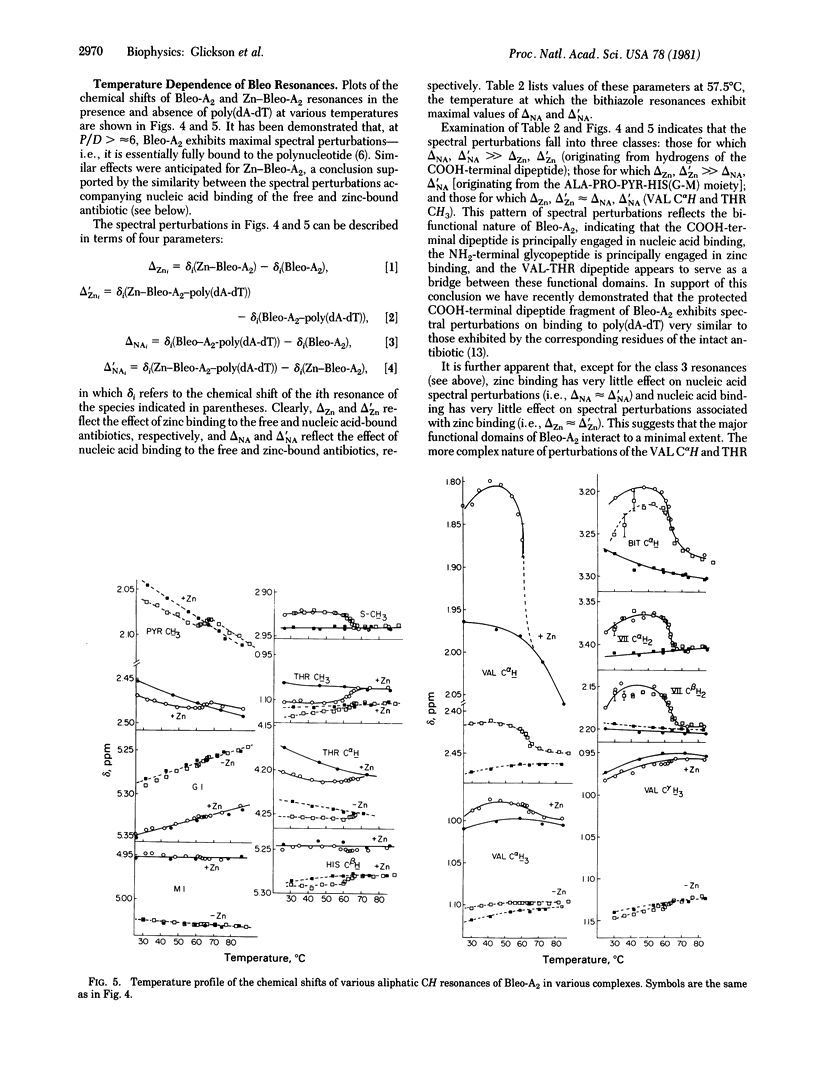
Proton NMR spectra demonstrate the formation of a ternary complex, Zn(II)--bleomycin-A2--poly(dA-dT), which serves as an analog of the putative active complex, Fe(II)--bleomycin-A2--DNA. Specific sites of metal--drug and drug--nucleic acid interaction have been delineated on the basis of chemical shift perturbations. On the basis of this criterion there appear to be three distinct regions of the drug: (i) the NH2 terminus up to and including the disaccharide and hydroxyhistidine residues, whose resonances are perturbed only by metal interactions; (ii) the COOH-terminal dipeptide, whose resonances are displaced only by nucleic acid interactions; and (iii) the methylvaleric acid-threonine dipeptide, which links these domains and whose resonances are sensitive to both types of interactions. The spectral perturbations in the first and second domains are very similar to changes observed in the corresponding binary complexes--i.e., Zn(II)--bleomycin-A2 and bleomycin-A2--poly(dA-dT), respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen D. M., Hawkins B. L., Glickson J. D. Proton nuclear magnetic resonances study of bleomycin in aqueous solution. Assignment of resonances. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2731–2738. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. M., Sakai T. T., Glickson J. D., Patel D. J. Bleomycin-A2 complexes with poly(dA--dT): a proton nuclear magnetic resonance study of the nonexchangeable hydrogens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91539-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons W. A., Beyer C. F., Dadok J., Sprecher R. F., Wyssbrod H. R. Studies of individual amino acid residues of the decapeptide tyrocidine A by proton double-resonance difference spectroscopy in the correlation mode. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 28;14(2):420–429. doi: 10.1021/bi00673a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. H., Galvan L., Crooke S. T. Interactions of bleomycin analogues with deoxyribonucleic acid and metal ions studied by fluorescence quenching. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1761–1767. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Naganawa H., Takita T., Umezawa H. Chemistry of bleomycin. XXII. Interaction of bleomycin with nucleic acids, preferential binding to guanine base and electrostatic effect of the terminal amine. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Dec;31(12):1316–1320. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer N. J., Rodriguez L. O., Hecht S. M. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance study of the structure of bleomycin and the zinc-bleomycin complex. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3439–3445. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer N. J., Rodriguez L. O., Hecht S. M. Structural studies of of "active complex" of bleomycin: assignment of ligands to the ferrous ion in a ferrous-bleomycin-carbon monoxide complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5616–5620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai R. P., Krishna N. R., Sakai T. T., Glickson J. D. Proton NMR studies of ternary complexes of bleomycin with metal ions and nucleic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 17;97(1):270–278. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai R. P., Lenkinski R. E., Sakai T. T., Geckle J. M., Krishna N. R., Glickson J. D. Proton NMR study of iron(II)-bleomycin: assignment of resonances by saturation transfer experiments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):341–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T. T., Riordan J. M., Booth T. E., Glickson J. D. Synthesis and DNA binding of [3-[2'-(2-acetamidoethyl)-2,4'-bithiazole-4-carboxamido]propyl[dimethylsulfonium chloride, a fragment of bleomycin A2. J Med Chem. 1981 Mar;24(3):279–285. doi: 10.1021/jm00135a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



