Abstract
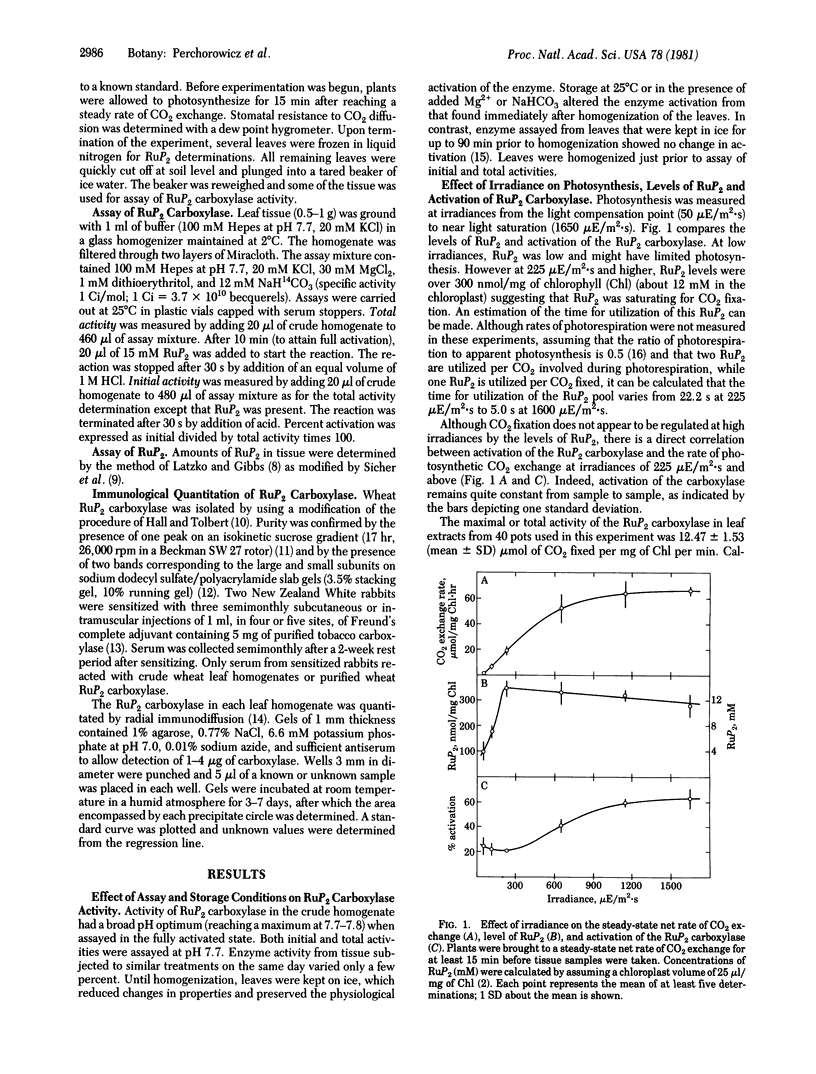
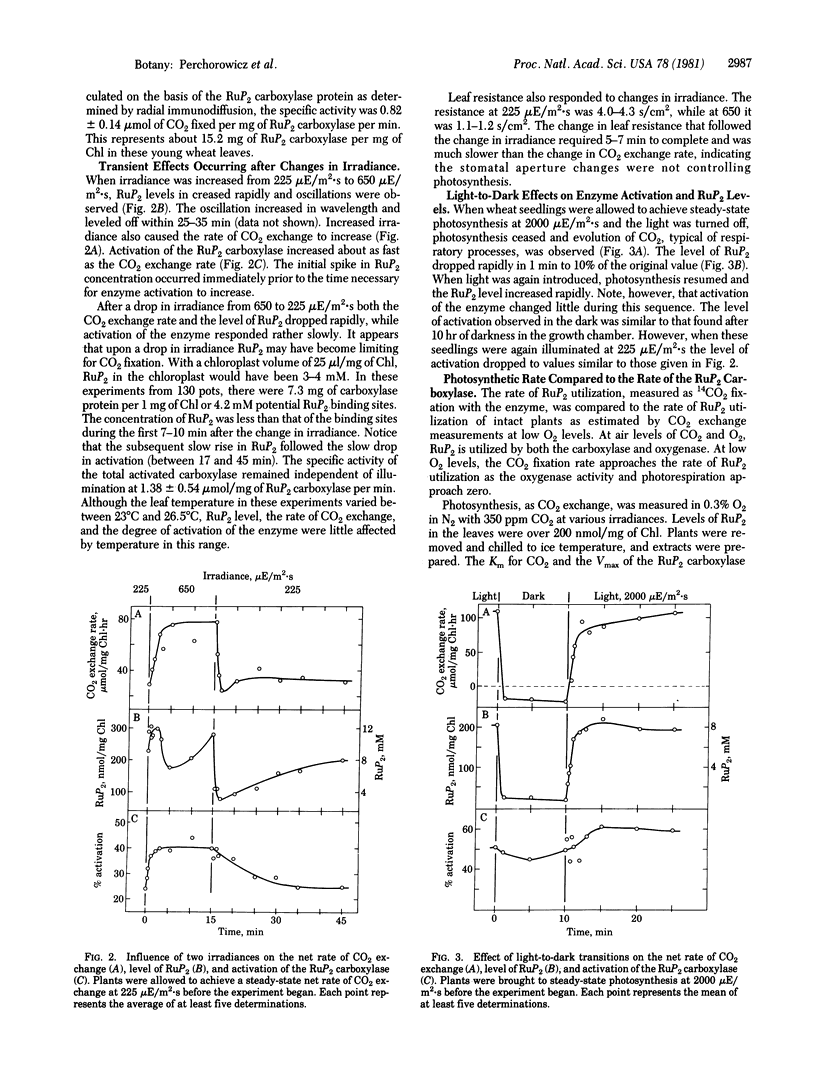
In limiting light the activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuP2) carboxylase [3-phospho-D-glycerate carboxylyase (dimerizing), EC 4.1.1.39] in leaf extracts of 7- to 8-day-old wheat seedlings changed proportionally with the photosynthetic rate of the intact plants. Higher rates of photosynthesis, induced by increasing irradiances, were accompanied by an increase in activation of the leaf RuP2 carboxylase, while RuP2 levels remained unchanged. The degree of activation varied from 20% to 60% of full activation at irradiances of 225-1650 μE/m2·s (photosynthetically active radiation; E = einstein, 1 mol of photons). Between 225 μE/m2·s and darkness, activation approached 50% while RuP2 levels dropped more than 90%. During steady-state photosynthesis, levels of the substrate RuP2 were 250-300 nmol/mg of chlorophyll in the leaves and were similar at all irradiances above 225 μE/m2·s (25% of light saturation). When velocities of the carboxylase in leaf extracts were corrected for CO2 levels estimated to exist within the leaf, they compared favorably with the photosynthetic rates of the intact seedlings. Comparison of CO2 exchange rate, RuP2 level, and activation of the carboxylase indicates that light limitation of photosynthesis can be due to two factors: the availability of RuP2 in dark to dim light and activation of the RuP2 carboxylase in dim light and higher irradiances.
Keywords: CO2 exchange, carbon reduction cycle
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chollet R., Anderson L. L. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase activities by temperature pretreatment and chloroplast metabolites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Sep;176(1):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch A. L., Jensen R. G. Regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from tobacco: changes in pH response and affinity for CO2 and Mg2+ induced by chloroplast intermediates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):587–594. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing W. A., Christeller J. T. A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):563–570. doi: 10.1042/bj1590563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latzko E., Gibbs M. Measurement of the intermediates of the photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle, using enzymatic methods. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:261–268. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):529–536. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty K. S., Stafford D., Brown O. Resolution and fractionation of macromolecules by isokinetic sucrose density gradient sedimentation. Anal Biochem. 1968 Aug;24(2):314–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. P., McNeil P. H., Walker D. A. Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase--lack of dark inactivation of the enzyme in experiments with protoplasts. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 15;97(2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Bahr J. T., Jensen R. G. Measurement of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate from spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):876–879. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Jensen R. G. Photosynthesis and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate levels in intact chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):880–883. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



