Abstract
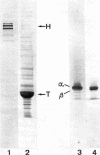
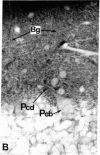
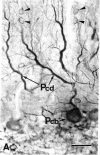
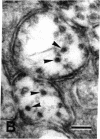
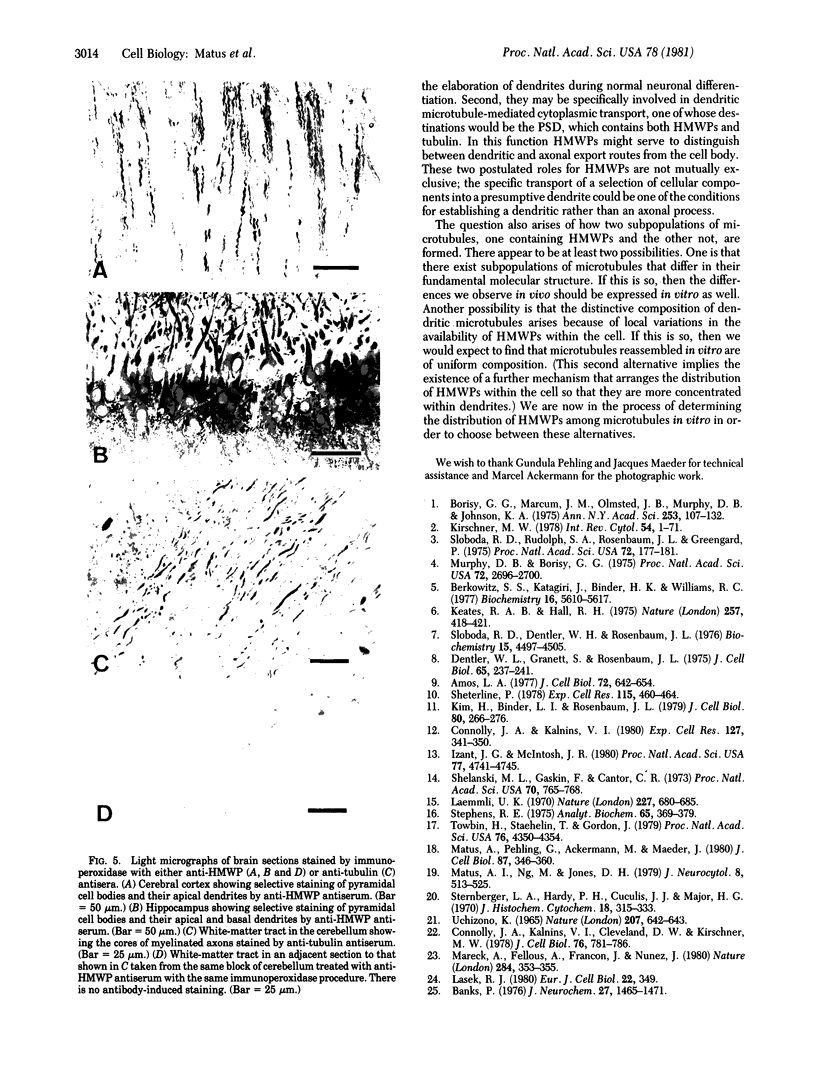
The distributions of tubulin and high molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins (HMWPs) in brain were determined by immunoperoxidase histochemistry with specific antisera. Tubulin was found in microtubules of both neurons and glia and both axons and dendrites. HMWPs were found only in neurons where, in all cases examined, they were associated with dendritic microtubules but not those in axons. Both tubulin and HMWPs were also found in postsynaptic densities. These results indicate that brain microtubules vary in chemical composition. The preferential association of HMWPs with dendritic microtubules suggests that they may play a role in distinguishing between dendritic and axonal export routes from the cell body.
Full text
PDF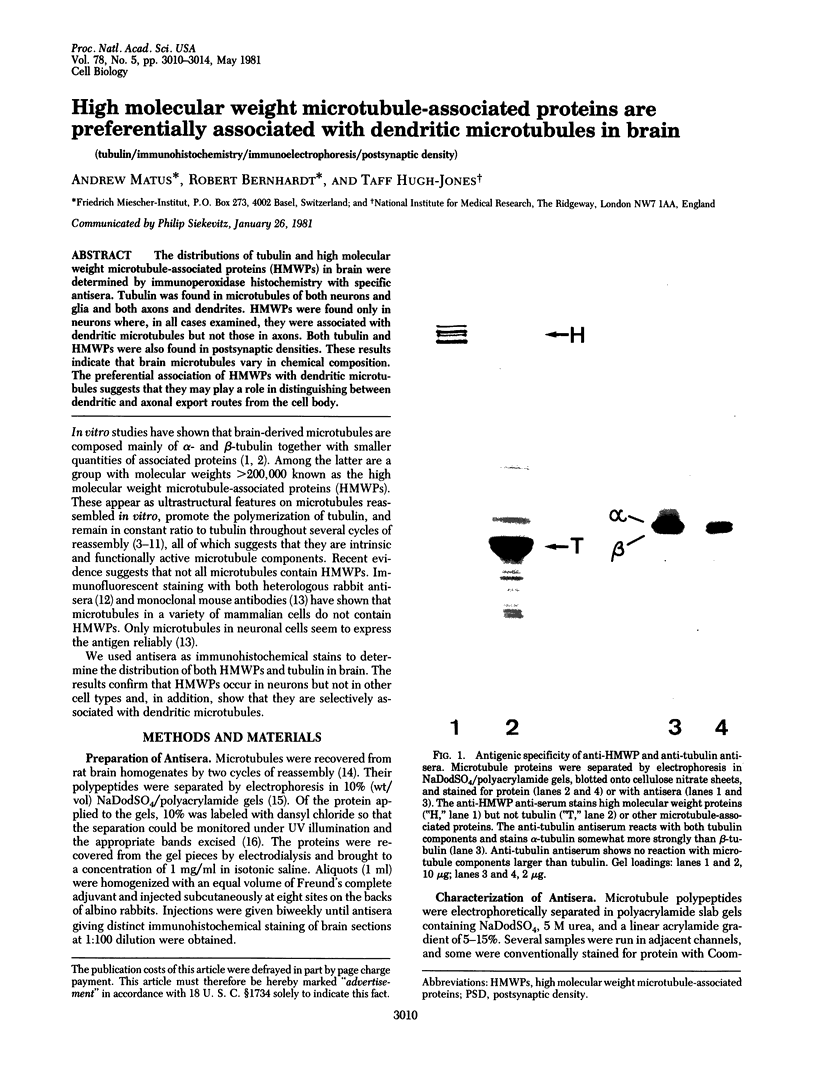



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos L. A. Arrangement of high molecular weight associated proteins on purified mammalian brain microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):642–654. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks P. ATP hydrolase activity associated with microtubules reassembled from bovine splenic nerve--a cautionary tale. J Neurochem. 1976 Dec;27(6):1465–1471. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb02631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz S. A., Katagiri J., Binder H. K., Williams R. C., Jr Separation and characterization of microtubule proteins from calf brain. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5610–5617. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G., Marcum J. M., Olmsted J. B., Murphy D. B., Johnson K. A. Purification of tubulin and associated high molecular weight proteins from porcine brain and characterization of microtubule assembly in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:107–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. A., Kalnins V. I., Cleveland D. W., Kirschner M. W. Intracellular localization of the high molecular weight microtubule accessory protein by indirect immunofluorescence. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):781–786. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. A., Kalnins V. I. The distribution of tau and HMW microtubule-associated proteins in different cell types. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jun;127(2):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90439-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Granett S., Rosenbaum J. L. Ultrastructural localization of the high molecular weight proteins associated with in vitro-assembled brain microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):237–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., McIntosh J. R. Microtubule-associated proteins: a monoclonal antibody to MAP2 binds to differentiated neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4741–4745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keates R. A., Hall R. H. Tubulin requires an accessory protein for self assembly in microtubules. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):418–421. doi: 10.1038/257418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Binder L. I., Rosenbaum J. L. The periodic association of MAP2 with brain microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):266–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. W. Microtubule assembly and nucleation. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;54:1–71. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mareck A., Fellous A., Francon J., Nunez J. Changes in composition and activity of microtubule-associated proteins during brain development. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):353–355. doi: 10.1038/284353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A. I., NG M., Jones D. H. Immunohistochemical localization of neurofilament antigen in rat cerebellum. J Neurocytol. 1979 Aug;8(4):513–525. doi: 10.1007/BF01214806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A., Pehling G., Ackermann M., Maeder J. Brain postsynaptic densities: the relationship to glial and neuronal filaments. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):346–359. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Borisy G. G. Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheterline P. Localisation of the major high-molecular-weight protein on microtubules in vitro and in cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Sep;115(2):460–464. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda R. D., Dentler W. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Microtubule-associated proteins and the stimulation of tubulin assembly in vitro. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4497–4505. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda R. D., Rudolph S. A., Rosenbaum J. L., Greengard P. Cyclic AMP-dependent endogenous phosphorylation of a microtubule-associated protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. High-resolution preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: fluorescent visualization and electrophoretic elution-concentration of protein bands. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90521-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchizono K. Characteristics of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the central nervous system of the cat. Nature. 1965 Aug 7;207(997):642–643. doi: 10.1038/207642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]