Abstract
Background
Genetic diversity is a key factor that enables adaptation and persistence of natural populations towards environmental conditions. It is influenced by the interaction of a natural population's dynamics and the environment it inhabits. Anopheles gambiae s.s. and Anopheles arabiensis are the two major and widespread malaria vectors in sub-Saharan Africa. Several studies have examined the ecology and population dynamics of these vectors. Ecological conditions along the Kilombero valley in Tanzania influence the distribution and population density of these two vector species. It remains unclear whether the ecological diversity within the Kilombero valley has affected the population structure of An. gambiae s.l. populations. The goal of this study was to characterise the genetic structure of sympatric An. gambiae s.s and An. arabiensis populations along the Kilombero valley.
Methodology
Mosquitoes were collected from seven locations in Tanzania: six from the Kilombero valley and one outside the valley (~700 km away) as an out-group. To archive a genome-wide coverage, 13 microsatellite markers from chromosomes X, 2 and 3 were used.
Results
High levels of genetic differentiation among An. arabiensis populations was observed, as opposed to An. gambiae s.s., which was genetically undifferentiated across the 6,650 km2 of the Kilombero valley landscape. It appears that genetic differentiation is not attributed to physical barriers or distance, but possibly by ecological diversification within the Kilombero valley. Genetic divergence among An. arabiensis populations (FST = 0.066) was higher than that of the well-known M and S forms of An. gambiae s. s. in West and Central Africa (FST = 0.035), suggesting that these populations are maintained by some level of reproductive isolation.
Conclusion
It was hypothesized that ecological diversification across the valley may be a driving force for observed An. arabiensis genetic divergence. The impact of the observed An. arabiensis substructure to the prospects for new vector control approaches is discussed.
Background
The genetic structure of a population is shaped by interactions between the behaviour of individuals and their prevailing environment [1]. These factors in combination, can influence the magnitude of gene flow within and between populations and the genetic structure of populations of a species throughout its range [2]. Ecological diversification has been suggested to be one of the factors that can interrupt the movement of genes by creating landscape or genetic barriers such as rapid chromosomal evolution that may ultimately result in reproductive divergence and speciation [3]. Understanding the relationship between individuals and their surrounding environment can, therefore, provide information about the movement of genes from one individual/population to another. This information is important not only for understanding species evolution, but also, in the case of disease vectors, for their control.
The method commonly used to study patterns of gene flow includes identifying genetic units within an ecological landscape and the features that help to shape the spatial distribution of these units [4]. This involves describing genetic boundaries among pre-selected collection sites, presumed to be Mendelian populations, and estimating levels of gene flow among them using FST values or other parameters. Using this information it may be possible to deduce which features/factors are responsible for restricting or promoting movements of genes between or within these populations [5,6]. Although this method has been useful, it suffers from drawbacks. It may for example, not be informative for small areas and relies on prior assumptions of population limits [4,7,8]. The development of Bayesian clustering methods have proven useful since they use individual genotypes as a sole source of information and individuals can be partitioned into genetic units with genotype frequencies in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium [9]. Bayesian clustering methods have gained popularity and have been applied to population genetic studies of a range of organisms such as humans [10], animals [4,11] and plants [10].
Mosquitoes of the Anopheles gambiae complex, include the two primary vectors (An. gambiae s.s. and Anopheles arabiensis) of human malaria in sub-Saharan Africa, that are responsible for an estimated 240 million cases and 280,000 deaths worldwide, with over 80% occurring in Africa [12]. These two species are the most widespread members of the An. gambiae complex and major vectors of malaria [13]. Although they are commonly found occupying similar ecological niches, An. gambiae s. s. is associated with more humid climates than An. arabiensis, which has a greater tolerance for drier environments [14,15]. Additionally, An. gambiae s.s. are highly anthropophagic [13,16], endophagic and typically endophilic [16], whereas An. arabiensis are more zoophagic, exophagic [17], and exophilic [18,19]. A strong pre-copulatory barrier exists between the two species. Although the post-mating isolation mechanism is incomplete, hybrids which are fertile [20] are competitively inferior as evidenced by rare hybrids in nature (0.02-0.76%) [6,21].
Population substructure is more pronounced in An. gambiae s. s and is thought to be influenced by environmental heterogeneity [22]. For example based on chromosomal inversions, five distinct An gambiae s.s. subpopulations, which exist in sympatry, have been revealed in West and Central Africa [6,23]. Studies from north, south and western Africa have reported some degrees of genetic differentiation between An. arabiensis populations [24-26]. However, neither physical barriers nor geographic distance has been reported to be forces responsible for An. arabiensis population differentiation [26,27], except for island populations whose genetic differentiation has been associated with historical drifts [24].
Anopheles gambiae s.s. subpopulations have been studied intensively and are of great epidemiological importance as they have been suggested to undermine available malaria vector control efforts. For example the two molecular forms (S and M) of An. gambiae s.s. have been reported to respond differently to control interventions, as the S form has developed resistance to pyrethroids (insecticides used for impregnating bed-nets) while the M form remains largely susceptible [28,29]. In addition to undermining current control interventions, such population subdivisions are expected to pose more challenges to the application of new genetic control approaches. Such population subdivision may require genetic modification of multiple strains for successful introduction and spread of desired traits into wild populations [5,18]. Therefore, understanding the genetic structure and relative amount of gene flow taking place within and among wild populations is an important component for effective planning and implementation of available insecticide-based vector control approaches. Additionally, poor understanding of the genetic structure and level of gene flow between target populations may possibly undermine proposed genetic control strategies, especially those that aim at reducing mating success of genetically-modified and/or sterile male mosquitoes from natural populations [30,31]. The existence of genetic substructure within vector populations would create barriers that may restrict the spread of desired genes [5,32].
This study, characterised the population structure of An. gambiae s.s. and An. arabiensis within the Kilombero valley (6650 km2) located in southern Tanzania. Although there are remarkable reductions in transmission intensities, this valley experienced some of the most intense malaria transmission in the world [33,34]. Epidemiological studies in the valley revealed that, malaria transmission intensities, as indexed by entomological inoculation rate (EIR, number of infective bites a person is exposed to in a year) are very high and range between 100 to 1000s of infective bites per annum [33,35-37]. It remains unclear whether such high levels of transmission can be attributed to environmental factors that affect mosquito population density and distribution within the valley [38,39] or whether genetic factors that increase vectorial capacity play a larger role. Several studies have examined the ecology and population dynamics of malaria vectors within the Kilombero Valley [36,38,39], but there are no studies of the population structure of An. gambiae s. s. and An. arabiensis in it. In this study therefore, a Bayesian clustering analysis was used and 13 polymorphic microsatellite loci originally designed for use in An. gambiae s. s. [40] were employed to characterise the genetic structure of each of the two malaria vectors throughout the Kilombero Valley. The hypothesis that physical distance between collection sites may affect gene flow was tested and discrete genetic units within each of the two species were created.
Methods
Study site and mosquito collection
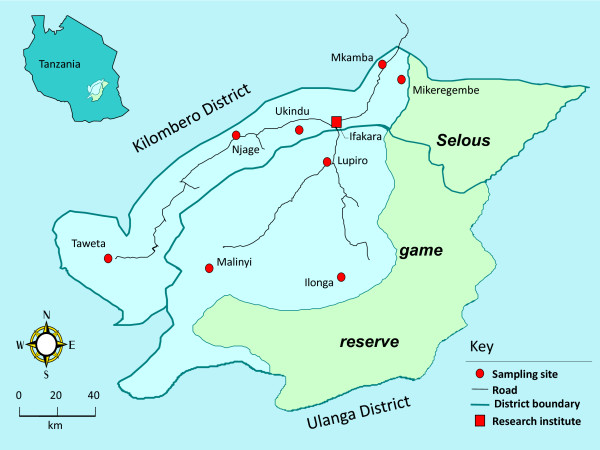
The Kilombero Valley is located in south-eastern Tanzania (Figure 1). The two major vectors of malaria, An. gambiae s.s. and An. arabiensis, are widely distributed along the valley, which is oriented from the northeast to southwest (7°44'-9°26'S/35°33'-36°56'E), The valley lies between the densely forested escarpment of the Eastern Arc mountains and covers an area of 6650 km2 [41]. Estimated mean annual rainfall ranges from 1200 mm/yr to >2000 mm/yr [39,42]. Mosquitoes were collected from seven localities from January - May 2007. Two locations are situated in close proximity with the forested Eastern Arc mountains (Mkamba and Ilonga) and four locations were situated along the river (Malinyi, Ukindu, Lupiro, and Mikeregembe). The distance between these collection sites ranged from 20 to 50 km. Mosquitoes were also collected from Kaliua village located >700 km west of the Kilombero Valley, as an out-group. In each village, five CDC light traps were placed in different randomly selected houses for three consecutive nights. Every morning, traps were retrieved and mosquitoes identified according to their morphological differences. Mosquitoes visually identified as belonging to the An. gambiae complex were individually stored on silica gel in Eppendorf tubes and taken for further molecular analysis to determine whether they were An. gambiae s.s. or An. arabiensis.
Figure 1.
Map of the Kilombero valley. The map of the Kilombero valley (Tanzania), showing mosquito collection sites.
DNA extraction and species identification
Prior to DNA extraction, individual mosquitoes were rehydrated in 100 μl of ultra pure water overnight. The following day, 10 μl of proteinase K and 90 μl of ATL buffer were added to each individual tube, and homogenized in a Qiagen Tissue Lyser®. DNA extraction was performed using a Qiagen 96 Biosprint® work station in 96 well plates using a BioSprint96 DNA Blood Kit (Qiagen, CA). Each individual of the An. gambiae complex was identified to species level using species-specific PCR primers [43].
Microsatellite DNA amplification
We screened PCR primers for 20 An. gambiae microsatellite loci [40]. These were initially developed for An. gambiae s.s., and only 13 gave good amplification in both An. gambiae s.s. and An. arabiensis. Consequently only these 13 were used in this study. These markers provide representative coverage of the entire genome as they are distributed relatively evenly throughout the genome as follows: X chromosome: AGXH25, AGXH100 and AGXH71; Chromosome 2: AG2H175, AG2H85, AG2H164, AG2H197 and AG2H675; and Chromosome 3: AG3H127, AG3H249, AG3H311, AG3H811 and AG3H9 [40].
Microsatellite loci were PCR-amplified for each mosquito sample. Each 25 μl PCR reaction consisted of 12.5 μl of Multiplex master mix, 2.5 μl primer mix and 9 μl of RNase free water. The primer mix was made to a final volume of 250 μl, consisting of 10 pmol of each primer. The forward primer in each reaction was labeled with a fluorescent marker (FAM, NED or HEX) compatible with ABI PRISM (Perkin-Elmer, Norwalk, Conn.) capillary electrophoresis. DNA amplification was completed in MJ Research PTC-200 thermal cyclers (MJ Research, Watertown, MA). A 5 min denaturation step at 95°C was followed by 29 cycles of 20 s at 95°C, 30 s at 55°C and 30 s at 72°C. A final incubation at 72°C was extended for 1 hour to alleviate problems associated with addition of non-template nucleotide (dA) to the PCR products. PCR products were mixed with a GeneScan (Perkin-Elmer, Norwalk, CT) size standard and deionized formamide as directed by the manufacturer. Mixtures were run on an ABI 3130 Genetic analyzer. Output was analysed using ABI PRISM® 3130 Genemapper (Applied Biosystems) to identify alleles.
Statistical analysis of microsatellite allele frequencies
Microsatellite allele and genotype frequencies were examined using Arlequin [44] developed by Excoffier and colleagues [45]. Each microsatellite locus was tested separately for significant departure from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, using a Markov-chain algorithm [46]. Significance threshold were adjusted for multiple comparisons using the formula 1-(1-0.05) ^ (1/n), where n is the number of independent comparisons [47]. The Arlequin software was used to calculate pair-wise FST values [45], and 10,000 permutations were used to determine the significance of FST distance. The neighbour-joining algorithm implemented in neighbour, a part of the Phylip software package [48] was used to calculate the unrooted tree based on the matrix of pair-wise FST distances. The cladogram was drawn using the drawtree programme, also provided in Phylip. As an estimate of gene flow, the number of migrants per population per generation (Nm) was calculated for FST according to the equation, Nm ≈ (1-FST)/4FST [49]. A Bayesian clustering analysis was applied based on the 13 microsatellite markers on chromosomes X, 2 and 3. Using structure software [9], individuals that share the same alleles (unique to that group) are placed into groups/clusters termed as (K), chosen in advance. This model calculates the probabilities of each individual for each subgroup, within which Hardy-Weinberg (H-W) equilibrium and linkage equilibrium are met. These probabilities are used to infer the membership of each individual at their most probable subgroup, and these are referred to as membership coefficients which sum to 1. The probability distribution of an individual X in a putative population K (P(X/K)) was also plotted. Based on allele diversity, individuals with unique alleles are grouped together into assumed population (K) which is pre-determined. The K value with the maximum posterior probability (P(X/K)) is retained and assumed to be the most probable number of clusters in that putative population.
Results
A total of 603 female An. gambiae s. l. mosquitoes were collected in this study from the seven localities. Of these, 113 (18.7%) were An. gambiae s. s. and 490 (81.2%) were An. arabiensis. A total of 386 (288 An. arabiensis and 98 An. gambiae s. s.) mosquitoes were screened for the 13 microsatellite loci.
Genotype frequencies
The result of Guo's Exact Hardy-Weinberg test [46] are shown in Table 1. There was substantial departure from H-W expectations: 22 out of 78 tests in An. arabiensis (28%) and 10 out of 39 tests in An. gambiae s.s. (25.6%) were significant (P < 0.00044). Further inspection in An. arabiensis populations revealed that nine out of 21 tests (42%) involving X-linked loci significantly deviated from H-W expectations and no test out of nine tests (0%) in An. gambiae s.s. significantly deviated from H-W expectations (Additional file 1) suggesting subdivision or admixture within An. arabiensis populations in the Kilombero Valley.
Linkage disequilibrium
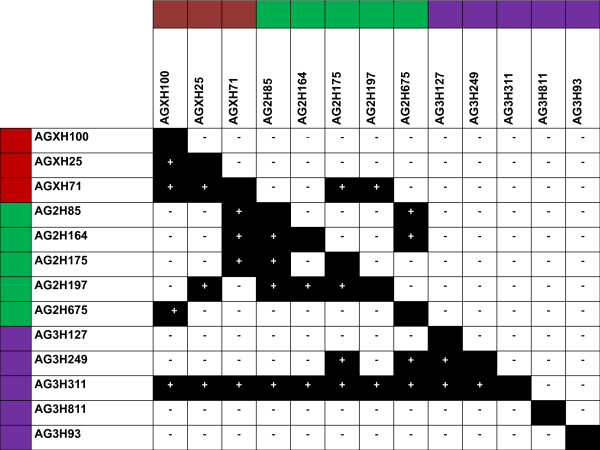
The non-random association between polymorphism at different loci is measured by the degree of linkage disequilibrium. Linkage disequilibrium was determined [49] and 33.3% of the overall pairwise comparisons among An. arabiensis populations were statistically significant (P < 0.00066), (Figure 2). In An. gambiae s.s. however, there was 5% overall pairwise comparison observed to be significant (P < 0.00066). It has been established that linkage disequilibrium is predicted to approach zero for an ideal population, in the absence of forces such as genetic drift, population mixing, mutation and natural selection [50]. It was, therefore, hypothesized that the high linkage disequilibrium 33% observed for An. arabiensis suggests the existence of population subdivision [51].
Figure 2.
Linkage disequilibrium. A pairwise linkage disequilibrium for 13 microsatellite loci for An. gambiae s.s. (above diagonal) and An. arabiensis (below diagonal). Black boxes with "+" indicates statistical significant at linkage disequilibrium (P < 0.00033). The " - " indicates a no significant linkage disequilibrium (P < 0.00033).
Population structure
Differences in allele frequencies among populations were described using FST estimates as a measure of differentiation between the two species and among populations. Results are presented in Table 2. Anopheles arabiensis was genetically distant from An. gambiae s.s. (FST ranging from 0.21-0.27) (Additional file 2). The level of genetic divergence between An. gambiae populations was low (FST ranging from 0.003 to 0.01) whereas the level of genetic divergence between An. arabiensis populations was substantially higher (FST ranging from 0.006 to 0.1). The product of effective population size Ne and the migration rates m was used to estimate the amount of gene flow within each species based on the observed FST values. Thus there is a low amount of gene flow between the two species (Nem, ranging from 0.7 to 0.9). These values are in line with other reported studies [5]. The estimates of gene flow among An. arabiensis populations indicate that there is a limited number of migrants between some populations (Nem ranging from 1.9 to 45; (Additional file 3), as would be expected for populations that are to some extent reproductively isolated.
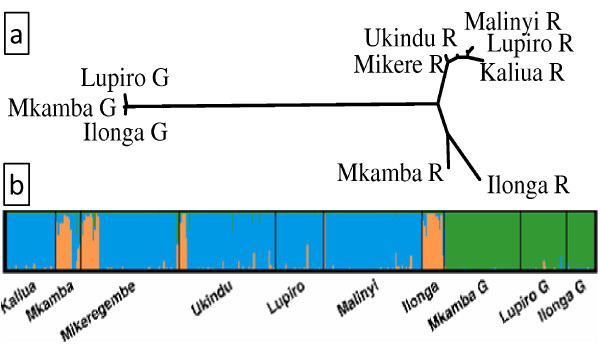
The relatively large genetic level of differentiation between An. arabiensis populations within the valley can be visualized in the unrooted neighbour-joining tree, based on the matrix of pairwise FST values (Figure 3a). Populations of An. arabiensis fall into two distinct clusters, with samples from all populations forming one cluster (cluster I) and populations from Mikeregembe, Mkamba and Ilonga forming the second cluster (Cluster II), (Figure 3b).
Figure 3.
Genetic distances and structuring. (a) Unrooted neighbour-joining cladogram for An. arabiensis and An. gambiae populations based on FST values. "GS" and "R" in each site indicate An. gambiae s. s. and An. arabiensis respectively. (b) Results from an individual level clustering analysis. The vertical bar indicates proportionate assignment of an individual to each cluster. Names of village sample sites are given below. "G" indicates An. gambiae s. s. The blue and green color denotes An. arabiensis and An. gambiae s. s. populations respectively and the pink color indicates an An. arabiensis subgroup.
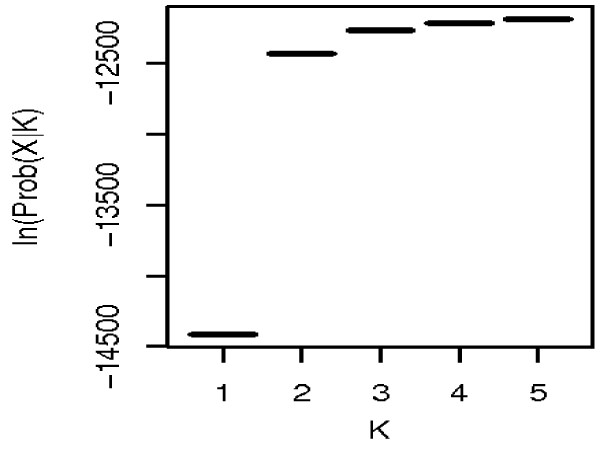
Bayesian clustering analysis was applied for all populations within and outside the Kilombero Valley. This approach is advantageous in that it does not require a prior population classification, but instead estimates the shared population ancestry based on observed genotypes, under the assumption of the presence of a H-W equilibrium and linkage equilibrium within each cluster [52]. Thus, based on the assumption that alleles occur in more than one population, individuals with unique alleles from all populations are placed into K clusters (chosen in advance), i.e. corresponding to the number of postulated Mendelian populations. As shown in Figure 4, solutions for hypothetical An. arabiensis population clusters from K = 4 and K = 5 showed a similar range of likelihood and the highest likelihood was observed at K = 3. Thus the most likely number of clusters (K) is three. This corresponds to three distinct genetic clusters: 1) The An. gambiae s. s. cluster 2) the An. arabiensis cluster I (present in all sites). and 3) the An. arabiensis cluster II (coexisting in Mkamba, Mikeregembe and Ilonga)
Figure 4.
Clustering analysis. A bayesian clustering analysis using structure suggesting the possibility of structured population in An. arabiensis. The high numbers (probabilities) on the Y-axis corresponding to the pre-defined cluster (K) supports the possibility of a subpopulation at that cluster (K-value).
Discussion
In this study, 13 microsatellite loci were used to describe the genetic structure of populations of An. gambiae s.s. and An. arabiensis in the Kilombero Valley, southern Tanzania. Both species occur in the Kilombero Valley with An. arabiensis more widespread. The An. gambiae s.s. populations sampled appear to represent a single genetic population, whereas An. arabiensis appear to occur as two discrete populations that are found in sympatry at some sites (for example, Mkamba, Ilonga and Mikeregembe, see Figure 3b). The higher genetic differentiation among An. arabiensis populations compared with that among An. gambiae populations is evidenced by (i) the genome-wide signature of departures from H-W equilibrium and high linkage disequilibrium between loci, (ii) higher FST estimates between An. arabiensis than between An. gambiae s.s. populations, (iii) higher levels of gene flow between An. gambiae s.s. than An. arabiensis populations and (iv) Bayesian probability distribution at K = 3. This clearly indicates that An. arabiensis gene pool across the Kilombero Valley is not homogeneous. In contrast, An. gambiae s. s. showed low levels of genetic differentiation with high level of gene flow across populations, indicative of a homogeneous gene pool.
Population substructure observed in Ilonga, Mikeregembe and Mkamba, among An. arabiensis populations may be a consequence of several factors that need further investigations. Cytogenetic evidence suggests that An. arabiensis is an ancient species from which other members of the complex descended and that this species inhabited East Africa more than 6,000 yrs ago [14], indicative of a possibility for population structuring [8]. Consequently, the Kilombero Valley is surrounded by the ancient Eastern Arc mountain ranges (e.g., the Udzungwa and Mahenge mountains) providing stable wet climatic conditions [53] estimated to have existed for over 30 million yrs and this is where the two sampling sites (Ilonga and Mkamba, Figure 1) are located. Climatic stability as provided by the Eastern Arc mountains and the environmental heterogeneity maintained within it, may be among the major forces driving the genetic structure of An. arabiensis populations inhabiting Mkamba and Ilonga, as opposed to An. arabiensis populations outside and along the rest of the Kilombero Valley, such as Kaliua, Ukindu and Malinyi. It is important to note that Mikeregembe is a fishing camp [39] thus it is plausible that a subpopulation of An. arabiensis existing in Mkamba and Ilonga may have been introduced in Mikeregembe by fishermen from Mkamba (20 kms away) who regularly visit the camp for fishing activities. These mountains also create unequal climatic conditions across the Kilombero Valley which correlate very well with the abundance of the two malaria vector species [39,54]. For example, (i) An. gambiae s.s is commonly found in close proximity with forested Eastern Arc mountain areas, where the climate is stable and annual rainfall is higher than in the rest of the valley (> 2,000 mm/yr), (ii) An. arabiensis is commonly found in riverine areas where the climate is less stable and annual rainfall is lower (<1,200 mm/yr) [39]. Therefore, it is plausible that An. arabiensis populations inhabiting sites along the Eastern Arc mountains are subjected to a higher degree of environmental heterogeneity typical to these mountains, promoting genetic variation and the emergence of new adaptive genotypes [55].
Based on the difference in allele frequency (FST), the level of genetic divergence between An. gambiae s. s. populations is lower (mean FST = 0.006) than that between An. arabiensis populations (mean FST = 0.066). The degree of divergence between An. arabiensis populations (mean FST = 0.066) is even greater than the reported divergence between the well-known M and S forms of An. gambiae s.s. in West Africa (mean FST = 0.035), [56]. From these observations it can be hypothesized that the An. arabiensis subpopulations are maintained by some degree of reproductive isolation. This hypothesis can also be supported by the absence of hybrids in sympatric An. arabiensis populations (e.g. in Mkamba, Mikeregembe and Ilonga; Figure 3b).
The FST estimate reported in this study is higher than the reported FST estimate for An. arabiensis from west, south and east Africa (0.035-0.038) where extensive An. arabiensis population differentiation was observed [25,27]. The FST estimate observed in this study (0.066 - 0.100) is in line with the largest reported An. arabiensis FST estimate (0.080-0.215). This is a comparison between mainland and island An. arabiensis populations [24], where gene flow is restricted by the ocean. Extensive An. arabiensis genetic differentiation was neither a result of any obvious physical barrier nor geographic distance, consistent with reports from other studies [26,27]. It can be deduced that factors other than physical barriers or geographical distance may be responsible for genetic differentiation in An. arabiensis [57]. In this study, highest genetic differentiation in An. arabiensis was recorded for markers located on chromosome X. 42% of tests involving markers on chromosome X deviated from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, in contrast to 0% in An. gambiae s.s. This does not only suggest the population to be structured, but also supports the hypothesis developed by Stump and colleagues that sex-linked differentiation is characterised by some degree of reproductive isolation mechanisms controlled by genes located in genomic regions within X chromosome [58].
The observed genetic An. arabiensis subgroups existing within the Kilombero Valley may be of great significance to malaria epidemiology. Anopheles arabiensis mosquitoes are reported to be phenotypicaly diverse. For example, An. arabiensis is more zoophilic and exophilic [59], and highly anthropophagic in other places [60]. Also An. arabiensis are able to tolerate higher temperatures and lower humidities than An. gambiae s.s. [61]. This phenomena, may prompt early biting activity for An. arabiensis and accelerate disease transmission. Therefore, if the observed population substructure is ignored, degrees of medically important phenotypes in An. arabiensis species, such as vectorial capacity, host preference and insecticide resistance, could be obfuscated. Thus, further investigations are needed to thoroughly understand the epidemiological significance of the observed population substructures.
Conclusions
This study provides evidence that An. arabiensis in East Africa has a complex genetic structure with distinct populations occurring in sympatry, apparently maintained by some degree of reproductive isolation. It was hypothesized that ecological differences rather than a physical barrier or geographical distance are responsible for the observed An. arabiensis population substructure. Further investigation is needed not only to clearly establish the specific mechanisms underlying genetic differentiation in An. arabiensis populations, but also to identify the number of discrete malaria vector populations sustaining transmission along the Kilombero Valley, important for guiding the implementation of available and future control strategies. Proposed new genetic control strategies such as sterile insect technique (SIT) and genetically modified mosquitoes (GMM), require a homogeneous population structure for success. The observed level of genetic substructure may pose a challenge to the successful implementation of these approaches [62,63]. Since An. arabiensis populations appear to be maintained by some degree of reproductive isolation, multiple genetic modifications of An. arabiensis may be needed if genetic control is to be successful. Furthermore, the observed An. arabiensis population substructure may have different malaria transmission intensity, as populations with distinct genetic composition may have different vectorial capacities [64]. Further investigation of the association between the observed subpopulations and their susceptibility to malaria parasite infection, would be useful to explore if and how these genotypes could be influencing malaria transmission intensity along the Kilombero Valley.
The study showed that there may still be another level of genetic subdivision within the An. gambiae complex, suggesting the possibility of population expansion [65], with potential implication not only in understanding the evolutionary process of this complex but also for the application of vector control approaches. Further studies are recommended to investigate the spatial and temporal distribution of the observed genetic variation and population substructure in both An. gambiae and An. arabiensis along the Kilombero Valley.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
KRN, BGJK, GCL and HMF designed this study. KRN carried out the laboratory and SFS work. KRN and YL analysed and interpreted the data. KRN, HMF, GCL and BGJK drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
P-values indicating statistical significance (P < 0.00044) of deviations from Hardy - Weinberg expectations for 13 microsatellite loci in populations of An. arabiensis and An. gambiae s. s. collected from within the Kilombero/Ulanga Valleys, Tanzania. Ag = An. gambiae s. s. and Aa = An. arabiensis. Significant test at P ≤ 0.00044 are in bold.
Pairwise estimates of genetic divergence (FST) between An. gambiae and An. arabiensis in the Kilombero Valley. The total numbers of mosquitoes screened in each location are in brackets. Underlined values indicate inter-species comparison between An. gambiae and An. arabiensis. The non-underlined values indicate intra-species comparisons, i.e. within An. gambiae and An. arabiensis. Values in italics are statistically significant. Significance levels at ¥P < 0.05, $P < 0.01 and *P < 0.001. 'Ag' = An. gambiae s. s. and 'Aa' = An. arabiensis.
Estimated number of migrants between An. gambiae s. l. populations within and outside Kilombero Valley (Kaliua). 'Ag' stands for An. gambiae s. s. and 'Aa' stands for An. arabiensis.
Contributor Information
Kija R Ng'habi, Email: kija@ihi.or.tz.
Bart GJ Knols, Email: bart@malariaworld.org.
Yoosook Lee, Email: yoslee@ucdavis.edu.
Heather M Ferguson, Email: Heather.Ferguson@glasgow.ac.uk.
Gregory C Lanzaro, Email: gclanzaro@ucdavis.edu.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Entomology team at the IHI, specifically, Japhet Kihonda, Hassani Ngonyani and Hasani Mtambala for helping with mosquito collections in the field. We also thank Prof. Marcel Dicke for reviewing this manuscript prior to submission. We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments that have helped to shape this manuscript. We acknowledge financial support from the Caroline MacGillavry Fund (KNAW, The Netherlands) through a fellowship awarded to KRN. This research was supported by a VIDI grant (#864.03.004) from the Dutch Scientific Organisation (NWO) to BGJK. We also acknowledge support from BBSRC through a fellowship awarded to HMF (BB/D020042/1).
References
- Waples RS, Gaggiotti O. What is a population? An empirical evaluation of some genetic methods for identifying the number of gene pools and their degree of connectivity. Mol Ecol. 2006;15:1419–1439. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clobert J, Dhont AA, Nichols JD. Dispersal. Oxford, UK.: Oxford University Press; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider JC. Natural selection and speciation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:12398–12399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.240463297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulon A, Guillot G, Cosson JF, Angibault JM, Aulagnier S, Cargnelutti B, Galan M, Hewison AJ. Genetic structure is influenced by landscape features: empirical evidence from a roe deer population. Mol Ecol. 2006;15:1669–1679. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzaro GC, Toure YT, Carnahan J, Zheng L, Dolo G, Traore S, Petrarca V, Vernick KD, Taylor CE. Complexities in the genetic structure of Anopheles gambiae populations in West Africa as revealed by microsatellite DNA analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:14260–14265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touré YT, Petrarca V, Traore SF, Coulibaly A, Maiga HM, Sankare SF, Sow M, DI Deco MA, Coluzzi M. The distribution and inversion polymorphism of chromosomally recognized taxa of the Anopheles gambiae complex in Mali, West Africa. Parassitol. 1998;40:477–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster MW, Sharp RR. Race, ethnicity, and genomics: social classifications as proxies of biological heterogeneity. Genome Res. 2002;12:844–850. doi: 10.1101/gr.99202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaeuffer R, Re'ale D, Coltman DW, Pontier D. Detecting population structure using structure software: effect of background linkage disequilibrium. Heredity. 2007;99:374–380. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6801010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P. Inference of population structure using multilocus geneotype data. Genetics. 2000;155:945–959. doi: 10.1093/genetics/155.2.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson SR, Jones TA, Jensen KB. Population structure in Pseudoroegneria spicata (Poaceae: Triticeae) modeled by Bayesian clustering of AFLP genotypes. Am J Bot. 2004;91:1789–1801. doi: 10.3732/ajb.91.11.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg NA, Pritchard KJ, Weber LJ, Cann MH, Kidd KK, Zhivotovsky AL, Feldman WM. Genetic structure of human population. Science. 2002;298:2381–2385. doi: 10.1126/science.1078311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHO. World Malaria report. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2009. http://www.who.int/malaria/world_malaria_report_2009/en/index.html [Google Scholar]
- Coluzzi M, Sabatini A, Petrarca V, Di Deco MA. Chromosomal differentiation and adaptation to human environments in the Anopheles gambiae complex. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73:483–497. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayala FJ, Coluzzi M. Chromosome speciation: Humans, Drosophila and mosquitoes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:6535–6542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501847102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly MJ, Cuamba N, Charlwood JD, Collins FH, Townson H. Population structure in the malaria vector, Anopheles arabiensis patton, in East Africa. Heredity. 1999;83:408–417. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6885930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White GB. Anopheles gambiae complex and disease transmission in Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1974;68:278–298. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(74)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White GB, Magayuka SA, Boreham PFL. Comparative studies on sibling species of the Anopheles gambiae Giles complex (Diptera: Culicidae): bionomics and vectorial activity of species A and species B at Segera, Tanzania. Bull Entomol Res. 1972;62:295–317. doi: 10.1017/S0007485300047738. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Coluzzi M, Sabatini A, Della Torre A, Di Deco MA, Petrarca V. A polytene chromosome analysis of the Anopheles gambiae species complex. Science. 2002;298:1415–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.1077769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies MT, DeMeillon B. The Anophelinae of Africa South of the Sahara (Ethiopian zoogeographical region) Johannesburg: South African Institute for Medical Research; 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Besansky NJ, Krzywinski J, Lehmann T, Simard F, Kern M, Mukabayire O, Fontenille D, Toure Y, Sagnon N. Semipermeable species boundaries between Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles arabiensis: evidence from multilocus DNA sequence variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:10818–10823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1434337100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temu EA, Hunt RH, Coetzee M, Minjas JN, Shiff CJ. Detection of hybrids in natural populations of the Anopheles gambiae complex by the rDNA-based, PCR method. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1997;91:963–965. doi: 10.1080/00034989760383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touré YT, Petrarca V, Traore SF, Coulibaly A, Maiga HM, Sankare SF, Sow M, DI Deco MA, Coluzzi M. Ecological genetic studies in the chromosomal form Mopti of Anopheles gambiae s.s. in Mali, West Africa. Genetica. 1994;94:213–223. doi: 10.1007/BF01443435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- della Torre A, Costantini C, Besansky NJ, Caccone A, Petrarca V, Powell JR, Coluzzi M. Speciation within Anopheles gambiae--the glass is half full. Science. 2002;298:115–117. doi: 10.1126/science.1078170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard F, Fontenille D, Lehmann T, Girod R, Brutus L, Gopaul R, Dournon C, Collins FH. High amounts of genetic differentiation between populations of the malaria vector Anopheles arabiensis from West Africa and eastern outer islands. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;60:1000–1009. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1999.60.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly MJ, Townson H. Evidence for extensive genetic differentiation among populations of the malaria vector Anopheles arabiensis in Eastern Africa. Insect Mol Biol. 2000;9:357–367. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2583.2000.00197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyanjom SR, Chen H, Gebre-Michael T, Bekele E, Shililu J, Githure J, Beier JC, Yan G. Population genetic structure of Anopheles arabiensis mosquitoes in Ethiopia and Eritrea. J Hered. 2003;94:457–463. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esg100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besansky NJ, Lehmann T, Fahey GT, Fontenille D, Braack LEO, Hawley WA, Collins FH. Patterns of mitochondrial variation within and between African malaria vectors, Anopheles gambiae and An. arabiensis, suggest extensive gene flow. Genetics. 1997;147:1817–1828. doi: 10.1093/genetics/147.4.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripet F, Wright J, Cornel A, Fofana A, Mcabee R, Meneses C, Reimer L, Slotman M, Thiemann T, Dolo G, Traore S, Lanzaro GC. Longitudinal survey of knockdown resistance to pyrethroid (kdr) in Mali, West Africa, and evidence of its emergence in the Bamako form of Anopheles gambiae s.s. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;76:81–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer L, Fondjo E, Patchoké S, Diallo B, Lee Y, Ng A, Ndjemai HM, Atangana J, Traore SF, Lanzaro G, Cornel AJ. Relationship between kdr mutation and resistance to pyrethroid and DDT insecticides in natural populations of Anopheles gambiae. Med Vet Entomol. 2008;45:260–266. doi: 10.1603/0022-2585(2008)45[260:rbkmar]2.0.co;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandin S, Shiao SH, Moita LF, Janse CJ, Waters AP, Kafatos FC, Levashina EA. Complement-like protein TEP1 is a determinant of vectorial capacity in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Cell. 2004;116:661–670. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osta MA, Christophides GK, Kafatos FC. Effects of mosquito genes on Plasmodium development. Science. 2004;303:2030–2032. doi: 10.1126/science.1091789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzaro GC, Tripet F. In: Ecological aspects for application of genetically modified mosquitoes. Takken W, Scott TW, editor. Vol. 2. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer; 2003. Geneflow among populations of Anopheles gambiae. a critical review. [Google Scholar]
- Smith T, Charlwood JD, Kihonda J, Mwankusye S, Billingsley P, Meuwissen J, Lyimo E, Takken W, Teuscher T, Tanner M. Absence of seasonal variation in malaria parasitemia in an area of intense seasonal transmission. Acta Trop. 1993;54:55–72. doi: 10.1016/0001-706X(93)90068-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen GF, Kihonda J, Lyimo E, Oketch FR, Kotas ME, Mathenge E, Schellenberg JA, Lengeler C, Smith TA, Drakeley CJ. Quantifying behavioural interactions between humans and mosquitoes: Evaluating the protective efficacy of insecticidal nets against malaria transmission in rural Tanzania. BMC Infect Dis. 2006;6:161. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-6-161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T, Charlwood JD, Takken W, Tanner M, Spiegelhalter DJ. Mapping densities of malaria vectors within a single village. Acta Trop. 1995;59:1–18. doi: 10.1016/0001-706X(94)00082-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen GF, Kihonda J, Lyimo E, Oketch FR, Kotas ME, Mathenge E, Schellenberg JA, Lengeler C, Smith TA, Drakeley CJ. Quantifying behavioural interactions between humans and mosquitoes: evaluating the protective efficacy of insecticidal nets against malaria transmission in rural Tanzania. Infect Dis. 2006;6:161. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-6-161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen GF, Smith TA. Exploring the contributions of bed nets, cattle, insecticides and excitorepellency to malaria control: a deterministic model of mosquito host-seeking behaviour and mortality. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2007;101:867–880. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2007.04.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood JD, Kihonda J, Sama S, Billingsley PF, Hadji H, Verhave JP, Lyimo E, Luttikhuizen PC, Smith T. The rise and fall of Anopheles arabiensis (Diptera: Culicidae) in a Tanzanian village. Bull Entomol Res. 1995;85:37–44. doi: 10.1017/S0007485300051993. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood JD, Vij R, Billingsley PF. Dry season refugia of malaria-transmitting mosquitoes in a dry savannah zone of east Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000;62:726–732. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2000.62.726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng L, Benedict MQ, Cornel AJ, Collins FH, Kafatos FC. An integrated genetic map of the African human malaria vector mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Genetics. 1996;143:941–952. doi: 10.1093/genetics/143.2.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnington C, Weaver D, Fanning E. Livestock and large wild mammals in the Kilombero Valley, in southern Tanzania. Afr J Ecol. 2007;45:658–663. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2028.2007.00793.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- IIED. The International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED) London, and the Institute of Resource Assessment (IRA), University of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania; 1992. The environmental impact of the proposed Kilombero valley hardwood project. Tanzania. An assessment of a project proposed by the Commonwealth Development Corporation. [Google Scholar]
- Scott JA, Brogdon WG, Collins FH. Identification of single specimens of the Anopheles gambiae complex by the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1993;49:520–529. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1993.49.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlequin - A software for population data genetics analysis. http://anthropologie.unige.ch/arlequin/
- Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S. Arlequin ver. 3.0: An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinformat. 2005;1:47–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo S, Thompson E. Performing the exact test of Hardy-Weinberg proportions for multiple alleles. Biometrics. 1992;48:361–372. doi: 10.2307/2532296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdi H. In: Encyclopedia of Measurement and Statistics. Salkind NJ, editor. CA: sage; 2007. "Bonferroni and Šidák corrections for multiple comparisons".http://www.utdallas.edu/~herve/Abdi-Bonferroni2007-pretty.pdf Thousand Oaks. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) version 3.6. 3.6. Seattle: Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin M. A measure of population subdivision based on microsatellite allele frequencies. Genetics. 1995;139:457–462. doi: 10.1093/genetics/139.1.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T. Linkage disequilibrium due to random genetic drift in finite subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982;79:1940–1944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M, Li WH. Linkage disequilibrium in subdivided populations. Genetics. 1973;75:213–219. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlaender JS, Friedlaender FR, Reed FA, Kidd KK, Kidd JR, Chambers GK, Lea RA, Loo J, Koki G, Hodgson JA, Merriwether DA, Webel JL. The genetic structure of pacific islanders. PLoS Genetics. 2008;4:e19. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0040019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths CJ. In: Biogeography and Ecology of the rain forests of eastern Africa. Lovett JC, Wasser SK, editor. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1993. The geological evolution of East Africa; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ng'habi KR, Meneses CR, Cornel AJ, Slotman MA, Knols BGJ, Ferguson HM, Lanzaro GC. Clarification of anomalies in the application of a 2La molecular karyotyping method for the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Paras Vect. 2008;1:45. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-1-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno M, Salgueiro P, Vicente JL, Cano J, Berzosa PL, Lucio A, Simard F, Caccone A, Do Rosario VE, Pinto J. et al. Genetic population structure of Anopheles gambiae in Equatorial Guinea. Mal J. 2007;6:137. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-6-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wondji C, Simard F, Fontenille D. Evidence for genetic differentiation between the molecular forms M and S within the forest chromosomal form of Anopheles gambiae in an area of sympatry. Insect Mol Biol. 2002;11:11–19. doi: 10.1046/j.0962-1075.2001.00306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besansky NJ, Lehmann T, Fahey GT, Fontenille D, Braack LE, Hawley WA, Collins FH. Patterns of mitochondrial variation within and between African malaria vectors, Anopheles gambiae and An. arabiensis, suggest extensive gene flow. Genetics. 1997;147:1817–1828. doi: 10.1093/genetics/147.4.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stump AD, Shoener JA, Costantini C, Sagnon N, Besansky NJ. Sex-linked differentiation between incipient species of Anopheles gambiae. Genetics. 2005;169:1509–1519. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.035303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies MT. Studies in house leaving and outside resting of Anopheles gambiae Giles and Anopheles funestus Giles in East Africa. Part II. The exodus from houses and the house resting population. Bull Entomol Res. 1955;45:375–387. [Google Scholar]
- Fornadel CM, Norris LC, Glass GE, Norris DE. Analysis of Anopheles arabiensis blood feeding behavior in southern Zambia during the two years after introduction of Insecticide-Treated Bed Nets. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;83:848–853. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.10-0242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby MJ, Lindsay SW. Responses of adult mosquitoes of two sibling species, Anopheles arabiensis and Anopheles gambiae s.s. (Diptera: Culicidae) to high temperatures. Bull Entomol Res. 2004;94:441–448. doi: 10.1079/ber2004316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedict MQ, Robinson AS. The first releases of transgenic mosquitoes: an argument for the sterile insect technique. Trends Parasitol. 2003;19:349–355. doi: 10.1016/S1471-4922(03)00144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knols BGJ, Njiru BNN, Mukabana RW, Mathenge EM, Killeen GF. In: Ecology of transgenic mosquitoes. Scott TW, Takken W, editor. Dordrecht, The Netherlands.: Springer; 2003. Contained semi-field environments for ecological studies on transgenic African malaria vectors; pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Petrarca V, Beier JC. Intraspecific chromosomal polymorphism in the Anopheles gambiae complex as a factor affecting malaria transmission in the Kisumu area of Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992;46:229–237. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.46.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly MJ, Licht MC, Lehmann T. Evidence for recent population expansion in the evolutionary history of the malaria vectors Anopheles arabiensis and Anopheles gambiae. Mol Biol Evol. 2001;18:1353–1364. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
P-values indicating statistical significance (P < 0.00044) of deviations from Hardy - Weinberg expectations for 13 microsatellite loci in populations of An. arabiensis and An. gambiae s. s. collected from within the Kilombero/Ulanga Valleys, Tanzania. Ag = An. gambiae s. s. and Aa = An. arabiensis. Significant test at P ≤ 0.00044 are in bold.
Pairwise estimates of genetic divergence (FST) between An. gambiae and An. arabiensis in the Kilombero Valley. The total numbers of mosquitoes screened in each location are in brackets. Underlined values indicate inter-species comparison between An. gambiae and An. arabiensis. The non-underlined values indicate intra-species comparisons, i.e. within An. gambiae and An. arabiensis. Values in italics are statistically significant. Significance levels at ¥P < 0.05, $P < 0.01 and *P < 0.001. 'Ag' = An. gambiae s. s. and 'Aa' = An. arabiensis.
Estimated number of migrants between An. gambiae s. l. populations within and outside Kilombero Valley (Kaliua). 'Ag' stands for An. gambiae s. s. and 'Aa' stands for An. arabiensis.