Abstract
Albumin fusion proteins have demonstrated the ability to prolong the in vivo half-life of small therapeutic proteins/peptides in the circulation and thereby potentially increase their therapeutic efficacy. To evaluate if this format can be employed for antibody-based imaging, an anti-carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) single chain antibody-albumin fusion protein was designed, expressed and radiolabeled for biodistribution and imaging studies in athymic mice bearing human colorectal carcinoma LS-174T xenografts. The [125I]-T84.66 fusion protein demonstrated rapid tumor uptake of 12.3% injected dose per gram (ID/g) at 4 hr that reached a plateau of 22.7 %ID/g by 18 hr. This was a dramatic increase in tumor uptake compared to 4.9 %ID/g for the scFv alone. The radiometal [111In]-labeled version resulted in higher tumor uptake, 37.2 %ID/g at 18 hr, that persisted at the tumor site with tumor: blood ratios reaching 18:1 and with normal tissues showing limited uptake. Based on these favorable imaging properties, a pilot [64Cu]-PET imaging study was performed with promising results.
The anti-CEA T84.66 scFv-albumin fusion protein demonstrates highly specific tumor uptake that is comparable to cognate recombinant antibody fragments. The radiometal labeled version, which shows lower normal tissue accumulation than these recombinant antibodies, provides a promising and novel platform for antibody-based imaging agents.
Keywords: albumin-fusion protein, CEA, colorectal cancer, imaging
INTRODUCTION
Albumin fusion proteins have demonstrated the ability to prolong the in vivo half-life of small therapeutic proteins/peptides by coupling them to the well characterized protein, human serum albumin (HSA) [1]. Antibody-derived fusions have been generated by chemical conjugation or as recombinant single chain (scFv) antibody-HSA molecules [2, 3]. Alternatively, non-covalent approaches have been developed by incorporating peptides that bind to albumin [4, 5] or albumin-binding domains [6] and have been shown to enhance imaging in Her2 positive tumors.
Based on the high affinity anti-carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) T84.66 monoclonal antibody, our group has developed a series of cognate recombinant scFv-based antibody fragments, T84.66 scFv, diabody, and minibody as radiolabeled tumor imaging agents [7]. We and others have shown that the monovalent scFv does not provide sufficient accumulation of activity in tumors for in vivo imaging, due to its small molecular size, valency and very rapid blood clearance [8]. While the multivalent constructs, T84.66 minibody and diabody, have entered pilot human imaging trials [9], currently their use has been restricted to radioiodinated agents because the radiometal labeled versions have resulted in increased retention in normal liver and kidney [10].
Albumin is one of the most abundant proteins in both the vascular and extravascular spaces and has a half-life of 19 days in humans [11] as a result of recycling by the FcRn receptor [12]. In this report, we investigate whether the anti-CEA scFv-HSA fusion protein (“immunobumin”) can increase tumor targeting of the scFv construct and more importantly, if normal tissue clearance can be enhanced by coupling to albumin with its receptor-based recycling mechanism.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Molecular design and assembly
The murine T84.66 scFv has been expressed with variable length linkers, and for this construct the GS18 minibody linker was used as previously described [13]. The HSA plasmid #MGC-328500 was obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). Molecular modeling was performed using the atomic coordinates of the T84.66 VL-VH scFv, 1MOE [14], and HSA, 1BM0 [15]. Splice overlap PCR [16] was used to join the scFv to a truncated version of the mature HSA (minus amino acids 1-3, asp-ala-his). The T84.66 scFv-HSA gene and nucleotides encoding a six histidine tag were cloned into pEE12 vector as part of the Glutamine Synthetase mammalian expression/selection system (Lonza Biologics, Slough, UK).
Expression, selection and purification
The pEE12 immunobumin plasmid was transfected into murine myeloma NS0 cells, selected in glutamine-deficient media, supernatants screened for anti-CEA activity by ELISA and protein quantified by Protein L as previously described [17]. Clone 17F9 was expanded as a terminal culture in 500 mL LIFECELL tissue culture bags (Baxter, Deerfield, IL). Purification of the immunobumin used a two-step procedure consisting of IMAC capture of the His6 tagged protein and ceramic hydroxyapatite chromatography. Briefly, the culture supernatant was clarified in batch with 5% AG1-X8 resin (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA), sterile filtered and loaded on a Ni-charged Fractogel EMD Chelate column (4.6 mm × 100 mm, 1 mL/min; EMD Chemicals, Gibbstown, NJ). The column was washed in 0.01M imidazole, 0.3M NaCl, 0.02M sodium phosphate, (pH 7.5) and eluted with a linear gradient of 0.01 to 0.2M imidazole in 0.3M NaCl, 0.02M sodium phosphate, (pH 7.5) over 20 column volumes. The eluted immunobumin was dialyzed in 0.02M MES (pH 7) buffer and loaded on a ceramic hydroxyapatite CHT® type I column (4.6 mm × 100 mm, 1 mL/min; Bio-Rad Laboratories). A linear gradient to 0.1M sodium phosphate/0.02M MES, (pH 7) eluted the fusion protein in a single peak and the purified material was dialyzed vs. PBS prior to concentration (Centriprep-30, Millipore, Billerica, MA).
Characterization of purified T84.66 immunobumin
Aliquots of the purified protein were analyzed by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions, isoelectric focusing gels and size exclusion chromatography (SEC) on a Superdex 75 10/300 column (GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ) as previously described [17].
Conjugation and radiolabeling
Radioiodination of T84.66-immunobumin with [125I] (PerkinElmer Life and Analytical Sciences Inc., Downers Grove, IL) was performed using the Iodogen methodology. Immunobumin (120 μg in 35 μl PBS) was added to a tube pre-coated with 20 μg Iodogen (Pierce, Rockford, IL), followed by 1.2 mCi [125I] NaI diluted to 65 μl in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) and incubated at room temperature for 3 minutes. For the radiometal labeled studies, the purified immunobumin was conjugated with DOTA-NHS-ester (Macrocylics, Dallas, TX) at a ratio of 17:1 followed by dialysis in 0.25M ammonium acetate (pH 7, final conc. 2 mg/ml). Radiolabeling with [111In] chloride (Mallinckrodt, St Louis, MO) was performed as follows: 29 μl 0.1 N HCl was added to 60 μl (0.88 mCI) [111In] followed by 100 μl (200 μg) DOTA-immunobumin. The reaction mixture (pH ~5.5) was incubated at 43°C for 30 minutes. Labeling with [64Cu] chloride (Trace Life Sciences, Denton, TX) was performed by addition of 20 μl 0.1M ammonium citrate (pH 5.5) to 4 μl (1.85 mCi) [64Cu] followed by 90 μl (180 μg) DOTA-immunobumin. The reaction mixture (pH ~6) was incubated at 43°C for 45 minutes. At the end of the incubation, 10 mM DTPA was added to give a final concentration of 0.001 M DTPA. All radiolabeled products were purified by Superdex 75 FPLC 30/100 chromatography (GE Healthcare).
Immunoreactivity
The [125I]-, [111In]-, [64Cu]-immunobumins were analyzed for retained immunoreactivity in a liquid phase assay by incubating radiolabeled protein with 10 equivalents by mass of purified CEA at 37°C for 15 min. The resultant solution was analyzed by HPLC-SEC using a Superose-6 10/300 GL column (GE Healthcare). Immunoreactivity was determined by integrating the area on the HPLC trace and calculating the percentage of radioactivity shifting to higher molecular weights consistent with complexation with CEA.
Animal biodistribution and imaging studies in tumor-bearing mice
All animal handling was done in accordance with protocols approved by the City of Hope Research Animal Care Committee. Seven to eight week old female athymic mice (Charles River Laboratories, Wilmington, MA) were injected subcutaneously in the flank region with 106 LS-174T human colon carcinoma cells obtained from ATCC. After 10 days, when tumor masses were in the range of 100-300 mg, 10 μCi on 1 μg of [125I]-immunobumin and 4 μCi on 1 μg of [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin per animal were co-injected via the tail vein. At selected time points (0, 4, 18, 24, 48, and 72 hr), groups of five mice were euthanized, necropsy performed, organs weighed and counted for radioactivity. All data presented are mean values ±SEM and have been corrected for background and radioactive decay from the time of injection, allowing organ uptake to be reported as percentage of the injected dose per gram (%ID/g).
For gamma imaging studies, 2 tumor bearing mice were injected intravenously with 25 μCi on 2.5 μg of [125I]-immunobumin and 4 mice were injected with 25 μCi on 6 μg of [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin. The mice were anaesthetized with isoflurane and placed on a planar scintigraphic camera, γ-IMAGER (BIOSPACE Mesures S.A., Paris, France), ventral side down and a 15 minute image was acquired. Imaging was performed at 0, 4, 10, 24, 53, and 72 hr; all images were half-life corrected.
For PET imaging, a 20 g mouse was injected with 50 μCi on 10 μg of [64Cu]-DOTA-immunobumin and imaged at 1, 4, 8, 24 and 48 hr post injection with a small-animal PET scanner (microPET™ Model R4; Siemens/CTIMI, Knoxvillle, TN). Image processing and analysis were performed with the standard microPET software. Scan data were sorted into two-dimensional sinograms using the Fourier rebinning method and were corrected for half-life and detector non-uniformity and random coincidence noise. Images were reconstructed by the maximum a posteriori method [18]. At 48 hr the mouse was euthanized and blood, liver and tumor activity and weights were measured as above.
RESULTS
Molecular Design
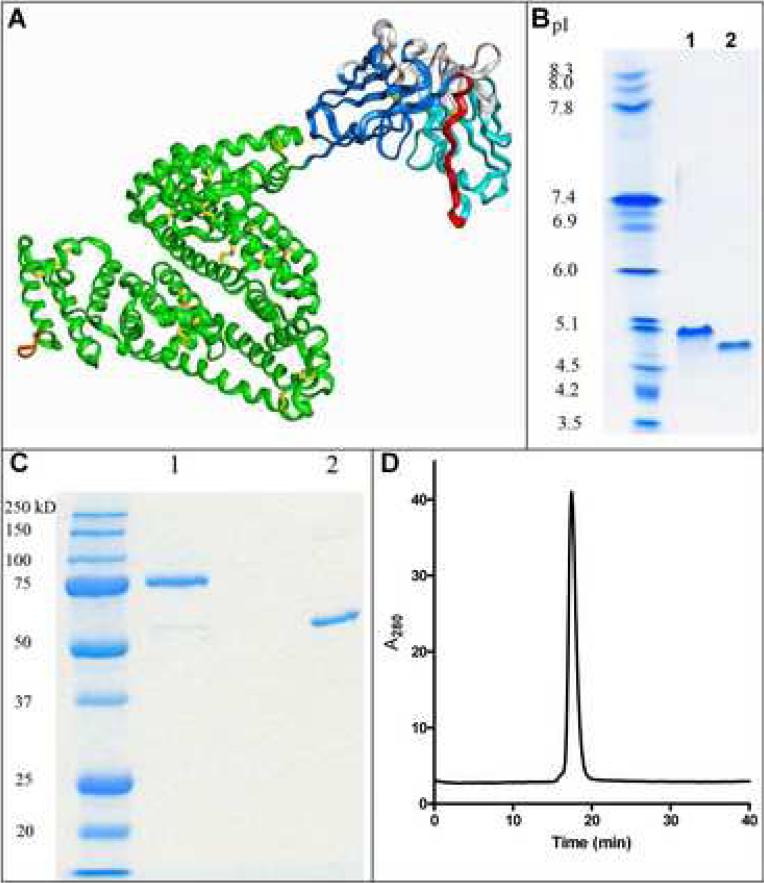
A molecular model of the T84.66 scFv-albumin fusion protein is illustrated in Figure 1A based on fusion of the individual protein crystal structures. Since the first three residues of HSA were not visible in the crystal structure, they were deleted rather than fusing the scFv directly to the amino-terminus of the mature HSA as previously reported [2].
Figure 1.
Molecular model and biochemical characterization of the scFv-albumin fusion protein. A) A molecular model of the fusion protein was developed based on the crystal structures of the individual proteins. Colors are VL (light blue), VH (dark blue), CDRs (white), GS18 linker (red), HSA (green), disulfide bonds (yellow) and His6 tag (orange). The purified immunobumin (lane 1) and HSA (lane 2) were analyzed by B) isoelectric focusing gel and C) SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions. D) The immunobumin was also analyzed by HPLC-SEC.
Mammalian expression, purification and characterization
The immunobumin was expressed in murine myeloma NS0 cells using the GS expression system. Clone 17F9 was selected with expression levels ranging from 5-45 μg/mL. The purification of this secreted His6 tagged protein consisted of clarification, affinity capture by IMAC and ceramic hydroxyapatite chromatography. Isoelectric focusing (Figure 1B) indicated that the immunobumin (lane 1) had an isoelectric point (pI) of 5.0 slightly higher than albumin's pI of 4.5 (lane 2). SDS-PAGE (Figure 1C) of the purified product (lane 1) versus HSA (lane 2) showed that the immunobumin had the expected apparent molecular weight and had a purity greater than 95%. A single peak was observed by HPLC-SEC (Figure 1D) that corresponded to the monomeric form.
Radiolabeling and immunoreactivity
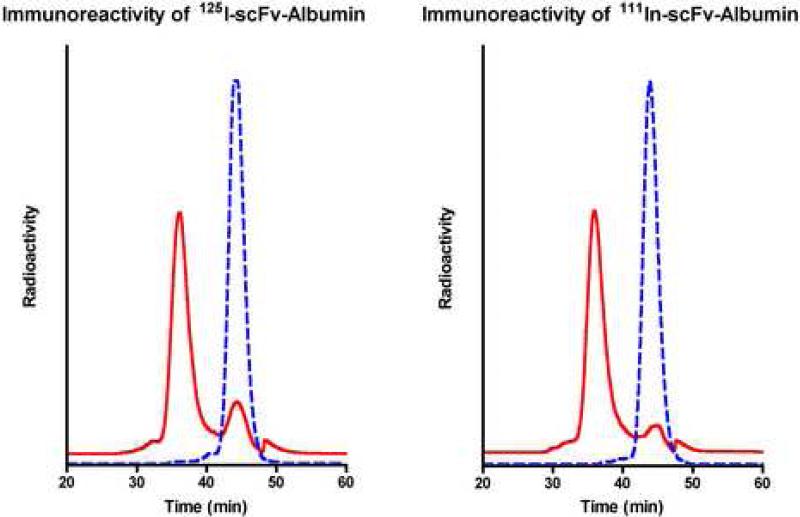
The immunobumin was directly radioiodinated or conjugated with N-hydroxysuccinimidyl DOTA for radiolabeling with [111In]. The radiolabeling yields of the [125I]- and [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin were 100%. Immunoreactivity to CEA was measured; both versions exhibited a shift to a higher molecular weight consistent with complexation with CEA, resulting in 81% and 88% immunoreactivity, respectively (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Immunoreactivity of [125I]- and [111In]-scFv-Albumin fusion protein. A) The [125I]-immunobumin and B) [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin were assayed for immunoreactivity. Radiochromatograms are shown with (solid line) and without (dotted line) incubation with CEA.
Biodistribution studies with [125I]-T84.66 immunobumin and [111In]-DOTA-T84.66 immunobumin
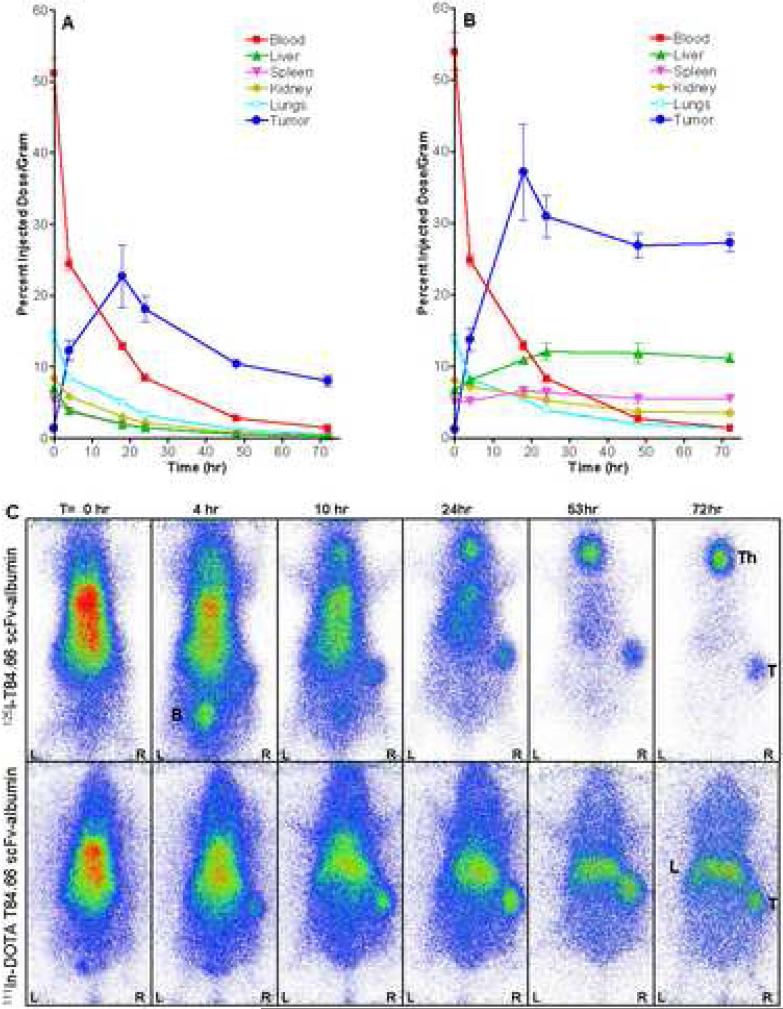
Dual label biodistribution studies were performed with [125I]- and [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin co-injected intravenously into athymic mice bearing human colon carcinoma LS-174T tumor xenografts. Groups of five mice were euthanized at 0, 4, 18, 24, 48 and 72 hr, the tissues analyzed and the data for both radionuclides plotted in Figure 3A and 3B. The [125I]-immunobumin demonstrated rapid uptake in the CEA-positive tumor reaching 12.3 ±1.4 %ID/g (mean±SEM) by 4 hr and reached a maximum of 22.7±6.0 %ID/g at 18 hr (Figure 3A). This was significantly higher than the [125I]-T84.66 scFv alone which reached a maximum of 4.9 %ID/g at 0.5 hr in the same animal model [8]. As expected for a radioiodinated molecule, there was no significant normal tissue uptake other than that due to blood pool activity. The [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin construct exhibited similarly rapid tumor uptake (13.8±1.5 %ID/g at 4 hr) reaching a maximum of 37.2±6.7 %ID/g by 18 hr (Figure 3B). The [111In] activity persisted at the tumor site until the last measured time point at 72 hr (27.3±1.3 %ID/g), at which point the tumor: blood ratio was 18.8:1. The liver had the highest normal tissue accumulation, reaching a plateau of 11-12 %ID/g from 18-72 hr. Kidneys (8.1±0.4 %ID/g at 0 hr) and spleen (6.6±0.5 %ID/g at 18 hr) had limited activity. Pharmacokinetic studies showed the [125I]- and [111In]-DOTA- versions had nearly identical blood clearance activity of radiolabel (T1/2α≈1 hr and T1/2β≈15 hr), which were comparable to the half-lives observed for an anti-TNF scFv-HSA fusion protein [2].
Figure 3.
Biodistribution and gamma camera imaging of the radiolabeled immunobumin in athymic mice bearing LS-174T xenografts. A) The [125I]-immunobumin and B) [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin were intravenously co-injected into xenograft-bearing mice, and tumor targeting and biodistribution studies performed. Groups of five mice were analyzed at each time point. Tumor and normal tissue uptake are expressed as percent injected dose per gram (%ID/g) and plotted with the standard error of the mean. C) Gamma camera imaging was performed by intravenously injecting 25 μCi on 2.5 μg of [125I]-immunobumin and 25 μCi on 6 μg of [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin. The mice were anaesthetized with isoflurane and placed on a planar scintigraphic camera, γ-IMAGER (BIOSPACE Mesures S.A., Paris, France), ventral side down and a 15 minute image was acquired. Imaging was performed at 0, 4, 10, 24, 53, and 72 hr; all images were half-life corrected. Tumor (T), bladder (B), thyroid (Th), and liver (L) are noted.
Imaging studies with [125I]-immunobumin and [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin
Planar gamma camera images of [125I]- and [111In]-DOTA immunobumin were acquired at 0, 4, 10, 24, 53 and 72 hours (Figure 3C). The images confirm the biodistribution data, i.e. both radiolabeled forms demonstrated tumor localization and rapid clearance from the vasculature. The thyroid gland was not blocked, resulting in free iodine/iodotyrosine accumulation in the thyroid. For the [111In]-DOTA-version, the liver was the only normal organ or tissue with appreciable uptake.
DISCUSSION
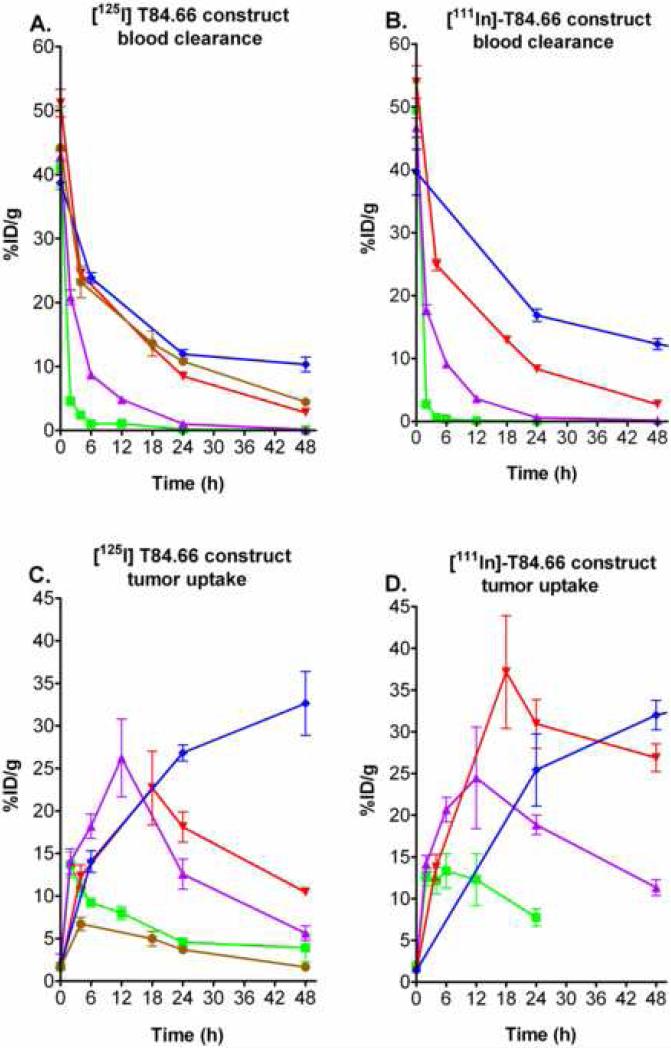
Small anti-tumor scFv antibody molecules exhibit low tumor uptake due to rapid renal clearance, but Adams et al. demonstrated that high tumor uptake can be achieved if the clearance mechanism is artificially altered [19]. The fusion of albumin to small therapeutic proteins or scFvs has been shown to extend their half-life in the circulation [1], but so far no biodistribution or imaging data has been published. The [125I]-immunobumin data presented here support this rationale with a dramatic increase in tumor uptake of 22.7 %ID/g at 18 hr compared to 4.9 %ID/g at 0.5 hr for the [125I]-T84.66 scFv alone [8]. A biodistribution of radioiodinated HSA, showed a similar blood clearance as the immunobumin (Figure 4A), yet the HSA tumor uptake was only 6.7 %ID/g at 4 hr (Figure 4C). These data provide evidence of the immunobumin's specific tumor uptake. While HSA had some tumor retention, at this point we can only speculate this is a result of blood flow/permeability activity and the presence of albumin-binding proteins on the cell surface [20, 21].
Figure 4.
Comparison of the blood clearance and tumor uptake of the radiolabeled T84.66 scFv-albumin fusion protein with the T84.66 diabody, minibody, humanized antibody and HSA. The [125I]- and [111In]- blood clearance [A) and B)] and [125I]- and [111In]- tumor uptake [C) and D)] of the immunobumin (red inverted diamond) were compared to the diabody (green square), minibody (purple triangle) and humanized antibody (blue diamond). The blood clearance and tumor uptake of radioiodinated HSA (brown circle) were also plotted for comparison. Groups of at least five mice were analyzed at each time point. Mean activity and standard error were expressed as percent injected dose per gram (%ID/g) versus time. In some instances, errors are smaller than the symbols used to indicate mean values.
Based on the high affinity T84.66 monoclonal antibody, our group has developed the T84.66 diabody (scFv dimer) and minibody (scFv-CH3 dimer) as in vivo imaging agents [7]. To provide a perspective on the immunobumin imaging potential, [125I]- and [111In]-DOTA immunobumin blood and tumor uptake data were compared with data for the T84.66 diabody [22], minibody [10] and humanized antibody [23] previously obtained in the same mouse tumor xenograft model (Figure 4). Although similar in molecular size, the immunobumin (90 kDa) had significantly slower blood clearance than the minibody (80 kDa), but cleared faster than the intact humanized antibody.
The albumin-fusion has potential as an imaging agent because of its high tumor uptake at a relatively early timepoint and low normal tissue accumulation. The radiometal labeled immunobumin achieved a tumor uptake of 37 %ID/g, which was substantially higher than the [111In]-minibody's 26.2 %ID/g. The key difference between the radiometal labeled immunobumin and the minibody is that the [111In]- labeled minibody had much higher hepatic retention that approached 19 %ID/g [10], resulting in tumor to liver ratios of 1.4 compared to 3.4 for the immunobumin. Previous reports suggested the albumin fusion protein's extended blood circulation time was due only to the increased molecular mass. Based on the [111In]-immunobumin biodistribution data, we speculate that these biodistribution differences result from recognition of the albumin-fusion protein by the FcRn receptor [12], which does not occur for the minibody (unpublished results).
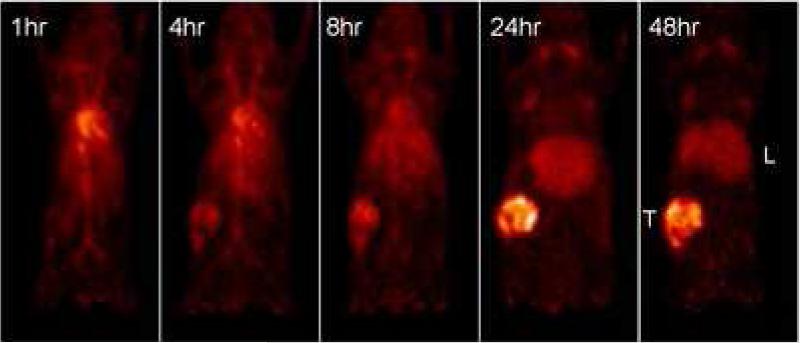
The [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin's high tumor uptake at an early time point and limited liver accumulation suggested the potential use as a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agent. In a pilot study, the DOTA-immunobumin was radiolabeled with [64Cu] and had a radiolabeling yield of 100% and immunoreactivity of 87% (data not shown). The [64Cu]-DOTA-immunobumin was injected into a xenografted mouse and imaged with a microPET™ scanner. Figure 5 shows serial maximum intensity projection (MIP) images acquired at various times. Tumor localization is evident at 4 hr and reaches the highest intensity at 24 hr. Direct measurement of radioactive accumulation at 48 hr showed the tumor had 32.3 %ID/g, blood 3.3 %ID/g and liver 13.3 %ID/g. While only from a single mouse, these levels reflect the [111In]-DOTA-immunobumin biodistribution. The striking high tumor to normal organ contrast provides compelling support for development of the DOTA-scFv-albumin fusion protein as a clinical immunoPET agent.
Figure 5.
PET imaging of the [64Cu]-radiolabeled immunobumin. [64Cu]-DOTA-immunobumin (50 μCi) was intravenously injected into a xenografted mouse and dynamic microPET imaging was performed under isoflurane anesthesia. Images are anterior-view maximum intensity projections (MIPs) normalized to reflect radiodecay-corrected relative image intensity. Image acquisition times were 20 min at 1, 4, and 8 hr, 45 min at 24 hr, and 60 min at 48 hr post injection. Tumor (T) and liver (L) are noted.
CONCLUSION
The anti-CEA scFv-albumin fusion protein demonstrates highly selective tumor uptake and shows low normal organ or tissue accumulation over cognate recombinant antibodies. PET imaging data provide support for the development of this antibody-based platform for new imaging agents.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Yim Wu, Lin Li, Amitkumar Ahuja, and Aaron Shoop for their expert technical assistance. This research was supported by NCI grant 43904.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
REFERENCES
- 1.Chuang VT, Kragh-Hansen U, Otagiri M. Pharmaceutical strategies utilizing recombinant human serum albumin. Pharm Res. 2002;19:569–577. doi: 10.1023/a:1015396825274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Smith BJ, Popplewell A, Athwal D, Chapman AP, Heywood S, West SM, Carrington B, Nesbitt A, Lawson AD, Antoniw P, Eddelston A, Suitters A. Prolonged in vivo residence times of antibody fragments associated with albumin. Bioconjug Chem. 2001;12:750–756. doi: 10.1021/bc010003g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Huhalov A, Chester KA. Engineered single chain antibody fragments for radioimmunotherapy. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;48:279–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dennis MS, Zhang M, Meng YG, Kadkhodayan M, Kirchhofer D, Combs D, Damico LA. Albumin binding as a general strategy for improving the pharmacokinetics of proteins. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:35035–35043. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205854200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dennis MS, Jin H, Dugger D, Yang R, McFarland L, Ogasawara A, Williams S, Cole MJ, Ross S, Schwall R. Imaging tumors with an albumin-binding Fab, a novel tumor-targeting agent. Cancer Res. 2007;67:254–261. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Orlova A, Tolmachev V, Pehrson R, Lindborg M, Tran T, Sandstrom M, Nilsson FY, Wennborg A, Abrahmsen L, Feldwisch J. Synthetic affibody molecules: a novel class of affinity ligands for molecular imaging of HER2-expressing malignant tumors. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2178–2186. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wu AM, Yazaki PJ. Designer genes: recombinant antibody fragments for biological imaging. Q J Nucl Med. 2000;44:268–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wu AM, Chen W, Raubitschek A, Williams LE, Neumaier M, Fischer R, Hu SZ, Odom-Maryon T, Wong JY, Shively JE. Tumor localization of anti-CEA single-chain Fvs: improved targeting by non-covalent dimers. Immunotechnology. 1996;2:21–36. doi: 10.1016/1380-2933(95)00027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wong JY, Chu DZ, Williams LE, Yamauchi DM, Ikle DN, Kwok CS, Liu A, Wilczynski S, Colcher D, Yazaki PJ, Shively JE, Wu AM, Raubitschek AA. Pilot trial evaluating an 123I-labeled 80-kilodalton engineered anticarcinoembryonic antigen antibody fragment (cT84.66 minibody) in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;15:5014–5021. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yazaki PJ, Wu AM, Tsai S-w., Williams L, Ikle DN, Wong JYC, Shively JE, Raubitschek AA. Tumor targeting of radiometal labeled anti-CEA recombinant T84.66 diabody and T84.66 minibody: Comparison to radioiodinated fragments. Bioconj Chem. 2001;12:220–228. doi: 10.1021/bc000092h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Peter T., Jr. All about albumin: biochemistry, genetics and medical applications. Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Anderson CL, Chaudhury C, Kim J, Bronson CL, Wani MA, Mohanty S. Perspective -- FcRn transports albumin: relevance to immunology and medicine. Trends Immunol. 2006;27:343–348. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2006.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wu AM. Engineering multivalent antibody fragments for in vivo targeting. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;248:209–225. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-666-5:209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carmichael JA, Power BE, Garrett TP, Yazaki PJ, Shively JE, Raubitschek AA, Wu AM, Hudson PJ. The crystal structure of an anti-CEA scFv diabody assembled from T84.66 scFvs in V(L)-to-V(H) orientation: implications for diabody flexibility. J Mol Biol. 2003;326:341–351. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sugio S, Kashima A, Mochizuki S, Noda M, Kobayashi K. Crystal structure of human serum albumin at 2.5 A resolution. Protein Eng. 1999;12:439–446. doi: 10.1093/protein/12.6.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Horton RM, Hunt HD, Ho SN, Pullen JK, Pease LR. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989;77:61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yazaki PJ, Wu AM. Expression of recombinant antibodies in mammalian cell lines. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;248:255–268. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-666-5:255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Qi J, Leahy RM. Resolution and noise properties of MAP reconstruction for fully 3-D PET. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2000;19:493–506. doi: 10.1109/42.870259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Adams GP, Schier R, McCall AM, Simmons HH, Horak EM, Alpaugh RK, Marks JD, Weiner LM. High affinity restricts the localization and tumor penetration of single-chain Fv antibody molecules. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4750–4755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tanaka T, Shiramoto S, Miyashita M, Fujishima Y, Kaneo Y. Tumor targeting based on the effect of enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) and the mechanism of receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME). Int J Pharm. 2004;277:39–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2003.09.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang J, Ueno H, Masuko T, Hashimoto Y. Binding of serum albumin on tumor cells and characterization of the albumin binding protein. J Biochem (Tokyo) 1994;115:898–903. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wu AM, Williams LE, Zieran L, Padma A, Sherman MA, Bebb GG, Odom-Maryon T, Wong JYC, Shively JE, Raubitschek A. Anti-carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) diabody for rapid tumor targeting and imaging. Tumor Targeting. 1999;4:47–58. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yazaki PJ, Sherman MA, Shively JE, Ikle D, Williams LE, Wong JYC, Colcher D, Wu AM, Raubitschek AA. Humanization of the anti-CEA T84.66 antibody based on crystal structure data. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection. 2004;17:481–489. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzh056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]