Abstract
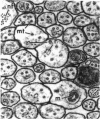
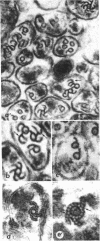
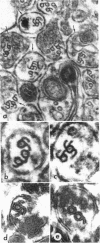
Pieces of olfactory nerve of the bullfrog were extracted in a tubulin assembly buffer medium containing detergents. With incubation at 37 degrees C in such medium containing soluble tubulin, ribbons of protofilaments are formed on the surfaces of microtubules, with the ribbons curving in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. The direction of hooking reflects the polarity of the microtubule. In nerve pieces oriented such that cross sections could be viewed toward the perikarya of the axons, over 90% of the ribbons on microtubules showed a clockwise orientation. When observers were looking toward the axonal terminals, most ribbons on microtubules showed a counterclockwise direction. In single axons in which ribbons appeared on all the contained microtubules, the ribbons showed a single directionality. The evidence suggests that microtubules in axons have a single polarity, probably reflecting their assembly from the perikarya outward through the axoplasm. If bidirectional transport is assumed in these axons, it is not reflected by the polarity of their microtubules, which may mean that the directionality of transport is provided by components other than microtubules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burton P. R., Fernandez H. L. Delineation by lanthanum staining of filamentous elements associated with the surfaces of axonal microtubules. J Cell Sci. 1973 Mar;12(2):567–583. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.2.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Himes R. H. Electron microscope studies of pH effects on assembly of tubulin free of associated proteins. Delineation of substructure by tannic acid staining. J Cell Biol. 1978 Apr;77(1):120–133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M., Thomson J. N. Organization of neuronal microtubules in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):278–289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Porter K. R. Microtrabecular structure of the axoplasmic matrix: visualization of cross-linking structures and their distribution. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):464–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euteneuer U., McIntosh J. R. Polarity of some motility-related microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):372–376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., McIntosh J. R. Visualization of the structural polarity of microtubules. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):517–519. doi: 10.1038/286517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., Zieve G. W., McIntosh J. R. Evidence for microtubule subunit addition to the distal end of mitotic structures in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):152–159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P. Axonal flow and fast transport in nerves. Adv Comp Physiol Biochem. 1975;6:75–163. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-011506-8.50008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himes R. H., Burton P. R., Gaito J. M. Dimethyl sulfoxide-induced self-assembly of tubulin lacking associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6222–6228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himes R. H., Burton P. R., Kersey R. N., Pierson G. B. Brain tubulin polymerization in the absence of "microtubule-associated proteins". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4397–4399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Binder L. I., Rosenbaum J. L. The periodic association of MAP2 with brain microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):266–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S. Fast transport of materials in mammalian nerve fibers. Science. 1972 Apr 21;176(4032):252–260. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4032.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson F. E., Jr Mechanism of axoplasmic transport. J Neurobiol. 1971;2(4):347–360. doi: 10.1002/neu.480020407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt F. O. Fibrous proteins--neuronal organelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1092–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]