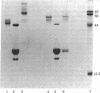
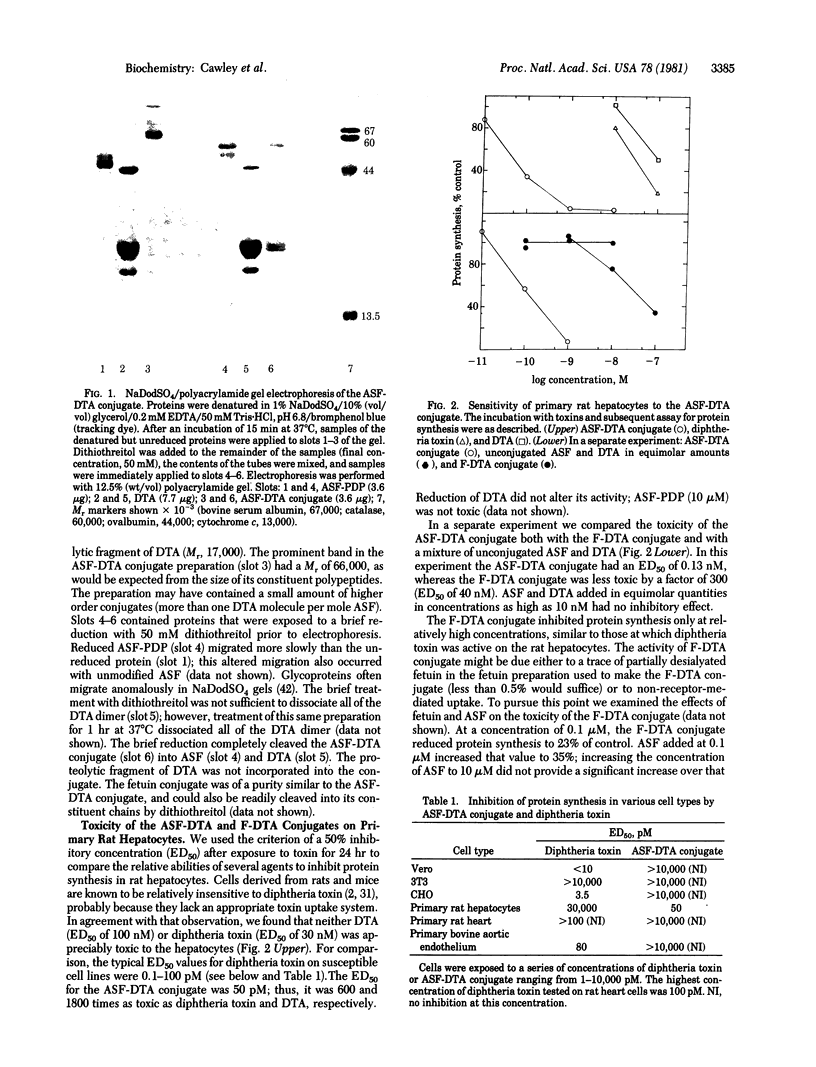
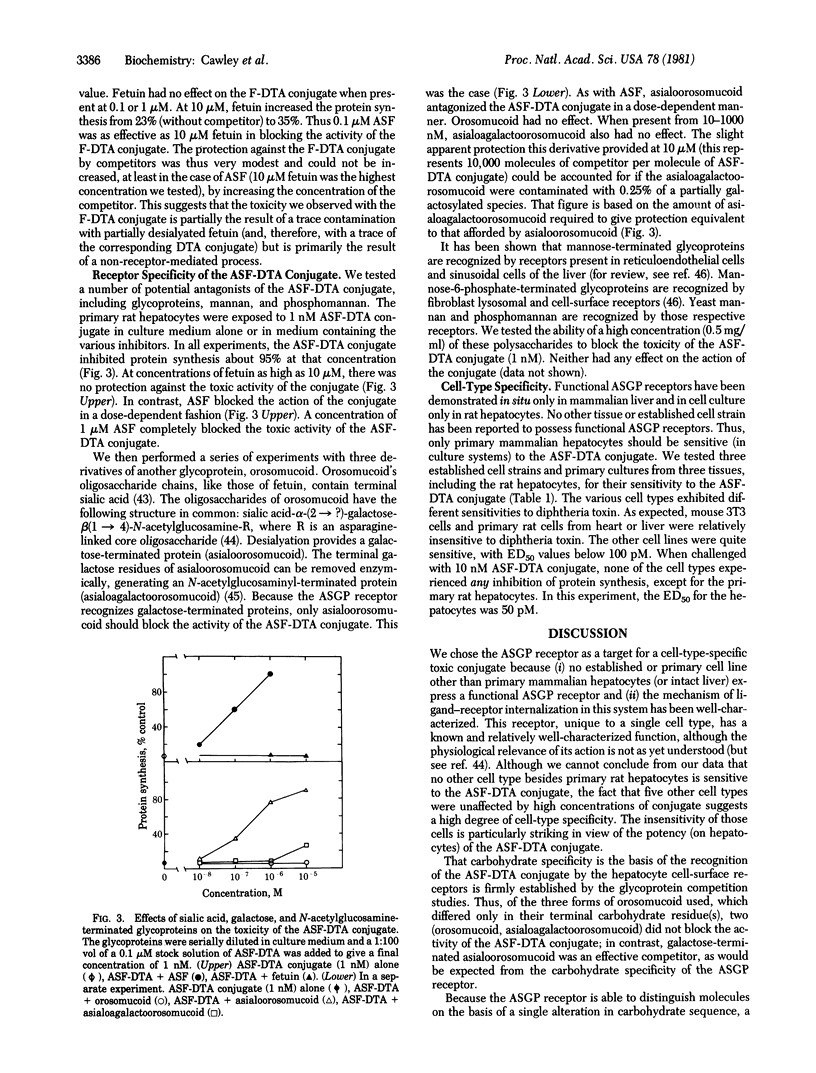
Abstract
We have constructed a toxic hybrid protein that is recognized by asialoglycoprotein (ASGP) receptors of cultured rat hepatocytes. The conjugate consists of fragment A of diphtheria toxin (DTA) linked by a disulfide bond to asialofetuin (ASF). This conjugate is highly toxic, inhibiting protein synthesis in primary rat hepatocytes at concentrations as low as 10 pM. The ASF-DTA conjugate was 600 and 1800 times as toxic as diphtheria toxin and DTA, respectively, on primary rat hepatocytes. The ASGP receptor recognizes galactose-terminated proteins. We tested a series of glycoproteins for their ability to block the action of the ASF-DTA conjugate. Fetuin and orosomucoid, two glycoproteins with terminal sialic acid on their oligosaccharide chains, did not block the action of the conjugate. Their galactose-terminated asialo derivatives, ASF and asialoorosomucoid, as expected, did block the action of the conjugate. The N-acetylglucosaminyl-terminated derivative (asialogalactoorsomucoid) had no appreciable effect on the activity of the conjugate. We tested the ASF-DTA conjugate on six cell types; except for primary rat hepatocytes, none of them were affected by a high concentration (10 nM) of ASF-DTA conjugate. A fetuin-DTA conjugate was less toxic by a factor of 300 than the ASF-DTA conjugate and exerted its effects primarily through non-receptor-mediated mechanisms. The highly toxic ASF-DTA conjugate is cell-type specific, and its action is mediated by a well-characterized receptor, whose mechanism of receptor-ligand internalization has been extensively investigated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attie A. D., Pittman R. C., Steinberg D. Metabolism of native and of lactosylated human low density lipoprotein: evidence for two pathways for catabolism of exogenous proteins in rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5923–5927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attie A. D., Weinstein D. B., Freeze H. H., Pittman R. C., Steinberg D. Unaltered catabolism of desialylated low-density lipoprotein in the pig and in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 15;180(3):647–654. doi: 10.1042/bj1800647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawley D. B., Hedblom M. L., Houston L. L. Homology between ricin and Ricinus communis agglutinin: amino terminal sequence analysis and protein synthesis inhibition studies. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):744–755. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawley D. B., Herschman H. R., Gilliland D. G., Collier R. J. Epidermal growth factor-toxin A chain conjugates: EGF-ricin A is a potent toxin while EGF-diphtheria fragment A is nontoxic. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):563–570. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90366-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. M., Dazord A., Neville D. M., Jr Artificial hybrid protein containing a toxic protein fragment and a cell membrane receptor-binding moiety in a disulfide conjugate. II. Biochemical and biologic properties of diphtheria toxin fragment A-S-S-human placental lactogen. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1515–1522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. M., Neville D. M., Jr Artificial hybrid protein containing a toxic protein fragment and a cell membrane receptor-binding moiety in a disulfide conjugate. I. Synthesis of diphtheria toxin fragment A-S-S-human placental lactogen with methyl-5-bromovalerimidate. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1505–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Collier R. J. The mechanism of ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 catalyzed by fragment A from diphtheria toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 11;483(2):248–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiume L., Mattioli A., Balboni P. G., Tognon M., Barbanti-Brodano G., de Vries J., Wieland T. Enhanced inhibition of virus DNA synthesis in hepatocytes by trifluorothymidine coupled to asialofetuin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 1;103(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournet B., Montreuil J., Strecker G., Dorland L., Haverkamp J., Vliegenthart F. G., Binette J. P., Schmid K. Determination of the primary structures of 16 asialo-carbohydrate units derived from human plasma alpha 1-acid glycoprotein by 360-MHZ 1H NMR spectroscopy and permethylation analysis. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5206–5214. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland D. G., Collier R. J., Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Chimeric toxins: toxic, disulfide-linked conjugate of concanavalin A with fragment A from diphtheria toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5319–5323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland D. G., Steplewski Z., Collier R. J., Mitchell K. F., Chang T. H., Koprowski H. Antibody-directed cytotoxic agents: use of monoclonal antibody to direct the action of toxin A chains to colorectal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4539–4543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harary I., Hoover F., Farley B. The isolation and cultivation of rat heart cells. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:740–745. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Stukenbrok H. An electron microscope autoradiographic study of the carbohydrate recognition systems in rat liver. II. Intracellular fates of the 125I-ligands. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):65–81. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Wilson G., Ashwell G., Stukenbrok H. An electron microscope autoradiographic study of the carbohydrate recognition systems in rat liver. I. Distribution of 125I-ligands among the liver cell types. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):47–64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G., Stockert R. J., Morell A. G. The isolation and properties of a rabbit liver binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Chemical and physical properties of an hepatic membrane protein that specifically binds asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1296–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Isolation and characterization of an avian hepatic binding protein specific for N-acetylglucosamine-terminated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6536–6543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunney J., Ashwell G. A hepatic receptor of avian origin capable of binding specifically modified glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):341–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuho Y., Hara T., Noguchi T. Preparation of a hybrid of fragment Fab' of antibody and fragment A of diphtheria toxin and its cytotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):320–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91627-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins W. K., Shimizu N. Synthesis of a cytotoxic insulin cross-linked to diphtheria toxin fragment A capable of recognizing insulin receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Selection and characterization of cells resistant to diphtheria toxin and pseudomonas exotoxin A: presumptive translational mutants. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Irvine R. A., Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H., Ashwell G. Physical and chemical studies on ceruloplasmin. V. Metabolic studies on sialic acid-free ceruloplasmin in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):155–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeltmann T. N., Heath E. C. A hybrid protein containing the toxic subunit of ricin and the cell-specific subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin. II. Biologic properties. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1028–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Prieels J. P., Glasgow L. R., Hill R. L. Sialyl- and fucosyltransferases in the biosynthesis of asparaginyl-linked oligosaccharides in glycoproteins. Mutually exclusive glycosylation by beta-galactoside alpha2 goes to 6 sialyltransferase and N-acetylglucosaminide alpha1 goes to 3 fucosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5617–5624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. Subcellular distribution of a mammalian hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7539–7544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. The binding of desialylated glycoproteins by plasma membranes of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4825–4833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Debanne M. T., Hatton M. C., Koj A. Elimination of asialofetuin and asialoorosomucoid by the intact rat. Quantitative aspects of the hepatic clearance mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 3;541(3):372–384. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M. Selection and characterization of bovine aortic endothelial cells. In Vitro. 1978 Dec;14(12):966–980. doi: 10.1007/BF02616210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer C. J., Ashwell G. Studies on a mammalian hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. Evidence for receptor recycling in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3008–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuchbury T., Shipton M., Norris R., Malthouse J. P., Brocklehurst K., Herbert J. A., Suschitzky H. A reporter group delivery system with both absolute and selective specificity for thiol groups and an improved fluorescent probe containing the 7-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole moiety. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):417–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1510417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg R. W., Day J. F., Baynes J. W., Thorpe S. R. Carbohydrate-mediated clearance of immune complexes from the circulation. A role for galactose residues in the hepatic uptake of IgG-antigen complexes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6820–6825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Nilsson M., Norum K. R. Uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled asialo-fetuin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Yamaizumi M., Mekada E., Okada Y., Tsuda M., Kurokawa T., Sugino Y. Reconstitution of hybrid toxin from Fragment A of diphtheria toxin and a subunit of Wistaria floribunda lectin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6307–6310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten L., Ashwell G. The binding of desialylated glycoproteins by plasma membranes of rat liver. Development of a quantitative inhibition assay. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4633–4640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall D. A., Wilson G., Hubbard A. L. The galactose-specific recognition system of mammalian liver: the route of ligand internalization in rat hepatocytes. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel P. H. Characterization of the asialoglycoprotein receptor on isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6111–6120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi T., Kato R., Beppu M., Terao T., Inoue Y., Ikawa Y., Osawa T. Preparation of concanavalin A-ricin A-chain conjugate and its biologic activity against various cultured cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jun;62(6):1387–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle R. J., Murray G. J., Neville D. M., Jr Ricin linked to monophosphopentamannose binds to fibroblast lysosomal hydrolase receptors, resulting in a cell-type-specific toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5559–5562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle R. J., Neville D. M., Jr Receptor-mediated transport of the hybrid protein ricin-diphtheria toxin fragment A with subsequent ADP-ribosylation of intracellular elongation factor II. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11089–11096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]