Abstract
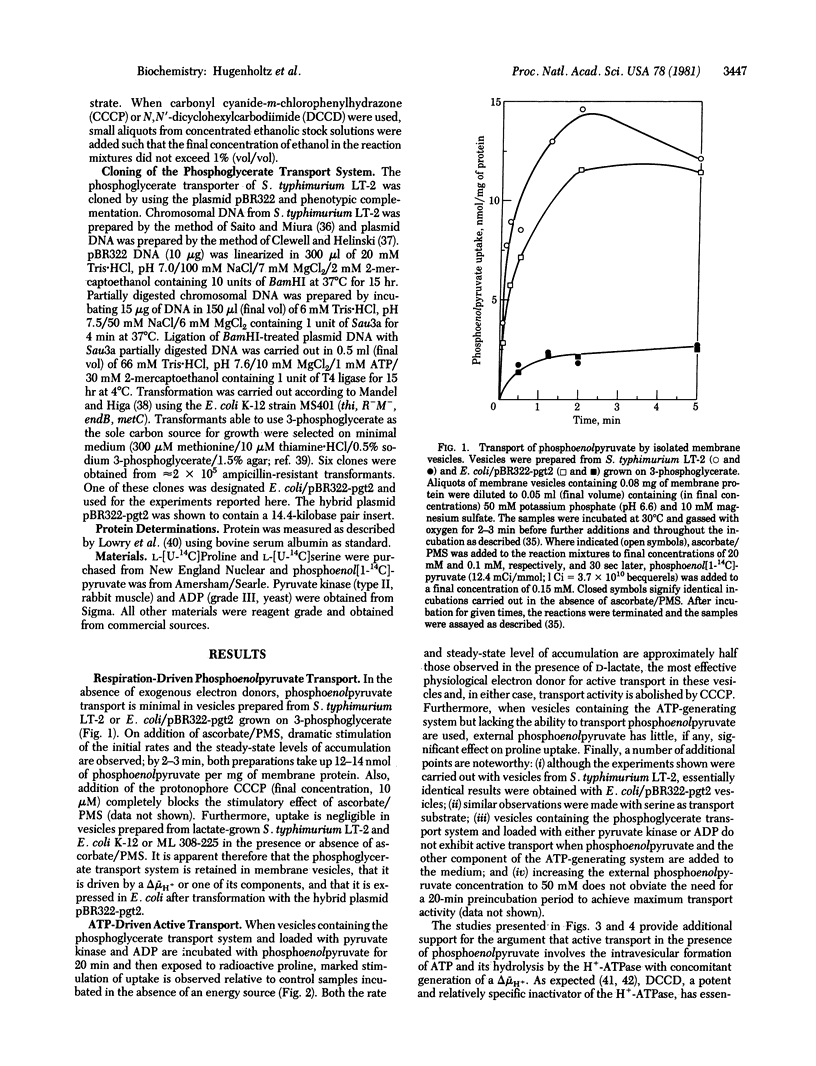
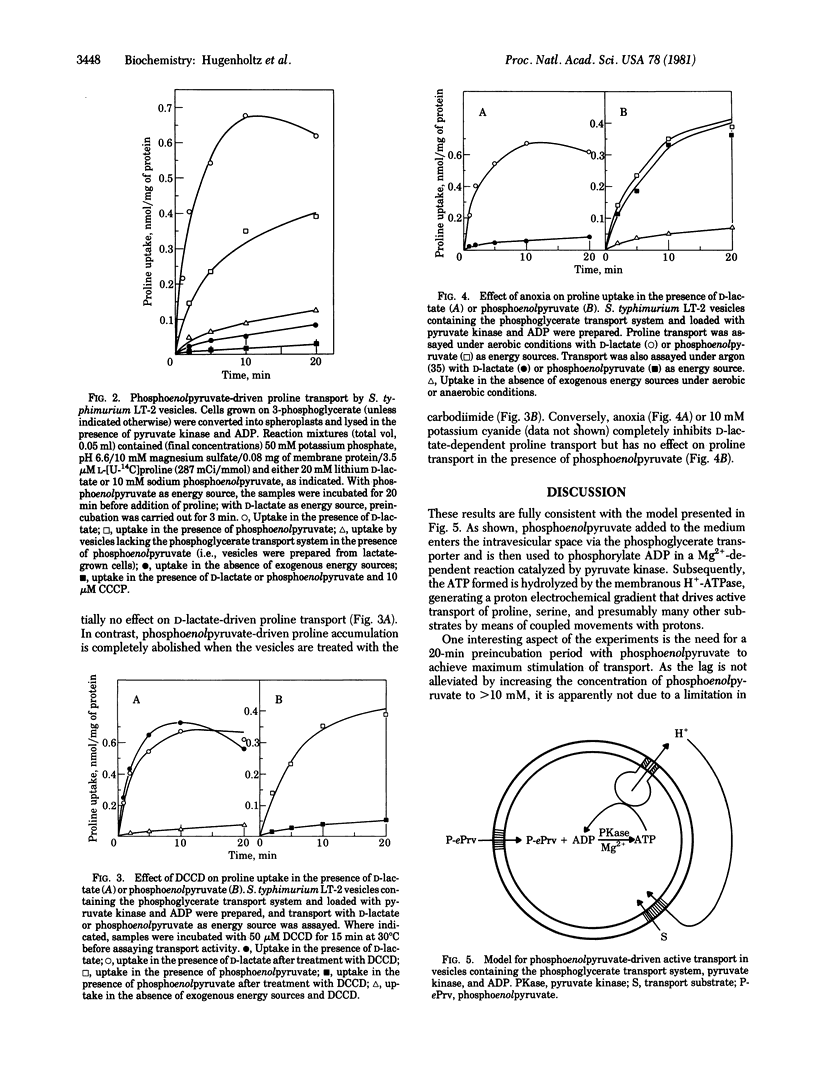
Membrane vesicles from Salmonella typhimurium induced for phosphoglycerate transport, were loaded with pyruvate kinase and ADP by lysing spheroplasts under appropriate conditions. Vesicles so prepared catalyze active transport of proline and serine in the presence of phosphoenolpyruvate; this activity is abolished by the protonophore carbonyl cyanide-m-chlorophenylhydrazone and by the H+-ATPase inhibitor N,N' dicyclohexylcarbodiimide but not by anoxia or cyanide. In contrast, D-lactate-driven active transport is abolished by the hydrazone and by anoxia or cyanide but not by the carbodiimide. Moreover, phosphoenolpyruvate does not drive transport effectively in vesicles that lack the phosphoglycerate transport system. The results are consistent with an overall mechanism in which phosphoenolpyruvate gains access to the interior of the vesicles by means of the phosphoglycerate transporter and is then acted on by pyruvate kinase to phosphorylate ADP. ATP formed inside of the vesicles is then hydrolyzed by the H+-ATPase, leading to the generation of a proton electrochemical gradient that drives H+/solute symport. By using pBR322 as vector and Escherichia coli as host, a fragment of S. typhimurium DNA coding for the phosphoglycerate transport system has been cloned. E. coli membrane vesicles containing the phosphoglycerate transport system also catalyze transport in the presence of phosphoenolpyruvate when they are loaded with pyruvate kinase and ADP.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K. H., Staehelin L. A. Orientation of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli as detected by freeze-cleave electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):888–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.888-899.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1588–1594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the calcium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1957–1963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Mosher M. E., Futai M., Fillingame R. H. Subunits of the H+-ATPase of Escherichia coli. Overproduction of an eight-subunit F1F0-ATPase following induction of a lambda-transducing phage carrying the unc operon. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12037–12041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M. Orientation of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli prepared by different procedures. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(1):15–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01870079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. L., Kennedy E. P. Energy-transducing adenosine triphosphatase from Escherichia coli: purification, properties, and inhibition by antibody. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):772–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.772-781.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heefner D. L., Harold F. M. ATP-linked sodium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. I. The sodium circulation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11396–11402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heefner D. L., Kobayashi H., Harold F. M. ATP-linked sodium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. II. Energy coupling in everted membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11403–11407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg E. L., Hinkle P. C. Oxidative phosphorylation and proton translocation in membrane vesicles prepared from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):178–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90908-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:698–709. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport studies in bacterial membrane vesicles. Science. 1974 Dec 6;186(4167):882–892. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4167.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster J. R., Jr, Hinkle P. C. Studies of the beta-galactoside transporter in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. I. Symmetrical facilitated diffusion and proton gradient-coupled transport. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7657–7661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature. 1961 Jul 8;191:144–148. doi: 10.1038/191144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels P. A., Konings W. N. The electrochemical proton gradient generated by light in membrane vesicles and chromatophores from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Performance and conservation of osmotic work by proton-coupled solute porter systems. J Bioenerg. 1973 Jan;4(1):63–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01516051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. The Ninth Sir Hans Krebs Lecture. Compartmentation and communication in living systems. Ligand conduction: a general catalytic principle in chemical, osmotic and chemiosmotic reaction systems. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar 15;95(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Antigenic architecture of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1422–1426. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1413–1422. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Molecular structure of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3148–3152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Kaback H. R. The role of the carbodiimide-reactive component of the adenosine-5'-triphosphatase complex in the proton permeability of Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2741–2746. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. Reversible effects of chaotropic agents on the proton permeability of Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3387–3391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical proton gradient in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):848–854. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The relationship between the electrochemical proton gradient and active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):854–859. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reenstra W. W., Patel L., Rottenberg H., Kaback H. R. Electrochemical proton gradient in inverted membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 8;19(1):1–9. doi: 10.1021/bi00542a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P., McClees J. S. Active transport of calcium in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5042–5046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U. Regulation of carbohydrate transport activities in Salmonella typhimurium: use of the phosphoglycerate transport system to energize solute uptake. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):611–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.611-617.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Wentzel D. L., Feucht B. U., Judice J. J. A transport system for phosphoenolpyruvate, 2-phosphoglycerate, and 3-phosphoglycerate in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5089–5096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Fishkes H. Sodium-proton antiport in isolated membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):706–711. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., Kaback H. R., Hawkins T., Kohn L. D. Immunochemical properties of the membrane-bound D-lactate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4285–4290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. P., Bragg P. D. Effect of inhibitors on the substrate-dependent quenching of 9-aminoacridine fluorescence in inside-out membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):177–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. P., Bragg P. D. The membrane potential in everted vesicles of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jun;195(1):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Kaback H. R. Sodium-dependent methyl 1-thio-beta-D-galactopyranoside transport in membrane vesicles isolated from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1977 May 17;16(10):2130–2136. doi: 10.1021/bi00629a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Rosen B. P. Calcium transport driven by a proton gradient and inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):962–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Rosen B. P. Characterization of an active transport system for calcium in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7687–7692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Cellular transport mechanisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:933–965. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



