Abstract
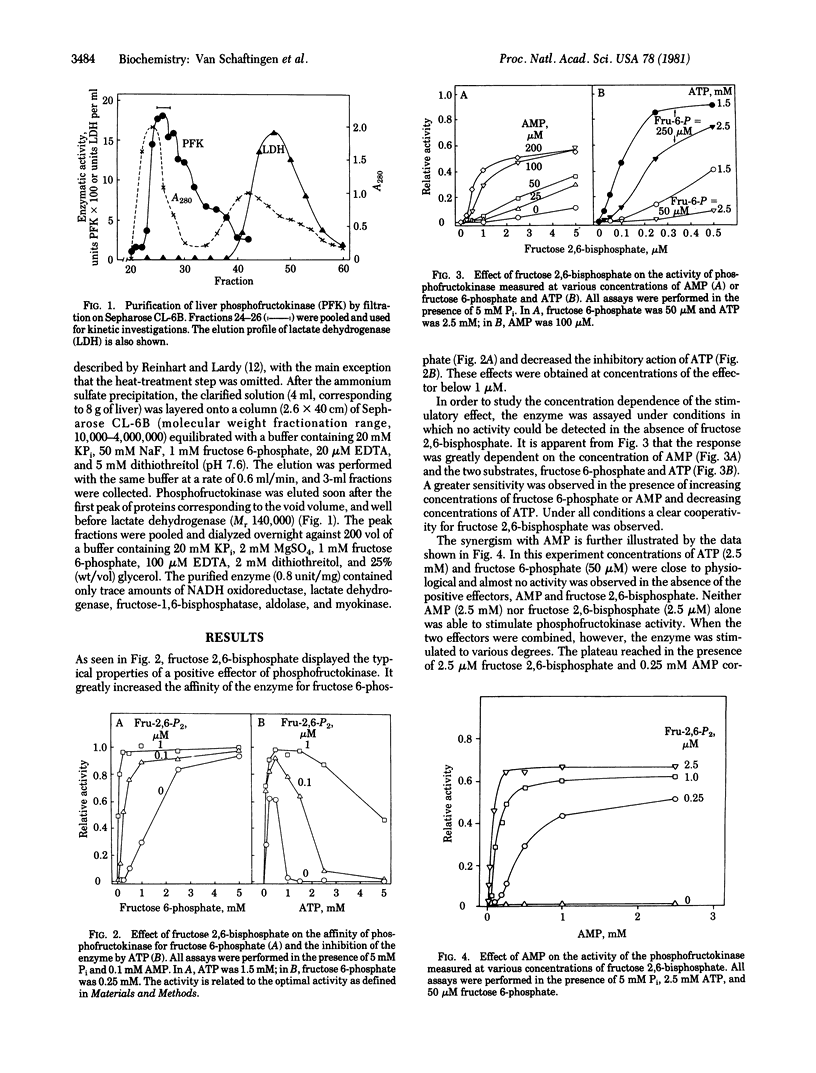
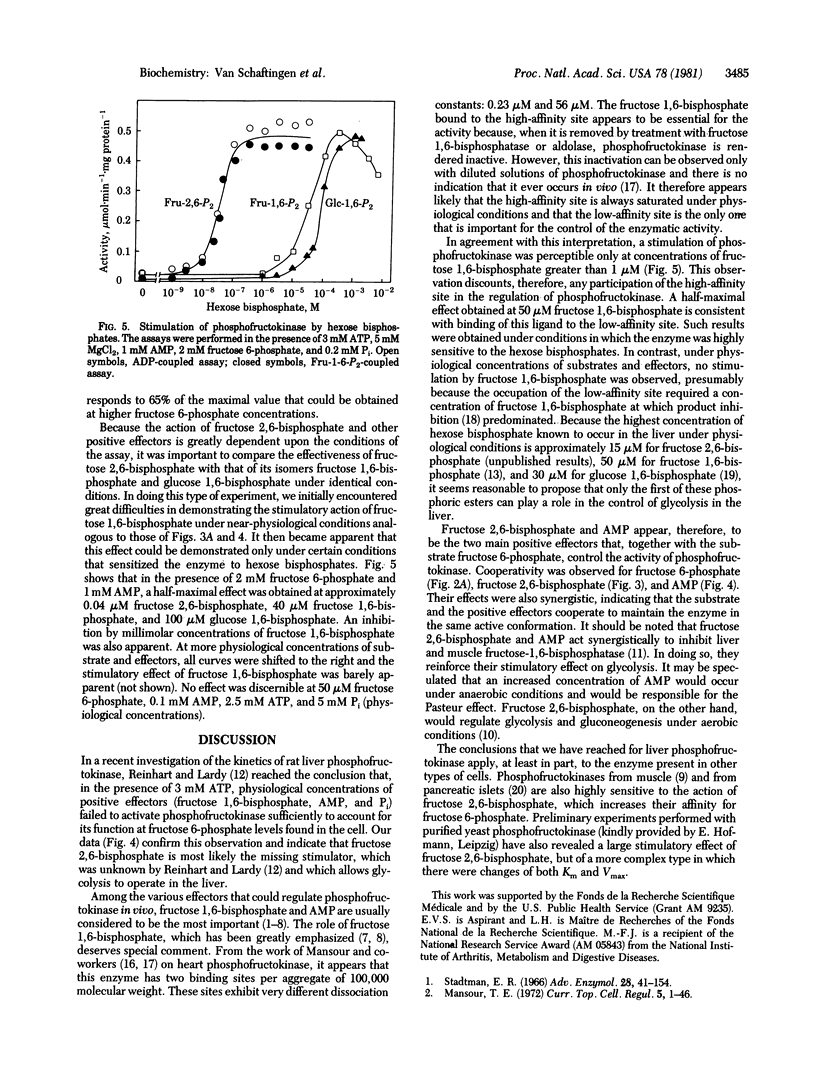
Rat liver 6-phosphofructokinase (ATP-D-fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.11) was partially purified free of interfering enzymes by a rapid procedure. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, at micromolar concentrations, greatly stimulated the enzyme by increasing its affinity for fructose 6-phosphate and relieving the inhibition by ATP. Its action was synergistic with that of AMP. As a stimulator of liver phosphofructokinase, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate was approximately 1000- and 2500-fold more efficient than fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and glucose 1,6-bisphosphate, respectively. The concentration at which a half-maximal effect was obtained with the hexose bisphosphates was dependent upon the experimental conditions. It was relatively high at physiological concentrations of substrates, AMP, and Pi, and under these conditions the positive effect of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate was no longer detectable. This was probably due to the negative effect of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate as a reaction product inhibitor. It is concluded that fructose 2,6-bisphosphate rather than fructose 1,6-bisphosphate controls, in association with other effectors, the activity of phosphofructokinase in the liver.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boiteux A., Hess B., Sel'kov E. E. Creative functions of instability and oscillations in metabolic systems. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1980;17:171–203. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152817-1.50010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand I. A., Söling H. D. Rat liver phosphofructokinase. Purification and characterization of its reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7824–7831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann E. The significance of phosphofructokinase to the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1976;75:1–68. doi: 10.1007/BFb0030484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A., van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Is the glucose-induced stimulation of glycolysis in pancreatic islets attributable to activation of phosphofructokinase by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate? FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):217–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80722-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour T. E. Phosphofructokinase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1972;5:1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passonneau J. V., Lowry O. H., Schulz D. W., Brown J. G. Glucose 1,6-diphosphate formation by phosphoglucomutase in mammalian tissues. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):902–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart G. D., Lardy H. A. Rat liver phosphofructokinase: kinetic activity under near-physiological conditions. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1477–1484. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Mansour T. E. Studies on heart phosphofructokinase. Binding of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, adenosine monophosphate, and of hexose phosphates to the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1478–1486. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R. Allosteric regulation of enzyme activity. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1966;28:41–154. doi: 10.1002/9780470122730.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornheim K. Co-ordinate control of phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase by fructose diphosphate: a mechanism for amplification and step changes in the regulation of glycolysis in liver. J Theor Biol. 1980 Jul 21;85(2):199–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(80)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K. Phosphofructokinase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1979;48:193–244. doi: 10.1002/9780470122938.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-biphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2861–2863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Control of the fructose-6-phosphate/fructose 1,6-bisphosphate cycle in isolated hepatocytes by glucose and glucagon. Role of a low-molecular-weight stimulator of phosphofructokinase. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):887–895. doi: 10.1042/bj1920887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, the probably structure of the glucose- and glucagon-sensitive stimulator of phosphofructokinase. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):897–901. doi: 10.1042/bj1920897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Study of the fructose 6-phosphate/fructose 1,6-bi-phosphate cycle in the liver in vivo. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):263–271. doi: 10.1042/bj1920263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Badry A. M., Otani A., Mansour T. E. Studies on heart phosphofructokinase. Role of fructose 1,6-diphosphate in enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):557–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



