Abstract
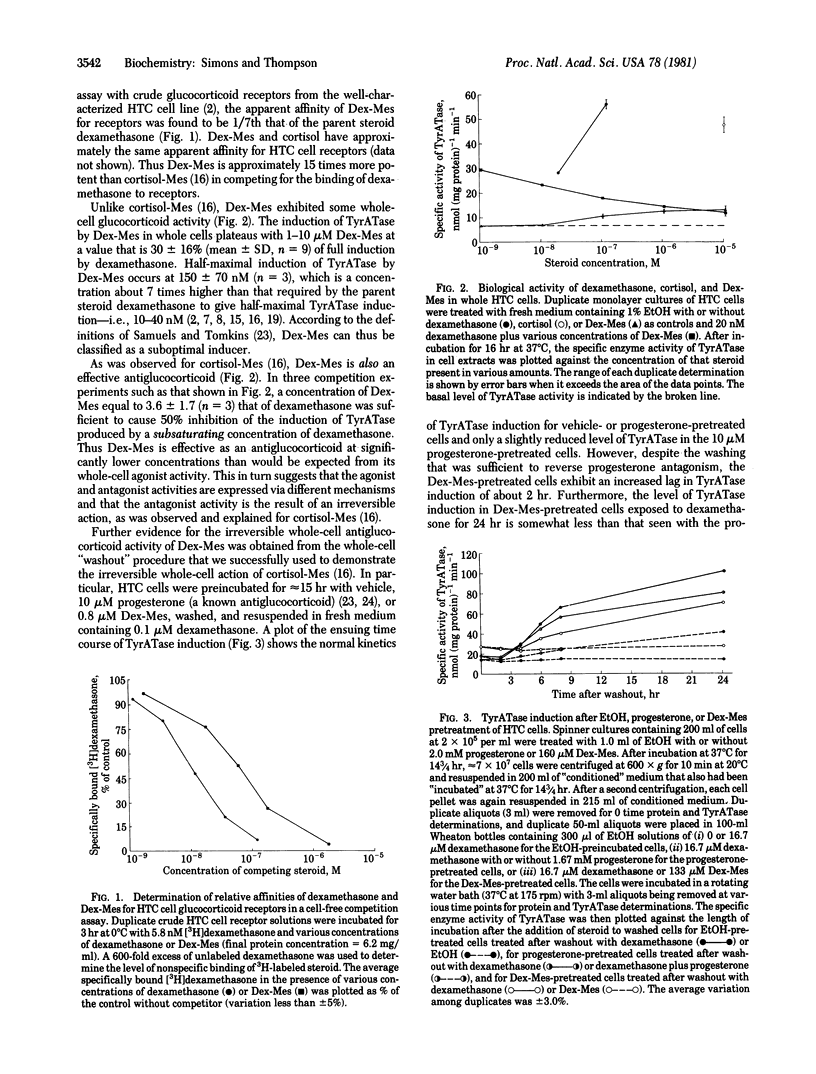
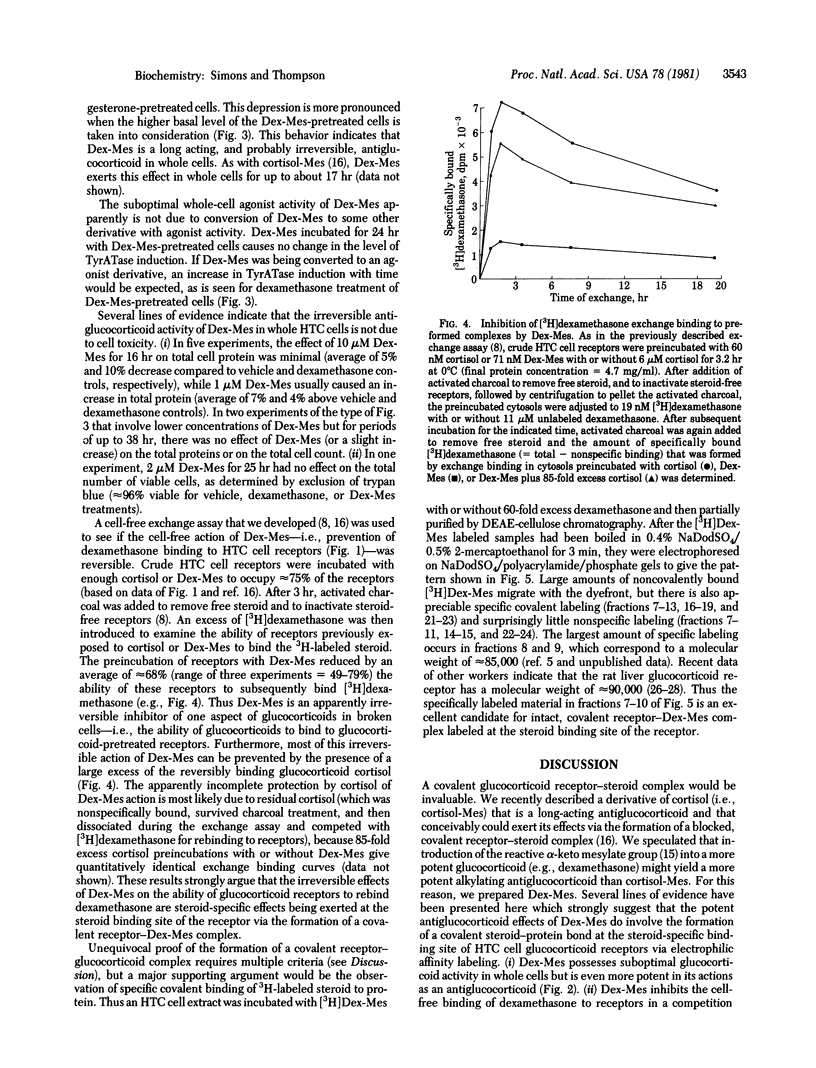
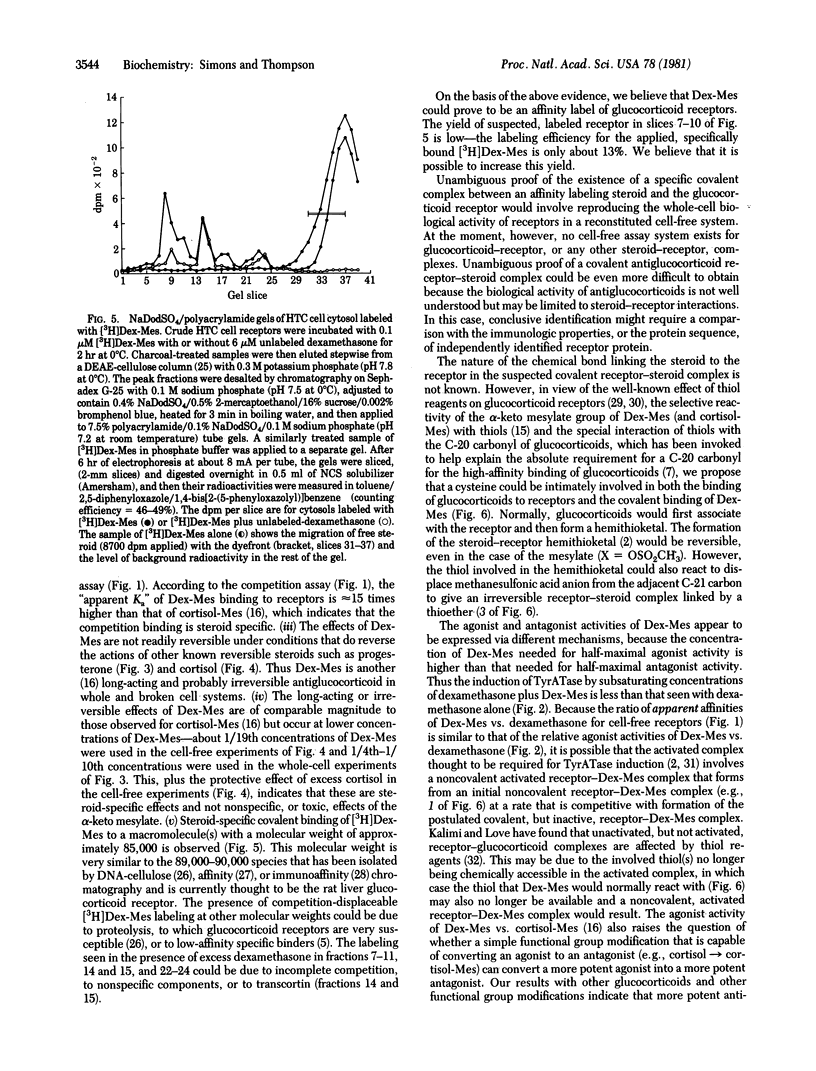
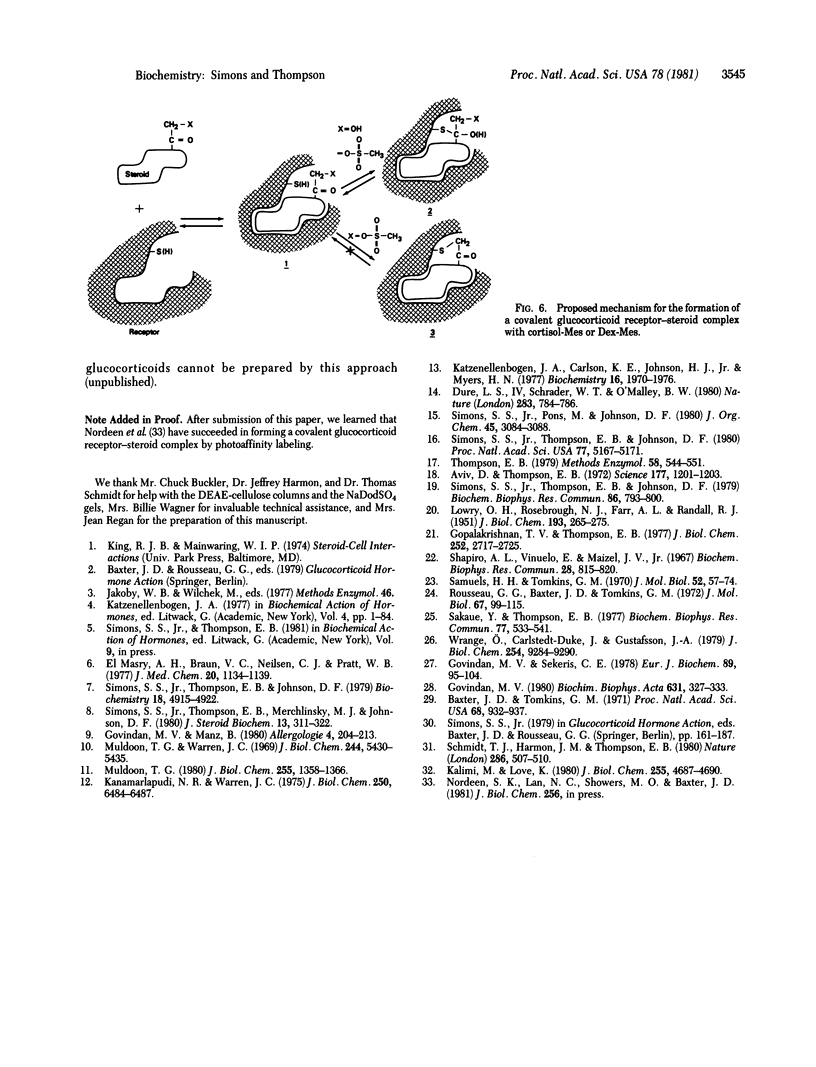
We recently described the biological properties of an alpha-keto mesylate derivative of cortisol, cortisol-Mes. Cortisol-Mes exhibited long-term antiglucocorticoid activity, but there was no firm evidence that this activity was irreversible or receptor-mediated. Here we report that dexamethasone mesylate (Dex-Mes), which is the alpha-keto mesylate derivative of the more active glucocorticoid dexamethasone, is a candidate for a steroid-specific affinity label of glucocorticoid receptors. Dex-Mes is relatively stable, like cortisol-Mes, but possesses greater whole-cell antiglucocorticoid activity. However, Dex-Mes also possesses partial agonist activity, which is expressed at somewhat higher concentrations of Dex-Mes than the antagonist activity. Dex-Mes is more efficient than cortisol-Mes in competing for dexamethasone binding to glucocorticoid receptors. Furthermore, Dex-Mes is effective at lower concentrations than cortisol-Mes in causing long-term apparently irreversible antiglucocorticoid effects in whole and broken cells. The cell-free effect of Dex-Mes is specifically prevented by coincubation with an excess of cortisol. These facts argue that the apparently irreversible effects of Dex-Mes are steroid mediated. [3H]Dex-Mes has been used to identify a glucocorticoid-specific, covalently labeled fraction on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels with a molecular weight of approximately 85,000. Thus Dex-Mes appears to have been established as an affinity label for glucocorticoid receptors.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv D., Thompson E. B. Variation in tyrosine aminotrasferase induction in HTC cell clones. Science. 1972 Sep 29;177(4055):1201–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4055.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Specific cytoplasmic glucocorticoid hormone receptors in hepatoma tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):932–937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dure L. S., 4th, Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Covalent attachment of a progestational steroid to chick oviduct progesterone receptor by photoaffinity labelling. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):784–786. doi: 10.1038/283784a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Masry A. H., Braun V. C., Nielsen C. J., Pratt W. B. Synthesis and biological action of two glucocorticoid alkylating agents. J Med Chem. 1977 Sep;20(9):1134–1139. doi: 10.1021/jm00219a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan T. V., Thompson E. B. Effect of concanavalin A on tyrosine aminotransferase in rat hepatoma tissue culture cells. Rapid reversible inactivation of soluble enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2717–2725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan M. V. Isolation and characterization of rat liver nuclear glucocorticoid receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 13;631(2):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan M. V., Sekeris C. E. Purification of two dexamethasone-binding proteins from rat-liver cytosol. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):95–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimi M., Love K. Role of chemical reagents in the activation of rat hepatic glucocorticoid-receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4687–4690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamarlapudi N. R., Warren J. C. Synthesis and study of the estrogenic activity of 2,4-bis(bromomethyl)estradiol-17 beta 3-methyl ether. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6484–6487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen J. A., Carlson K. E., Johnson H. J., Jr, Myers H. N. Estrogen photoaffinity labels. 2. Reversible binding and covalent attachment of photosensitive hexestrol derivatives to the uterine estrogen receptor. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1970–1976. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon T. G. Molecular and functional anomalies in the mechanism of the estrogenic action of 4-mercuri-17 beta-estradiol. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1358–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon T. G., Warren J. C. Characterization of steroid-binding sites by affinity-labeling. II. Biological activity of 4-mercuri-17 beta-estradiol. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5430–5435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau G. G., Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Glucocorticoid receptors: relations between steroid binding and biological effects. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 14;67(1):99–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaue Y., Thompson E. B. Characterization of two forms of glucocorticoid hormone-receptor complex separated by DEAE-cellulose column chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):533–541. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tomkins G. M. Relation of steroid structure to enzyme induction in hepatoma tissue culture cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug 28;52(1):57–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. J., Harmon J. M., Thompson E. B. 'Activation-labile' glucocorticoid-receptor complexes of a steroid-resistant variant of CEM-C7 human lymphoid cells. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):507–510. doi: 10.1038/286507a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr Factors influencing association of glucocorticoid receptor-steroid complexes with nuclei, chromatin, and DNA: interpretation of binding data. Monogr Endocrinol. 1979;12:161–187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81265-1_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr, Thompson E. B., Johnson D. F. Anti-inflammatory pyrazolo-steroids: potent glucocorticoids containing bulky A-ring substituents and no C3-carbonyl. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 14;86(3):792–800. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91782-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr, Thompson E. B., Johnson D. F. Fluorescent chemoaffinity labeling. Potential application of a new affinity labeling technique to glucocorticoid receptors. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4915–4922. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr, Thompson E. B., Johnson D. F. Unique long-acting antiglucocorticoid in whole and broken cell systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5167–5171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr, Thompson E. B., Merchlinsky M. J., Johnson D. F. Synthesis and biological activity of some novel, chemically reactive glucocorticoids. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Mar;13(3):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B. Liver cells (HTC). Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:544–552. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. Purification of the glucocorticoid receptor from rat liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9284–9290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


