Abstract
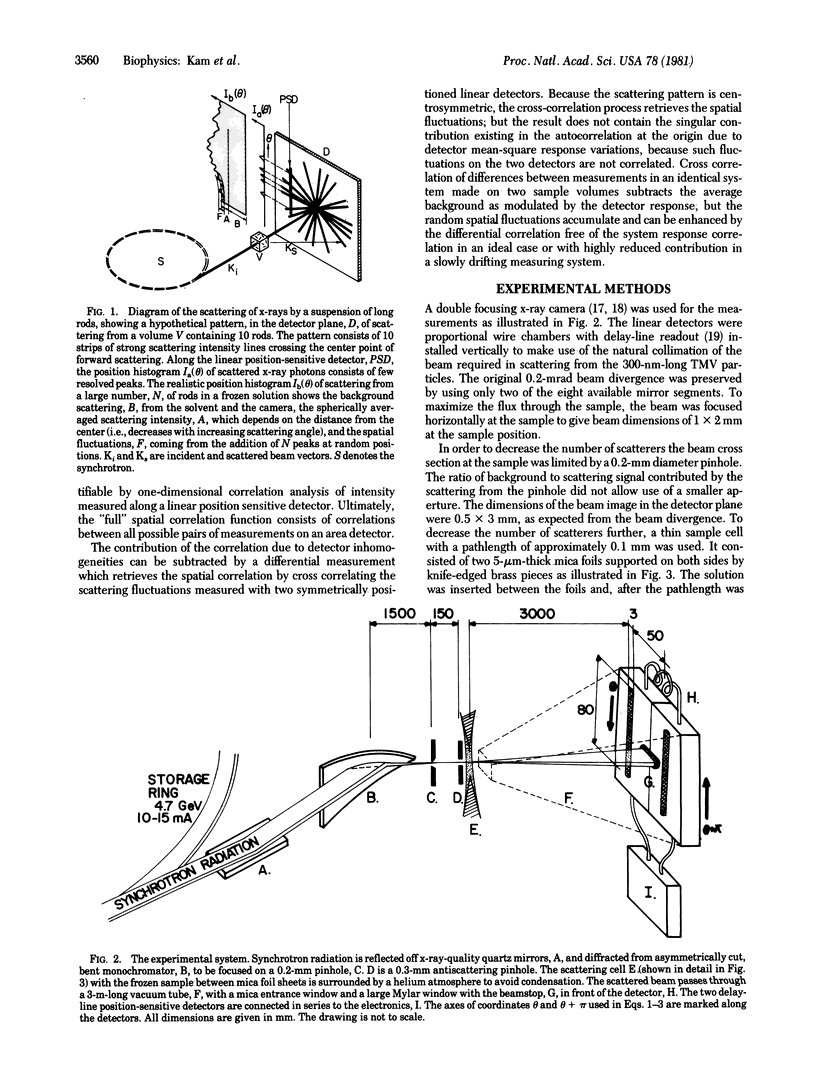
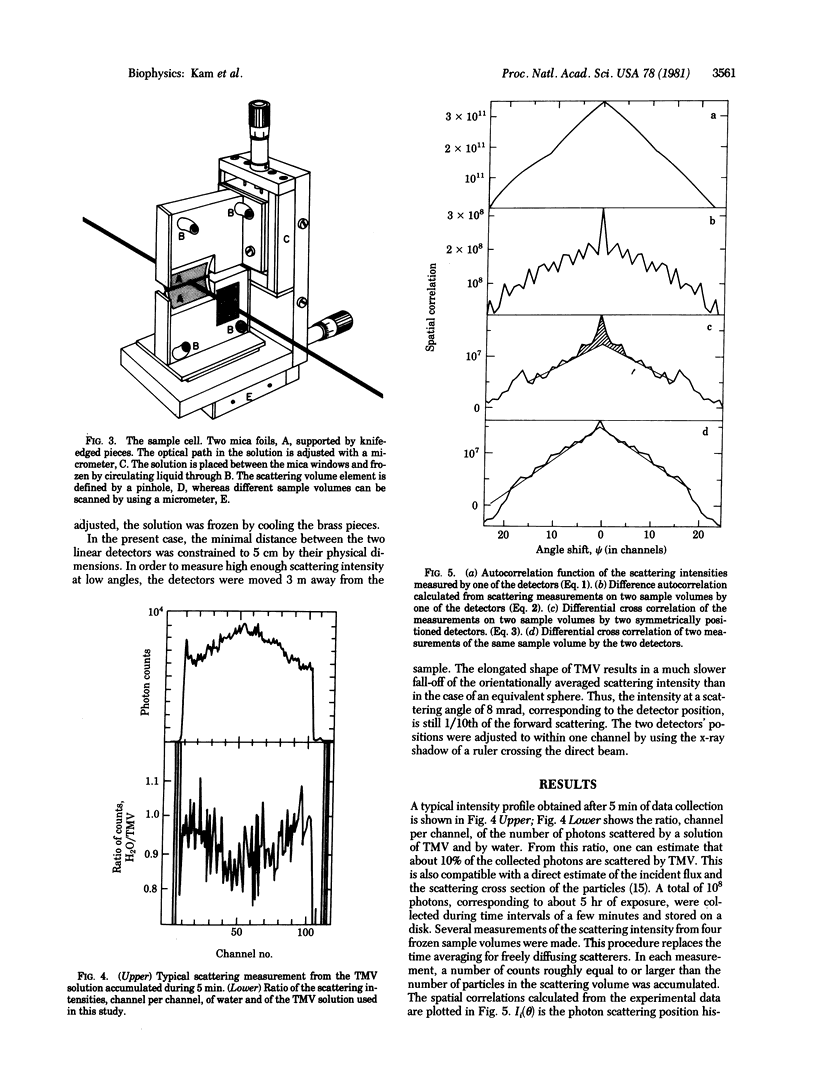
Determination of the structure of biological particles, randomly oriented in solution, from spatial correlation analysis of fluctuations in x-ray scattering has recently been proposed. The feasibility of scattering fluctuation measurements was evaluated by using an x-ray synchrotron radiation camera to obtain the spatial correlation for a solution of tobacco mosaic virus along a line. The experimental system, analysis of data, and requirements for the determination of structures in solution are discussed using this example.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borejdo J., Putnam S., Morales M. F. Fluctuations in polarized fluorescence: evidence that muscle cross bridges rotate repetitively during contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6346–6350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Amos L. A. Harmonic analysis of electron microscope images with rotational symmetry. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins H. Z., Carlson F. D., Herbert T. J., Woods G. Translational and rotational diffusion constants of tobacco mosaic virus from Rayleigh linewidths. Biophys J. 1969 Apr;9(4):518–546. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86402-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feher G., Weissman M. Fluctuation spectroscopy: determination of chemical reaction kinetics from the frequency spectrum of fluctuations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):870–875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kam Z. The reconstruction of structure from electron micrographs of randomly oriented particles. J Theor Biol. 1980 Jan 7;82(1):15–39. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(80)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M. H., Stuhrmann H. B. Neutron-scattering studies of ribosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:670–706. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppel D. E., Axelrod D., Schlessinger J., Elson E. L., Webb W. W. Dynamics of fluorescence marker concentration as a probe of mobility. Biophys J. 1976 Nov;16(11):1315–1329. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85776-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magde D., Elson E. L., Webb W. W. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. II. An experimental realization. Biopolymers. 1974 Jan;13(1):29–61. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360130103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman M., Schindler H., Feher G. Determination of molecular weights by fluctuation spectroscopy: application to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2776–2780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


