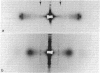
Abstract
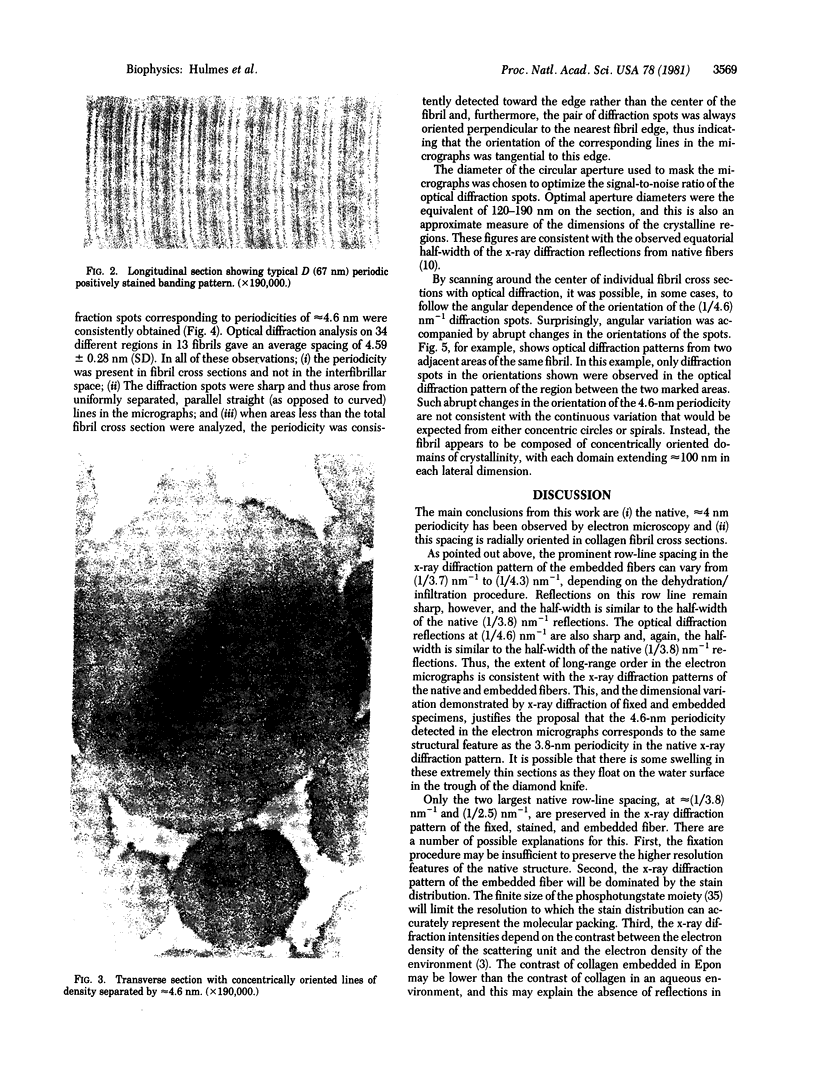
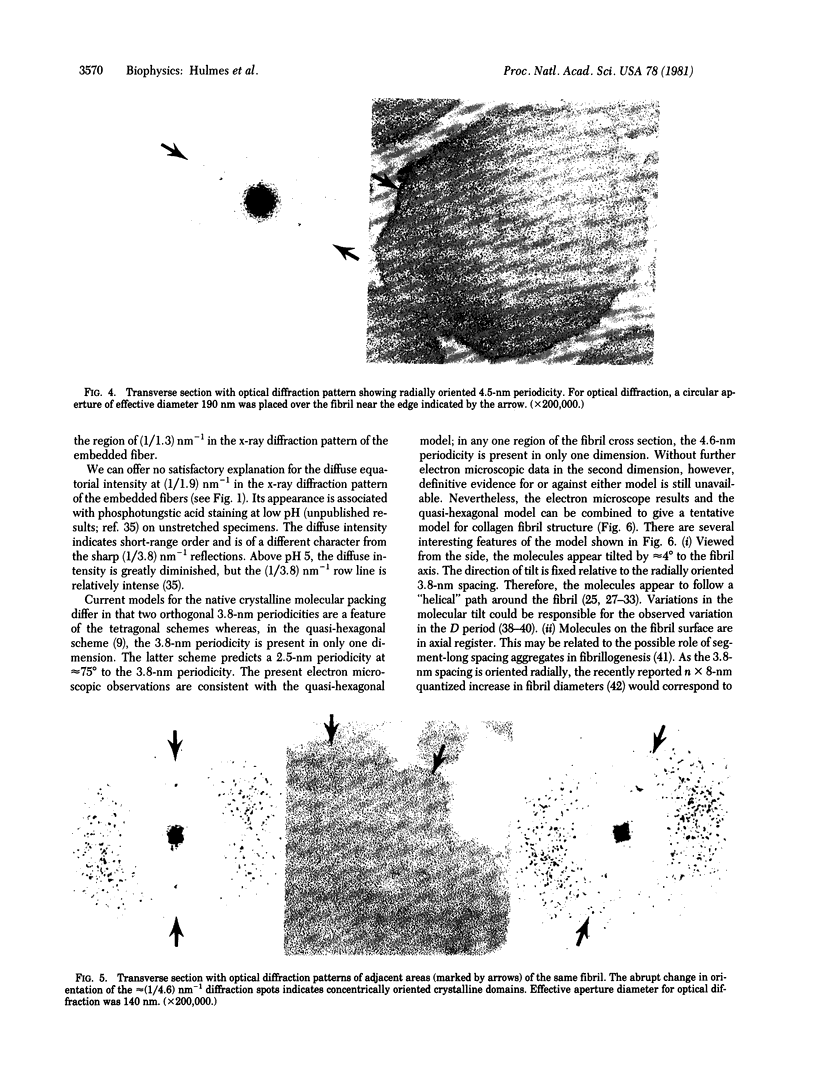
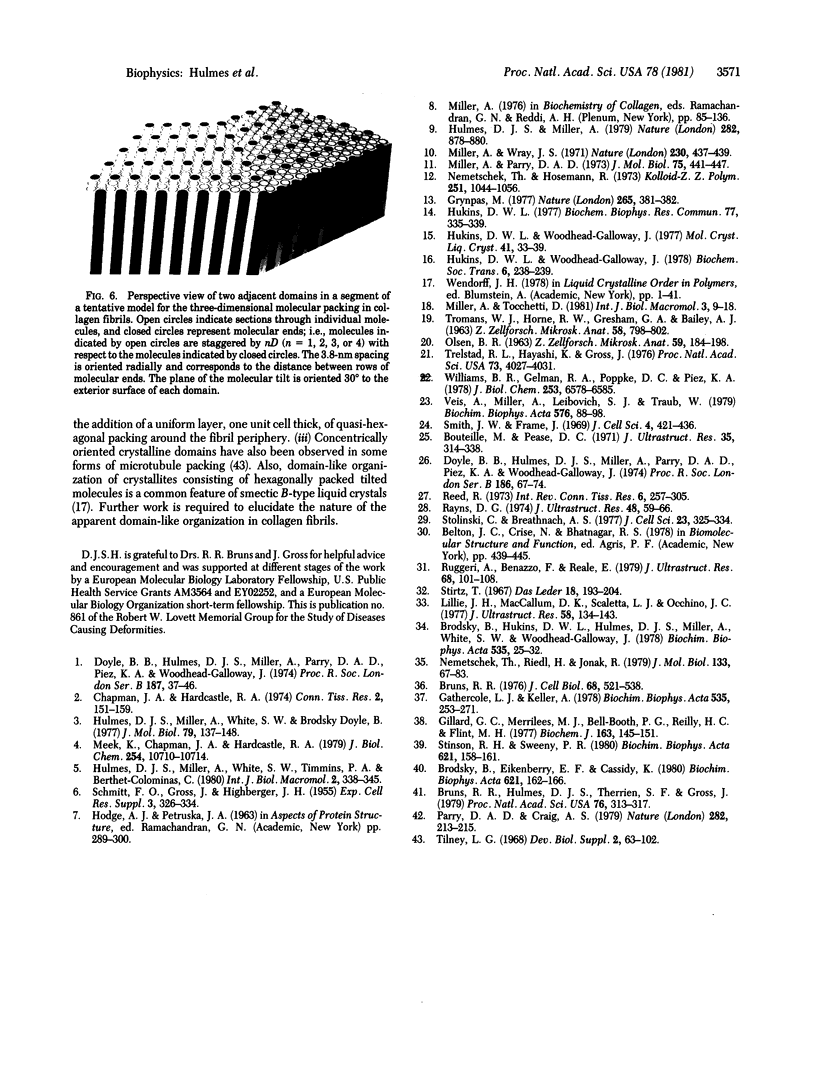
X-ray diffraction was used to monitor the effects of electron microscope fixation, staining, and embedding procedures on the preservation of the three-dimensional crystalline order in collagen fibrils of rat tail tendon. A procedure is described in which the characteristic 3.8-nm lateral spacing is preserved, with increased contrast, in the diffraction pattern of the embedded fiber. This spacing is correlated with the separation between the tangentially oriented equally spaced lines of density observed in electron microscope ultrathin fibril cross sections of the same material. Optical diffraction of electron micrographs gives an objective measure of the periodicity and suggests that the fibril is composed of concentrically oriented crystalline domains. These observations, when combined with a recent interpretation of the native x-ray diffraction data [Hulmes, D. J. S. & Miller, A. (1979) Nature (London) 282, 878-880] suggest a tentative model for the three-dimensional structure of collagen fibrils.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouteille M., Pease D. C. The tridimensional structure of native collagenous fibrils, their proteinaceous filaments. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 May;35(3):314–338. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky B., Eikenberry E. F., Cassidy K. An unusual collagen periodicity in skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 24;621(1):162–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky B., Hukins D. W., Hulmes D. J., Miller A., White S., Woodhead-Galloway J. Low angle X-ray diffraction studies on stained rat tail tendons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 21;535(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. R., Hulmes D. J., Therrien S. F., Gross J. Procollagen segment-long-spacing crystallites: their role in collagen fibrillogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):313–317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. R. Supramolecular structure of polymorphic collagen fibrils. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):521–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. A., Hardcastle R. A. The staining pattern of collagen fibrils. II. A comparison with patterns computer-generated from the amino acid sequence. Connect Tissue Res. 1974;2(2):151–159. doi: 10.3109/03008207409152100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle B. B., Hulmes D. J., Miller A., Parry A. D., Piez K. A., Woodhead-Galloway J. A D-periodic narrow filament in collagen. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 May 7;186(1082):67–74. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1974.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle B. B., Hulmes D. J., Miller A., Parry D. A., Piez K. A., Woodhead-Galloway J. Axially projected collagen structures. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 Aug 27;187(1086):37–46. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1974.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gathercole L. J., Keller A. X-ray diffraction effects related to superstructure in rat tail tendon collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 21;535(2):253–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard G. C., Merrilees M. J., Bell-Booth P. G., Reilly H. C., Flint M. H. The proteoglycan content and the axial periodicity of collagen in tendon. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 1;163(1):145–151. doi: 10.1042/bj1630145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynpas M. Three-dimensional packing of collagen in bone. Nature. 1977 Jan 27;265(5592):381–382. doi: 10.1038/265381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hukins D. W., Woodhead-Galloway J. Liquid-crystal model for the organization of molecules in collagen fibrils [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(1):238–239. doi: 10.1042/bst0060238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hukins D. W. X-ray diffraction by collagen tape shows that type I collagen fibrils need not have a three-dimensional lattice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):335–339. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Miller A., Parry D. A., Piez K. A., Woodhead-Galloway J. Analysis of the primary structure of collagen for the origins of molecular packing. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 5;79(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90275-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Miller A. Quasi-hexagonal molecular packing in collagen fibrils. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):878–880. doi: 10.1038/282878a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. H., MacCallum D. K., Scaletta L. J., Occhino J. C. Collagen structure: evidence for a helical organization of the collagen fibril. J Ultrastruct Res. 1977 Feb;(2):134–143. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(77)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek K. M., Chapman J. A., Hardcastle R. A. The staining pattern of collagen fibrils. Improved correlation with sequence data. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10710–10714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Parry D. A. Structure and packing of microfibrils in collagen. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Wray J. S. Molecular packing in collagen. Nature. 1971 Apr 16;230(5294):437–439. doi: 10.1038/230437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemetschek T., Riedl H., Jonak R. Topochemistry of the binding of phosphotungstic acid to collagen. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 5;133(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSEN B. R. Electron microscope studies on collagen. I. Native collagen fibrils. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1963;59:184–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00320444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Craig A. S. Electron microscope evidence for an 80 A unit in collagen fibrils. Nature. 1979 Nov 8;282(5735):213–215. doi: 10.1038/282213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayns D. G. Collagen from frozen fractured glycerinated beef heart. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Jul;48(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. Freeze-etched connective tissue. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1973;6:257–305. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363706-2.50012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri A., Benazzo F., Reale E. Collagen fibrils with straight and helicoidal microfibrils: a freeze-fracture and thin-section study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1979 Jul;68(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(79)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMITT F. O., GROSS J., HIGHBERGER J. H. Tropocollagen and the properties of fibrous collagen. Exp Cell Res. 1955;(Suppl 3):326–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Frame J. Observations on the collagen and proteinpolysaccharide complex of rabbit cornea stroma. J Cell Sci. 1969 Mar;4(2):421–436. doi: 10.1242/jcs.4.2.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson R. H., Sweeny P. R. Skin collagen has an unusual d-spacing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 24;621(1):158–161. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolinski C., Breathnach A. S. Freeze-fracture replication and surface sublimation of frozen collagen fibrils. J Cell Sci. 1977 Feb;23:325–334. doi: 10.1242/jcs.23.1.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROMANS W. J., HORNE R. W., GRESHAM G. A., BAILEY A. J. Electron microscope studies on the structure of collagen fibrils by negative staining. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1963;58:798–802. doi: 10.1007/BF00410661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Hayashi K., Gross J. Collagen fibrillogenesis: intermediate aggregates and suprafibrillar order. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4027–4031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veis A., Miller A., Leibovich S. J., Traub W. The limiting collagen microfibril. The minimum structure demonstrating native axial periodicity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 25;576(1):88–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90487-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R., Gelman R. A., Poppke D. C., Piez K. A. Collagen fibril formation. Optimal in vitro conditions and preliminary kinetic results. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6578–6585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]