Abstract
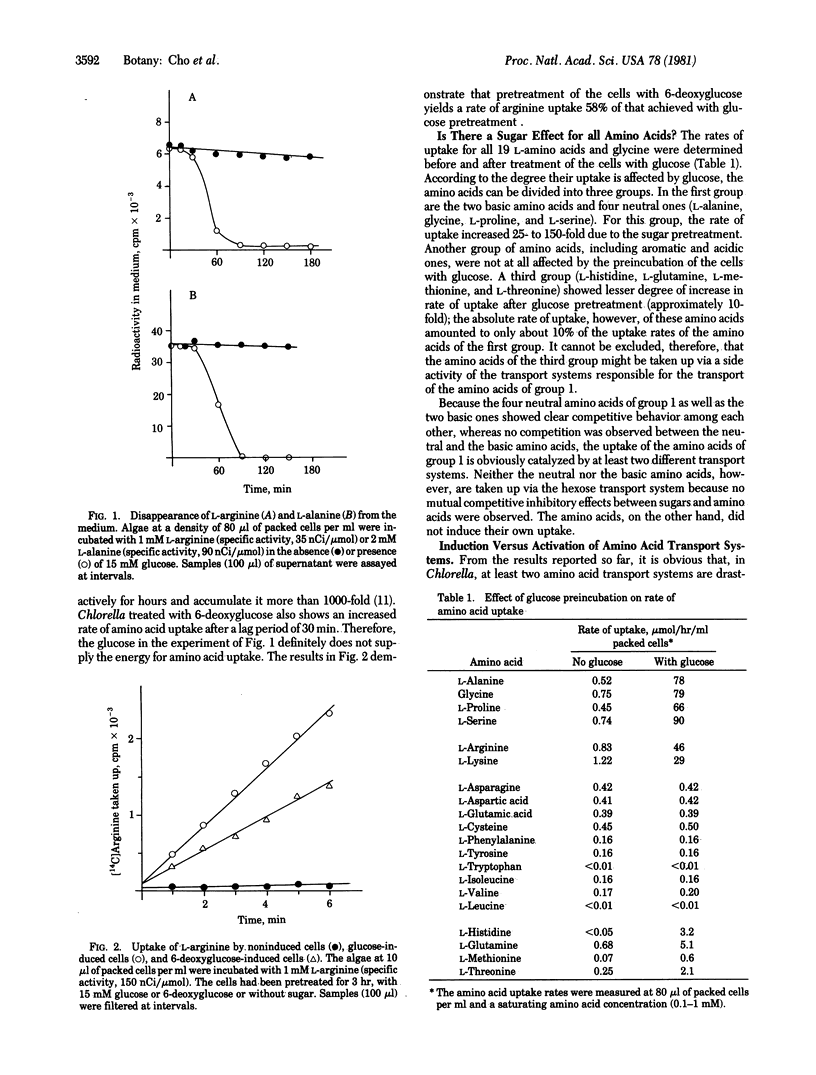
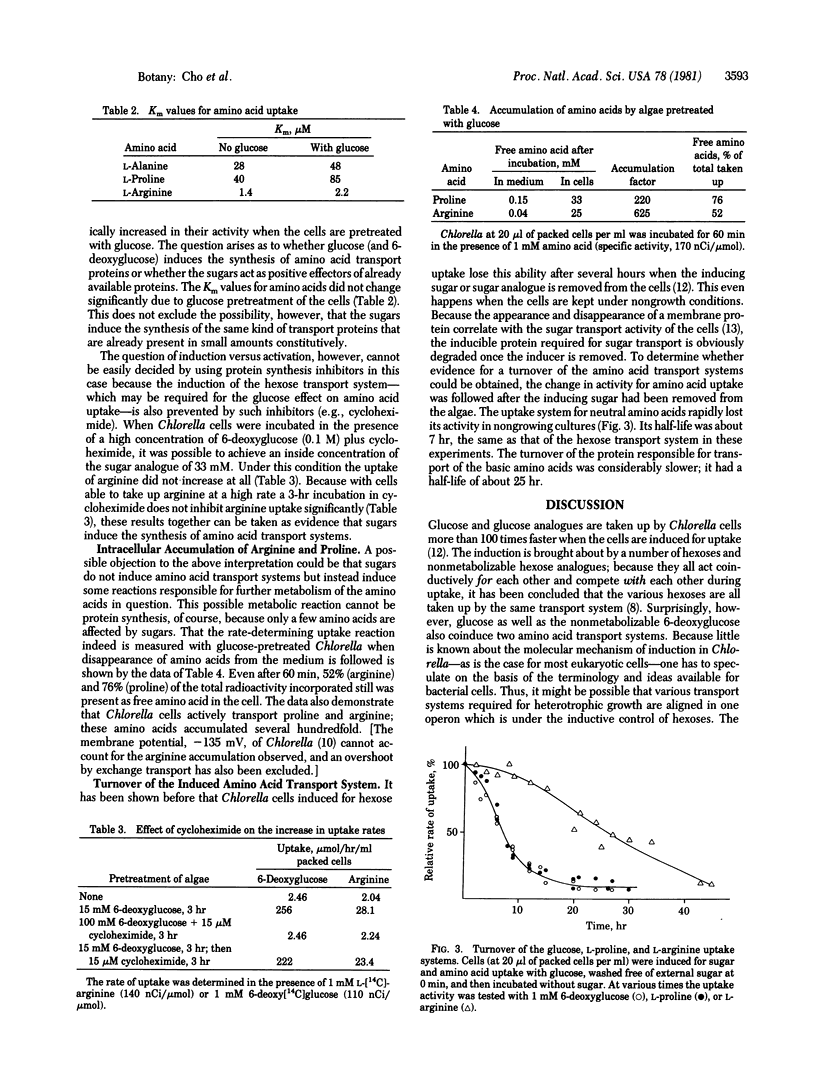
In autotrophically grown Chlorella cells, glucose induces a hexose transport system but, at the same time, the synthesis of two amino acid transport systems is also induced. Thus, the rates of uptake of glycine, L-alanine, L-proline, and L-serine, all of which compete with each other for entry into the cells, increase more than 100-fold when the algae are pretreated with glucose. The rates of L-arginine and L-lysine uptake increase by a factor of 25 to 50. The accumulation of proline and arginine within the cells amounts to 200- and 600-fold, respectively. Glucose does not cause the positive effect on amino acid uptake by serving as metabolic substrate because the nonmetabolizable 6-deoxyglucose also acts as inducer. Cycloheximide prevents the induction. The induced transport system for the four neutral amino acids has a turnover with a half-life of 7 hr, which corresponds closely to the half-life of the hexose transport system. The transport system for the basic amino acids, on the other hand, disappears with a half-life of 25 hr.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTTIN G., COHEN G. N., MONOD J., RICKENBERG H. V. La galactoside-perméase d'Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Dec;91(6):829–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W. Bacterial transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):123–146. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D. The teleonomic significance of biosynthetic control mechanisms. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:1–10. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenzl F., Decker M., Haass D., Tanner W. Characterization and partial purification of an inducible protein related to hexose proton cotransport of Chlorella vulgaris. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):509–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass D., Tanner W. Regulation of Hexose Transport in Chlorella vulgaris: Characteristics of Induction and Turnover. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jan;53(1):14–20. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskovec C., Kotyk A. Attempts at purifying the galactose carrier from galactose-induced baker's yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(3):343–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Bourgeois S. lac Repressor-operator interaction. VI. The natural inducer of the lac operon. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 28;69(3):397–408. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E., Haass D., Komor B., Tanner W. The active hexose-uptake system of Chlorella vulgaris. Km-values for 6-deoxyglucose influx and efflux and their contribution to sugar accumulation. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):193–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E. Proton-coupled hexose transport in Chlorella vulgaris. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 15;38(1):16–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80501-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E., Tanner W. Characterization of the active hexose transport system of Chlorella vulgaris. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 6;241(1):170–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E., Tanner W. The determination of the membrane ptoential of Chlorella vulgaris. Evidence for electrogenic sugar transport. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 1;70(1):197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner W. Light-driven active uptake of 3-O-methylglucose via an inducible hexose uptake system of Chlorella. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 23;36(2):278–283. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



