Abstract
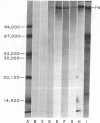
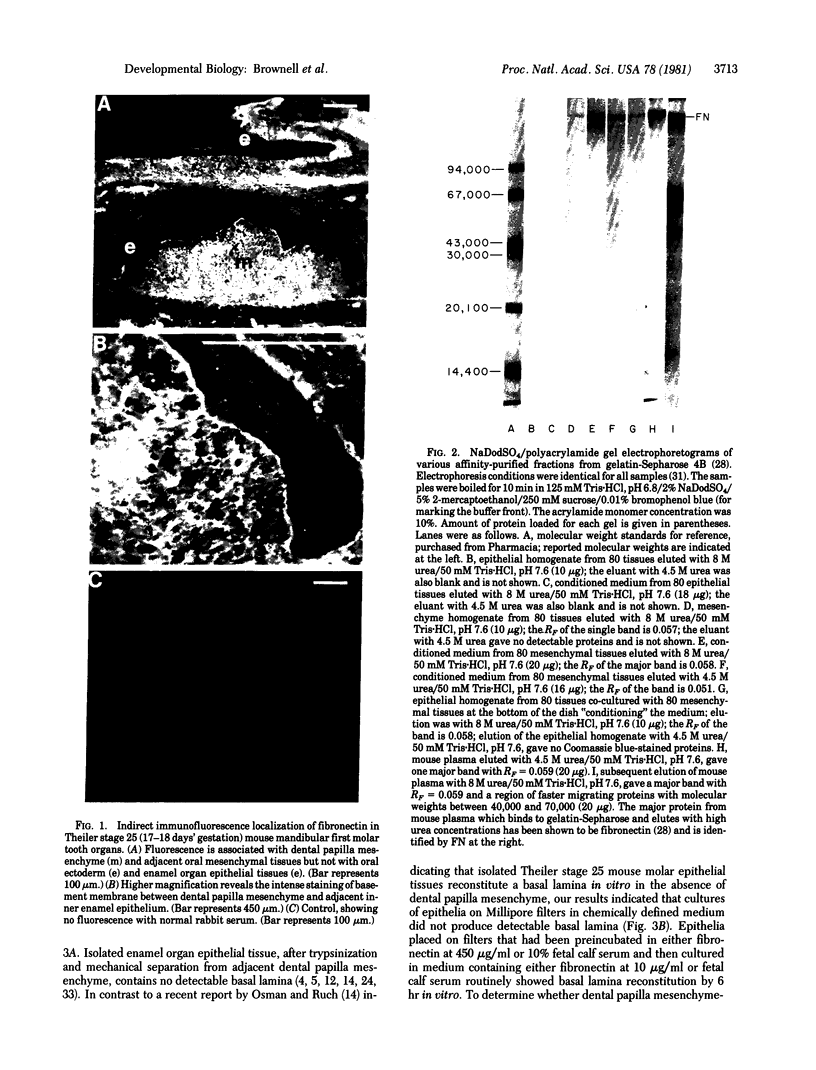
Epithelial synthesis and secretion of basal lamina has been considered to be a general feature of various vertebrate epithelium-mesenchyme interacting systems (e.g., salivary gland, mammary gland, feather, hair, and tooth morphogenesis). It has been repeatedly assumed that embryonic ectoderm and ectodermal derivatives, such as epithelial tissues associated with tooth morphogenesis, synthesize and secrete basal lamina. Basal lamina of embryonic mouse tooth organs contain laminin, type IV collagen, glycosaminoglycans, and possibly fibronectin. Ectodermally derived epithelia produce laminin, collagens, and glycosaminoglycans but they do not appear to produce fibronectin. Mesenchyme can effect basal lamina formation in vitro by releasing mesenchyme-derived fibronectin. Theiler stage 25 molar tooth mesenchymal and epithelial tissues were enzymatically separated and cultured in chemically defined media without serum, embryonic extracts, or antibiotics for periods not exceeding 24 hr. Isolated epithelia did not reconstitute a basal lamina. Mesenchymepreconditioned media, fibronectin substrata, or addition of 10% fetal calf serum induced reconstitution of epithelium-derived basal lamina. Dental mesenchyme-preconditioned medium contained, as a major component, a protein of Mr ≈2.3 × 105 identified as fibronectin by the criteria of gelatin binding and subunit molecular weight. Fibronectin was not produced by isolated epithelia. These results support the hypothesis that basal lamina ultrastructural organization results from supramolecular interactions between epithelium-derived macromolecules (e.g., type IV collagen, proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and laminin) with mesenchyme-derived cell surface fibronectin.
Keywords: tissue culture, epithelial cytodifferentiation, electron microscopy, immunofluorescence, tooth organ
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birdwell C. R., Gospodarowicz D., Nicolson G. L. Identification, localization, and role of fibronectin in cultured bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell A. G., Slavkin H. C. Role of basal lamina in tissue interactions. Ren Physiol. 1980;3(1-6):193–204. doi: 10.1159/000172761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R. H., Banerjee S. D., Bernfield M. R. Basal lamina of embryonic salivary epithelia. Nature of glycosaminoglycan and organization of extracellular materials. J Cell Biol. 1977 May;73(2):464–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G., Bernfield M. R. Collagen reduces glycosaminoglycan degradation by cultured mammary epithelial cells: possible mechanism for basal lamina formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):786–790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. P. Zone precipitation chromatography: its use in the isolation of different collagen types. Prep Biochem. 1979;9(4):407–425. doi: 10.1080/00327487908061703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Alitalo K., Vaheri A., Timpl R., Saxén L. Induction of a basement membrane glycoprotein in embryonic kidney: possible role of laminin in morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Bernfield M. R. The basal lamina of the postnatal mammary epithelium contains glycosaminoglycans in a precise ultrastructural organization. Dev Biol. 1980 Jan;74(1):118–135. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grobstein C. Mechanisms of organogenetic tissue interaction. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1967 Sep;26:279–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata R. I., Slavkin H. C. De novo induction of a gene product during heterologous epithelial--mesenchymal interactions in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2790–2794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Structure and biosynthesis of basement membranes. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1973;6:63–104. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363706-2.50008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Hewitt A. T., Murray J. C., Liotta L. A., Rennard S. I., Pennypacker J. P., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Fishman P. H. Cellular and metabolic specificity in the interaction of adhesion proteins with collagen and with cells. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(1):69–78. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madri J. A., Roll F. J., Furthmayr H., Foidart J. M. Ultrastructural localization of fibronectin and laminin in the basement membranes of the murine kidney. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):682–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. M., Karcher-Djuricic V., Osman M., Ruch J. V. Aspects ultrastructuraux de la reconstitution de la membrane basale dans des associations de constituants dentaires cultivées in vitro. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1978 Sep 11;287(4):329–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Chen A. B., Huseby R. M. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma: studies of its essential structural features. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 29;386(2):509–524. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Stingl G., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Katz S. I. Epidermal cells adhere preferentially to type IV (basement membrane) collagen. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jan;80(1):197–202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Sato G. Fibronectin mediates cytokinesis and growth of rat follicular cells in serum-free medium. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osman M., Ruch J. V. Secretion of basal lamina by trypsin-isolated embryonic mouse molar epithelia cultured in vitro. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar 15;75(2):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. E., Ji T. H., Hynes R. O. Cross-linking of fibronectin to sulfated proteoglycans at the cell surface. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):941–952. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Vuento M., Engvall E. Interaction of fibronectin with antibodies and collagen in radioimmunoassay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 21;534(2):210–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavkin H. C., Bringas P., Jr Epithelial-mesenchyme interactions during odontogenesis. IV. Morphological evidence for direct heterotypic cell-cell contacts. Dev Biol. 1976 Jun;50(2):428–442. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavkin H. C. Embryonic tooth formation. A tool for developmental biology. Oral Sci Rev. 1974;4(0):7–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavkin H. C., Mino W., Bringas P., Jr The biosynthesis and secretion of precursor enamel protein by ameloblasts as visualized by autoradiography after tryptophan administration. Anat Rec. 1976 Jul;185(3):289–312. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091850304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavkin H. C. The nature and nurture of epithelial-mesenchymal interactions during tooth morphogenesis. J Biol Buccale. 1978 Sep;6(3):189–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman S., Vaheri A. Distribution of a major connective tissue protein, fibronectin, in normal human tissues. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1054–1064. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesleff I., Stenman S., Vaheri A., Timpl R. Changes in the matrix proteins, fibronectin and collagen, during differentiation of mouse tooth germ. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):116–126. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Hayashi K., Toole B. P. Epithelial collagens and glycosaminoglycans in the embryonic cornea. Macromolecular order and morphogenesis in the basement membrane. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):815–830. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Mosher D. F. High molecular weight, cell surface-associated glycoprotein (fibronectin) lost in malignant transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 18;516(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Olden K. Fibronectins--adhesive glycoproteins of cell surface and blood. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):179–184. doi: 10.1038/275179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Bringas P., Jr, Grodin M., MacDougall M., Slavkin H. C. Developmental comparisons of murine secretory amelogenesis in vivo, as xenografts on the chick chorio-allantoic membrane, and in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 1980;31(2):161–171. doi: 10.1007/BF02407177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N. S., Kirkland W., Jorgensen T., Furmanski P. Absence of fibronectin and presence of plasminogen activator in both normal and malignant human mammary epithelial cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):120–130. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]