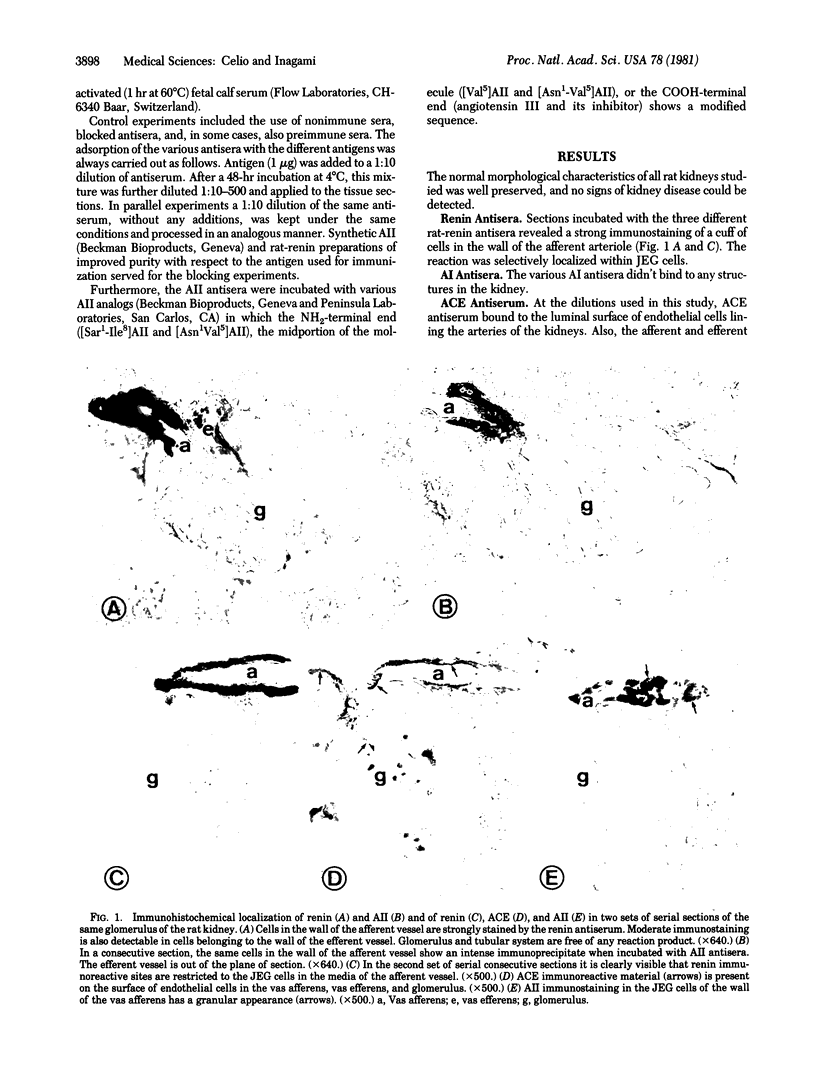
Abstract
The multiple physiologic functions of angiotensin II(AII) are generally supposed to be mediated by the peptide generated in the blood circulation. In addition to this extracellular mechanism of AII formation, we have obtained immunohistochemical evidence for the intracellular synthesis of AII in the kidney. Rats were perfused with fixative, and paraffin sections of the kidneys were processed with antisera against renin (EC 3.4.99.19), AII, and other components of the renin--angiotensin system. Renin immunoreactivity was regularly observed in the epithelioid granular cells in the media of the afferent vessel of the glomerulus. AII immunoreactivity was found to coexist within the same cells. This observation points to an intracellular production of AII in the juxtaglomerular epitheloid granular cells. AII may then be released concomitantly with renin in the interstitial fluid and in the blood. The paracrine secretion of AII could exert a local regulatory influence on the tonus of the glomerular vessels.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britton K. E. Renin and renal autoregulation. Lancet. 1968 Aug 10;2(7563):329–333. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90534-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. R., Seegal B. C., Hsu K. C., Das M., Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: vascular endothelial localization. Science. 1976 Mar 12;191(4231):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.175444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Soffer R. L. Pulmonary angiotensin-converting enzyme antienzyme antibody. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5088–5094. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devynck M. A., Pernollet M. G., Meyer P., Fermandjian S., Fromageot P. Angiotensin receptors in smooth muscle cell membranes. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 12;245(141):55–58. doi: 10.1038/newbio245055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkielman S., Nahmod V. E. In vitro production of angiotensin I by renal glomeruli. Nature. 1969 Jun 21;222(5199):1186–1188. doi: 10.1038/2221186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger P., Dahlheim H., Thurau K. Enzyme activities of the single juxtaglomerular apparatus in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1972 Feb;1(2):78–88. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmler W., Steiner D. F., Borg J. Studies on the conversion of proinsulin to insulin. 3. Studies in vitro with a crude secretion granule fraction isolated from rat islets of Langerhans. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4544–4551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARAGH J. H., ANGERS M., KELLY W. G., LIEBERMAN S. Hypotensive agents and pressor substances. The effect of epinephrine, norepinephrine, angiotensin II, and others on the secretory rate of aldosterone in man. JAMA. 1960 Sep 17;174:234–240. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03030030014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckie B., Gavras H., McGregor J., McElwee G. The conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II by rabbit glomeruli. J Endocrinol. 1972 Oct;55(1):229–230. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0550229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowitz H. D., Stumpe K. O., Ochwadt B. Micropuncture study of the action of angiotensin-II on tubular sodium and water reabsorption in the rat. Nephron. 1969;6(3):173–187. doi: 10.1159/000179727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn F. A. Evidence for the local occurrence of angiotensin II in rat kidney and its modulation by dietary sodium intake and converting enzyme blockade. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Aug;57(2):173–179. doi: 10.1042/cs0570173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navar L. G., Ploth D. W., Bell P. D. Distal tubular feedback control of renal hemodynamics and autoregulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:557–571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploth D. W., Navar L. G. Intrarenal effects of the renin-angiotensin system. Fed Proc. 1979 Aug;38(9):2280–2285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polsky-Cynkin R., Fanburg B. L. Immunochemical comparison of angiotensin 1 converting enzymes from different rat organs. Int J Biochem. 1979;10(8):669–674. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(79)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. E., Haber E. Inactive renin--"through a glass darkly". N Engl J Med. 1979 Aug 23;301(8):429–430. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197908233010810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Petrali J. P. Quantitative immunocytochemistry of pituitary receptors for luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Sep 17;162(2):141–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00209204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun A. M., Lin B. J., Haist R. E. Studies on the conversion of proinsulin to insulin in the isolated islets of Langerhans in the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;51(3):175–182. doi: 10.1139/y73-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland L. E. A fluorescent antibody study of juxtaglomerular cells using the freeze-substitution technique. Nephron. 1970;7(6):512–523. doi: 10.1159/000179859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner C., Poulsen K., Hackenthal E., Taugner R. Immunocytochemical localization of renin in mouse kidney. Histochemistry. 1979 Jul;62(1):19–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00537003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J., Geelhoed G. W. Inhibition of renin secretion by angiotensin. II. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Nov;120(2):399–403. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]