Abstract
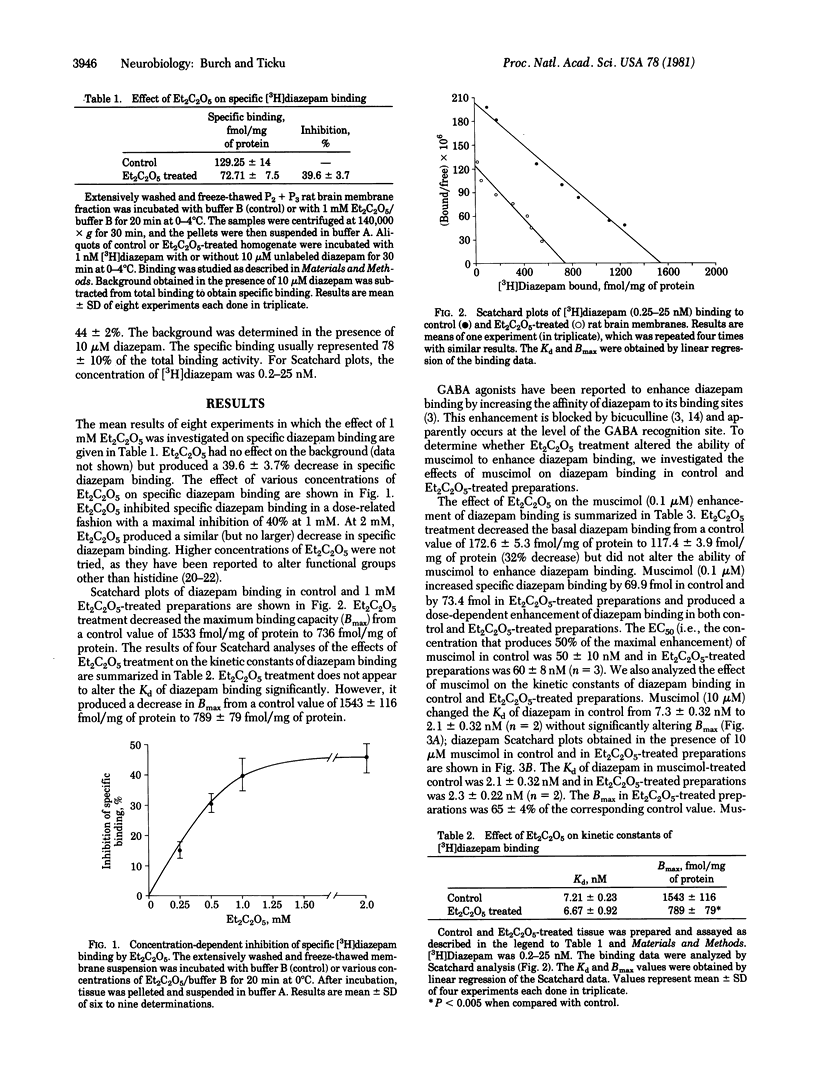
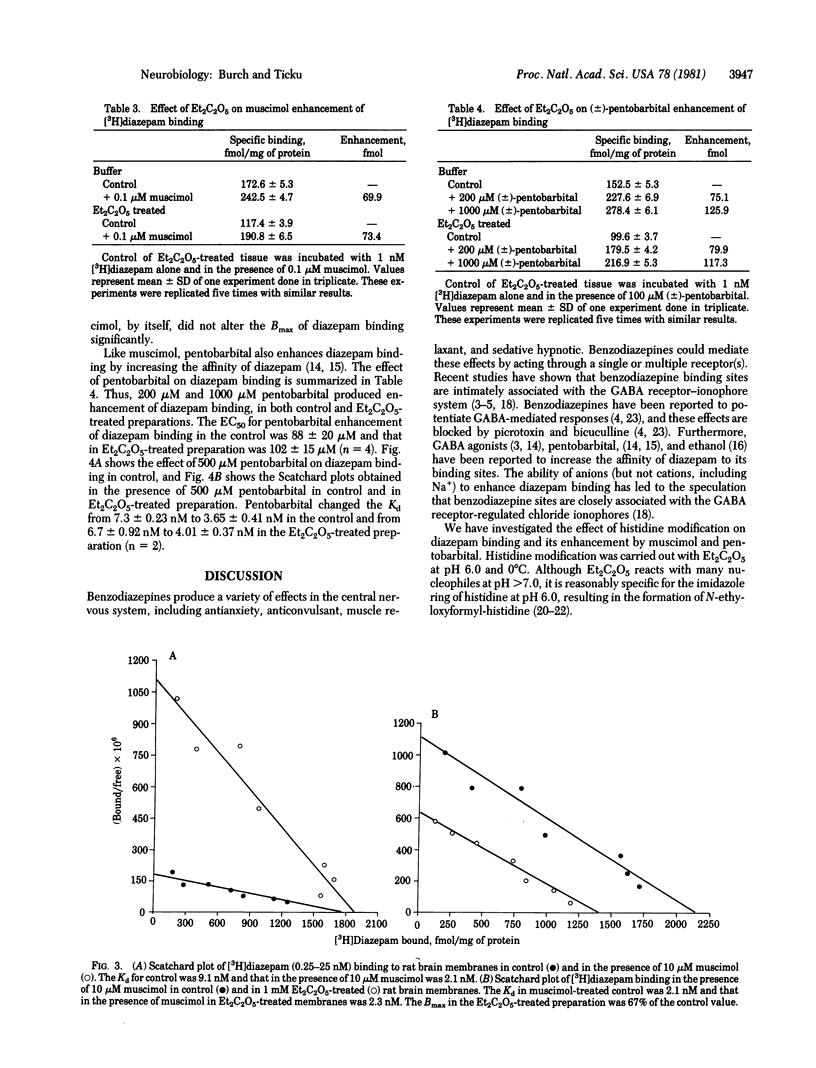
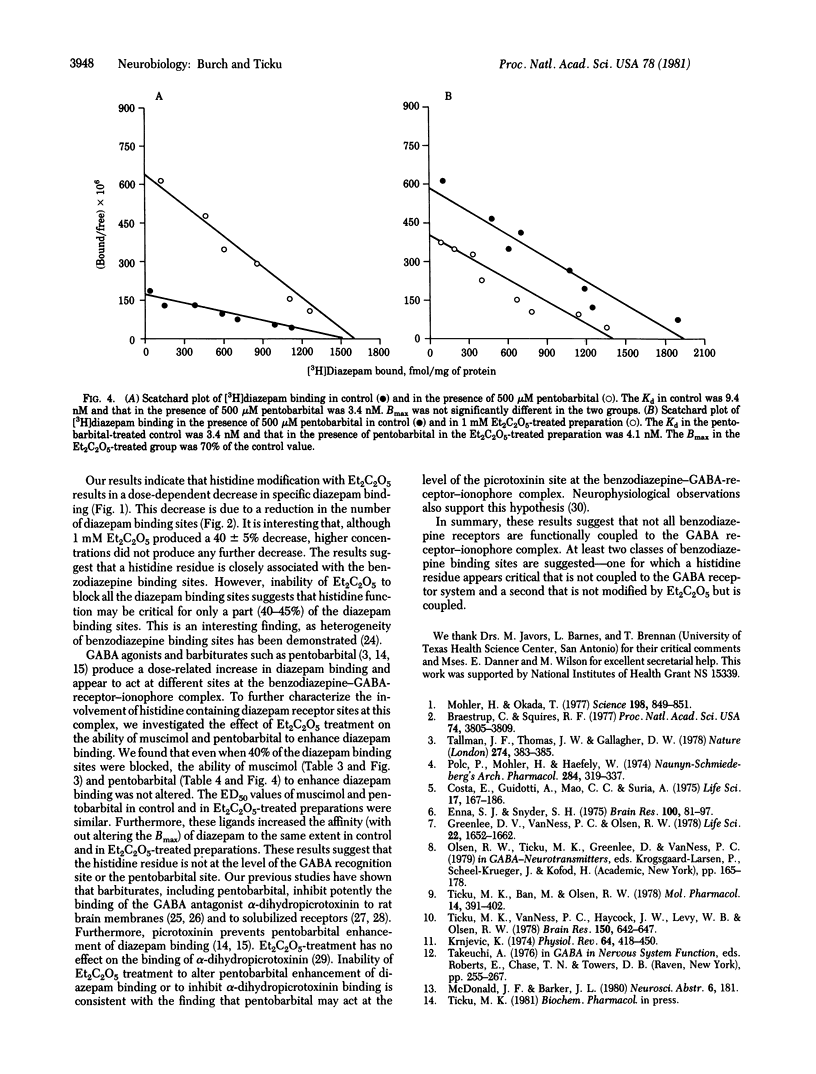
The effect of diethyl pyrocarbonate modification of histidine on the specific binding of [3H]diazepam and its enhancement with muscimol and (+/-)-pentobarbital was investigated. Diethyl pyrocarbonate treatment produced a dose-related inhibition of specific [3H]diazepam binding to rat brain membranes with a maximal inhibition of approximately 40% at 1 mM. Scatchard analysis of the binding data showed that diethyl pyrocarbonate, while having no effect on the affinity (Kd), decreased the binding capacity (Bmax) of diazepam from a control value of 1543 +/- 116 fmol/mg of protein to 789 +/- 79 fmol/mg of protein (mean +/- SD; P less than 0.005; n = 4). Under conditions in which approximately 40% of the diazepam binding sites were modified by diethyl pyrocarbonate treatment, the ability of muscimol and pentobarbital to enhance diazepam binding was not altered. These results suggest that a histidine residue is critical for a part (approximately 40%) of the benzodiazepine binding sites and that there may exist a heterogeneity of benzodiazepine binding sites. Furthermore, these results indicate that perhaps only a portion of the benzodiazepine binding sites are functionally coupled to the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-ionophore complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., ITO M., OSCARSSON O. Anion permeability of the synaptic and non-synaptic motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:410–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch T. P., Ticku M. K. Ethanol enhances [3H]diazepam binding at the benzodiazepine-GABA-receptor-ionophore complex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 17;67(2-3):325–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90519-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A., Mao C. C., Suria A. New concepts on the mechanism of action of benzodiazepines. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 15;17(2):167–185. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Rodbard D., Pert C. B. Is the benzodiazepine receptor coupled to a chloride anion channel? Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):315–317. doi: 10.1038/277315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. C., Ticku M. K. Solubilization of the picrotoxinin binding receptor from mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1981 Apr;36(4):1572–1579. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding in rat brain synaptic membrane fractions. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):81–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallager D. W. Benzodiazepines: potentiation of a GABA inhibitory response in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 May 15;49(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee D. V., Van Ness P. C., Olsen R. W. Endogenous inhibitor of GABA binding in mammalian brain. Life Sci. 1978 May 8;22(18):1653–1662. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg F., Snowman A., Olsen R. W. Barbiturate receptor sites are coupled to benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7468–7472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlrad A., Hegyi G., Horányi M. Studies on the properties of chemically modified actin. 3. Carbethoxylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May;181(1):184–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Wojtowicz J. M. The effects of pentobarbital and related compounds on frog motoneurons. Brain Res. 1980 Jun 2;191(1):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90325-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polc P., Möhler H., Haefely W. The effect of diazepam on spinal cord activities: possible sites and mechanisms of action. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;284(4):319–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00504702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P. Specific chemical groups involved in the control of ionic conductance in nerve. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:293–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Benson D. I., Braestrup C., Coupet J., Klepner C. A., Myers V., Beer B. Some properties of brain specific benzodiazepine receptors: new evidence for multiple receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1979 May;10(5):825–830. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(79)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Thomas J. W., Gallager D. W. GABAergic modulation of benzodiazepine binding site sensitivity. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):383–385. doi: 10.1038/274383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Ban M., Olsen R. W. Binding of [3H]alpha-dihydropicrotoxinin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid synaptic antagonist, to rat brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 May;14(3):391–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Olsen R. W. Interaction of barbiturates with dihydropicrotoxinin binding sites related to the GABA receptor-ionophore system. Life Sci. 1978 May 8;22(18):1643–1651. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Van Ness P. C., Haycock J. W., Levy W. B., Olsen R. W. Dihydropicrotoxinin binding sites in rat brain: comparison to GABA receptors. Brain Res. 1978 Jul 21;150(3):642–647. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90830-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


