Abstract
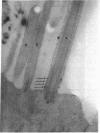
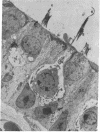
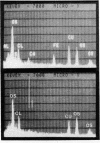
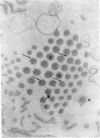
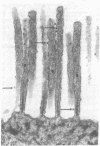
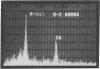
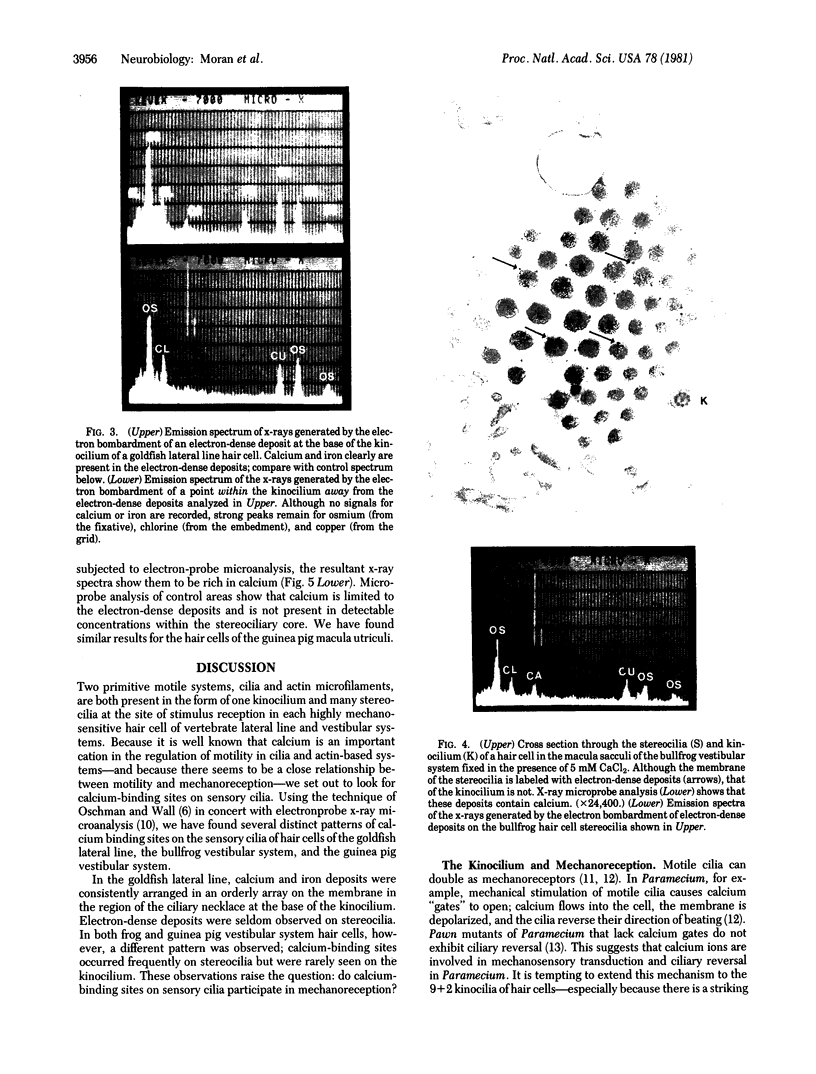
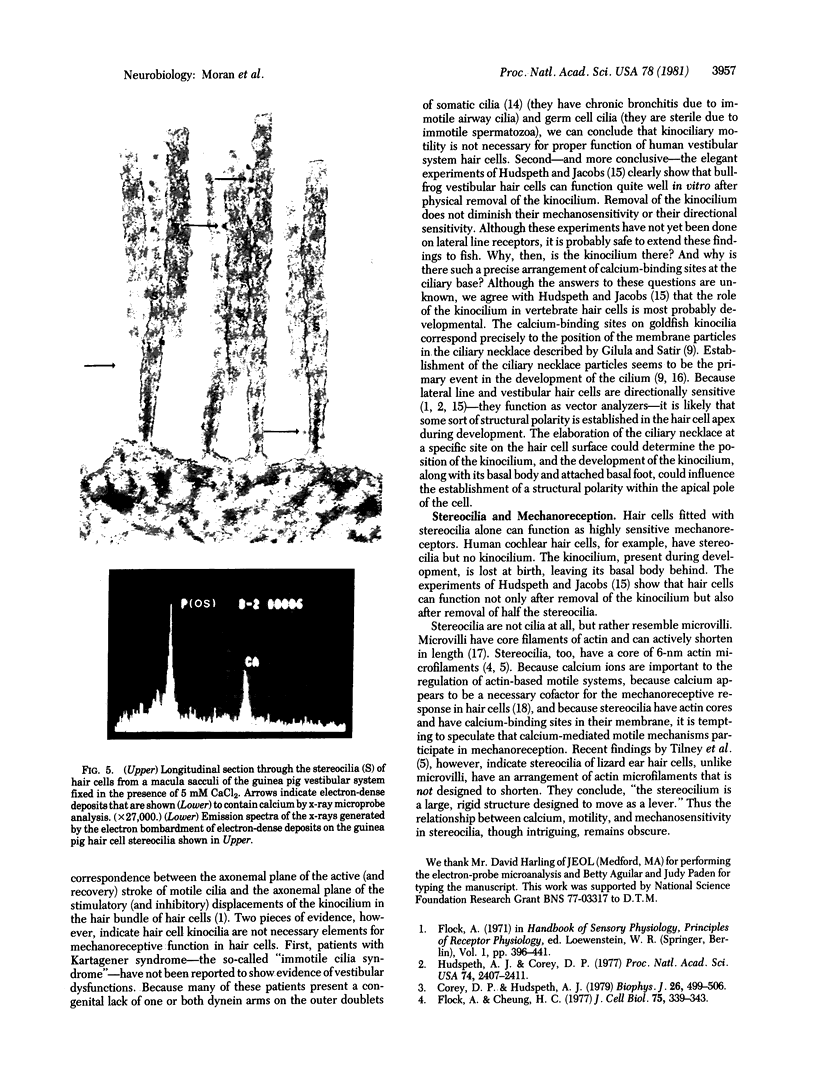
Vertebrate lateral line and vestibular systems center their function on highly mechanosensitive hair cells. Each hair cell is equipped with one kinocilium (which resembles a motile cilium) and 50-100 actin-containing stereocilia (which resemble microvilli) at the site of stimulus reception. This report describes electron-microscopic localization of calcium-binding sites on the sensory processes of vertebrate hair cells. Using the Oschman-Wall technique for calcium localization [Oschman, J. L. & Wall, B. J. (1972) J. Cell Biol. 55, 58-73] together with electron-probe x-ray microanalysis of thin sections, we observed: (i) calcium- and iron-containing deposits in the region of the ciliary necklace in goldfish lateral line hair cells, (ii) calcium deposits upon the surface of stereocilia of hair cells of the bullfrog inner ear, and (iii) calcium deposits upon stereocilia of hair cells of the guinea pig vestibular system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afzelius B. A., Eliasson R. Flagellar mutants in man: on the heterogeneity of the immotile-cilia syndrome. J Ultrastruct Res. 1979 Oct;69(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(79)80041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier A. C., Haumont S. Origin of necklace particles in thymic ciliating cells. Am J Anat. 1979 Sep;156(1):91–97. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001560109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. P., Hudspeth A. J. Ionic basis of the receptor potential in a vertebrate hair cell. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):675–677. doi: 10.1038/281675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. P., Hudspeth A. J. Response latency of vertebrate hair cells. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):499–506. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85267-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flock A., Cheung H. C. Actin filaments in sensory hairs of inner ear receptor cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):339–343. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilula N. B., Satir P. The ciliary necklace. A ciliary membrane specialization. J Cell Biol. 1972 May;53(2):494–509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.2.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J., Corey D. P. Sensitivity, polarity, and conductance change in the response of vertebrate hair cells to controlled mechanical stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2407–2411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J., Jacobs R. Stereocilia mediate transduction in vertebrate hair cells (auditory system/cilium/vestibular system). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1506–1509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oschman J. L., Hall T. A., Peters P. D., Wall B. J. Association of calcium with membranes of squid giant axon: ultrastructure and microprobe analysis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):156–165. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oschman J. L., Wall B. J. Calcium binding to intestinal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Oct;55(1):58–73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald R., Newman S. B., Karnovsky M. J. Contraction of isolated brush borders from the intestinal epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):541–554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. C., 3rd, Moran D. T. A simple procedure for mounting wrinkle-free sections on formvar-coated slot grids. Ultramicroscopy. 1975 Dec;1(2):151–155. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3991(75)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]